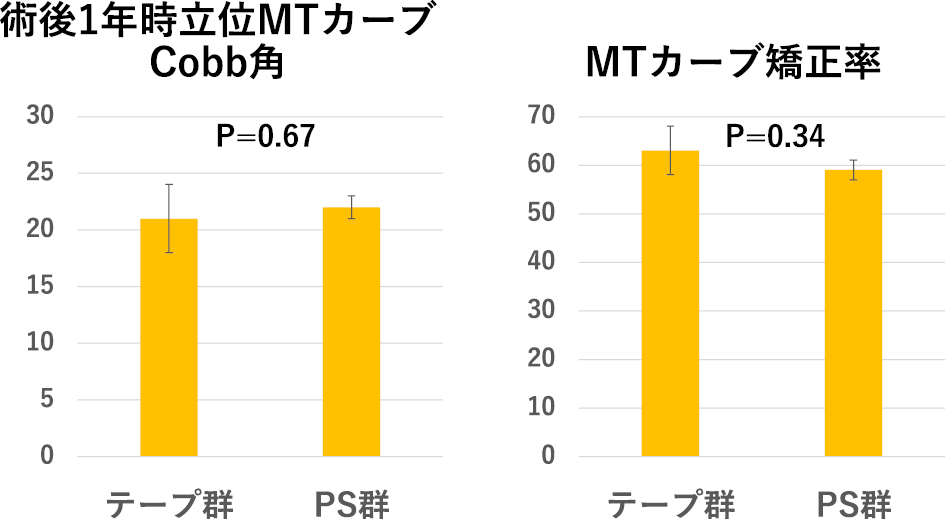
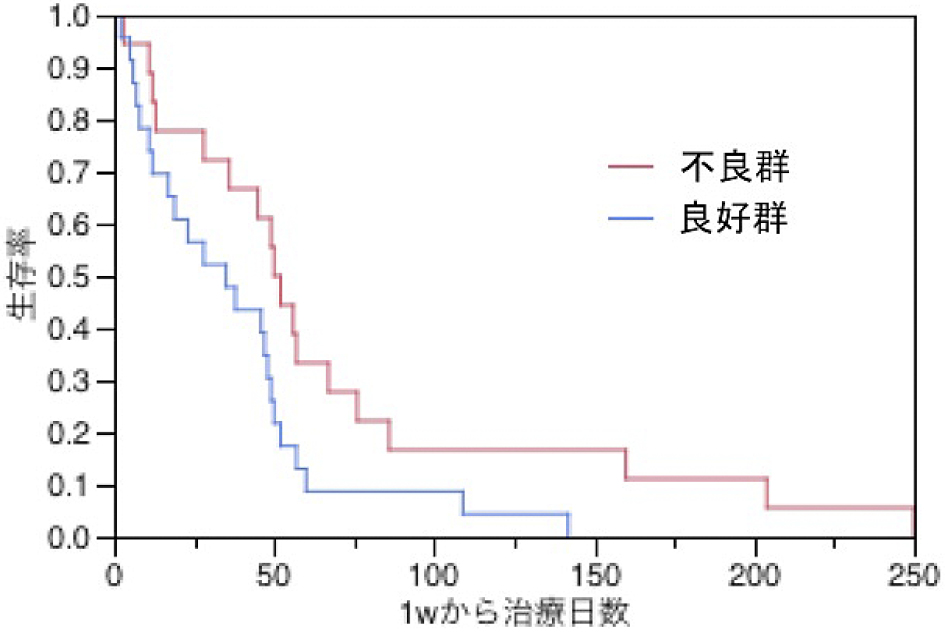
Volume 11, Issue 2
Displaying 1-5 of 5 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Editorial
-
2020Volume 11Issue 2 Pages 27-28
Published: February 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 20, 2020
Download PDF (348K)
Review Article
-
2020Volume 11Issue 2 Pages 29-37
Published: February 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 20, 2020
Download PDF (2938K) -
2020Volume 11Issue 2 Pages 38-45
Published: February 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 20, 2020
Download PDF (7369K)
Original Article
-
2020Volume 11Issue 2 Pages 46-50
Published: February 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 20, 2020
Download PDF (825K) -
2020Volume 11Issue 2 Pages 51-55
Published: February 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 20, 2020
Download PDF (889K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|