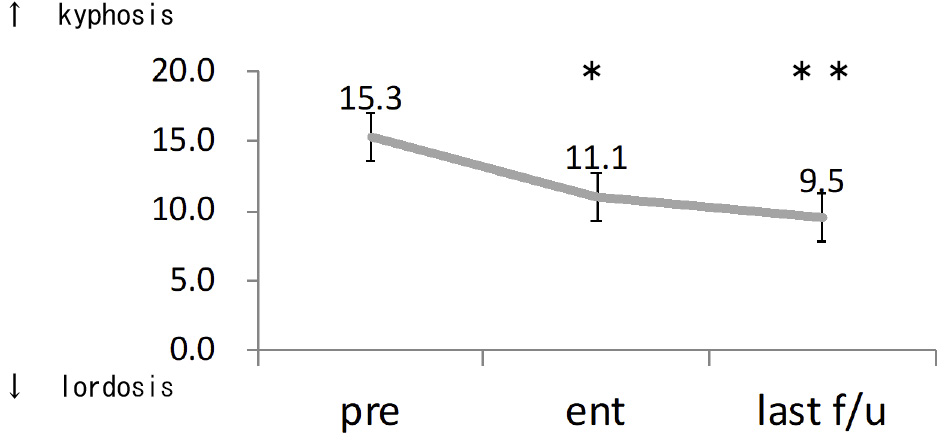
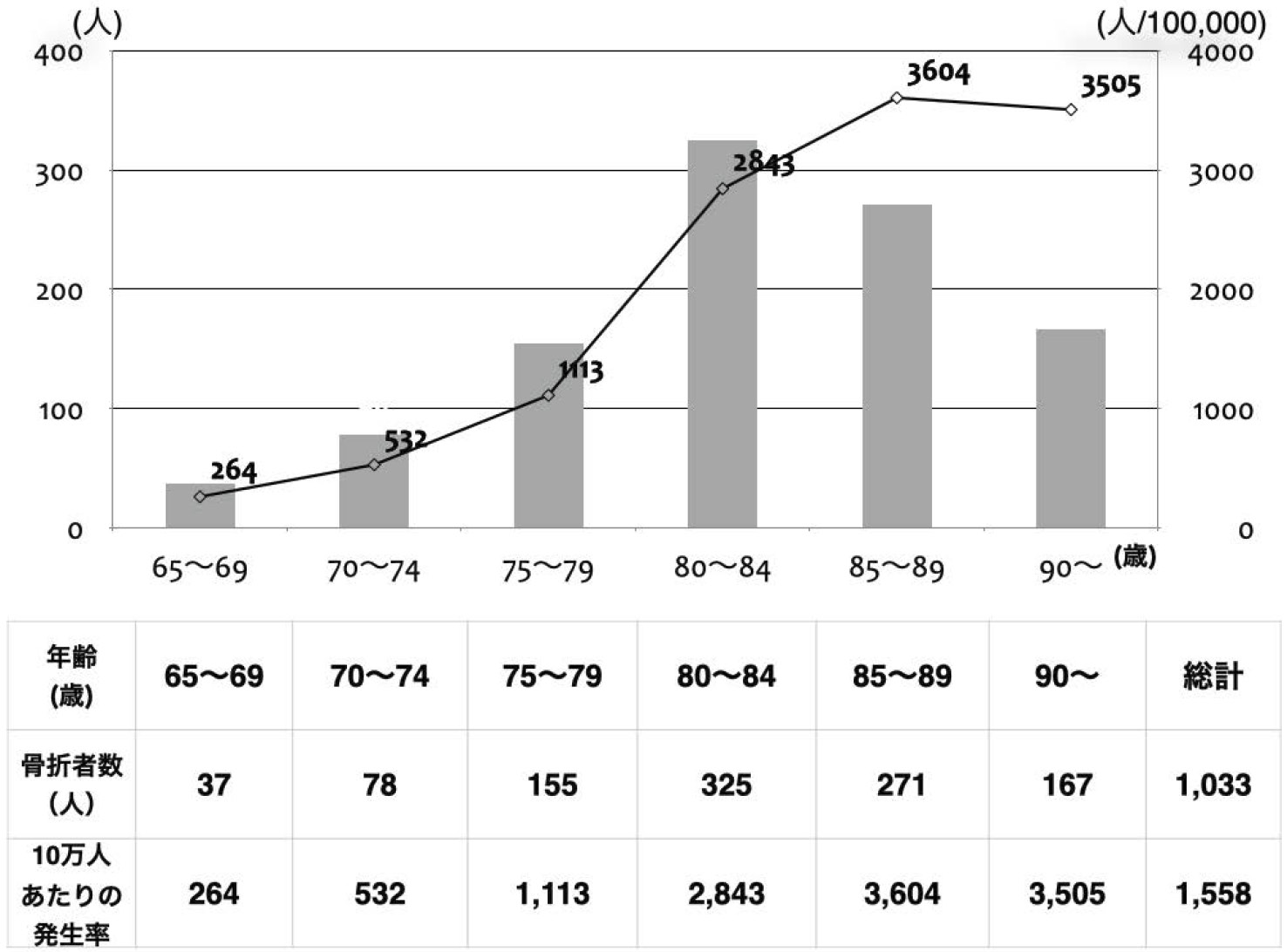
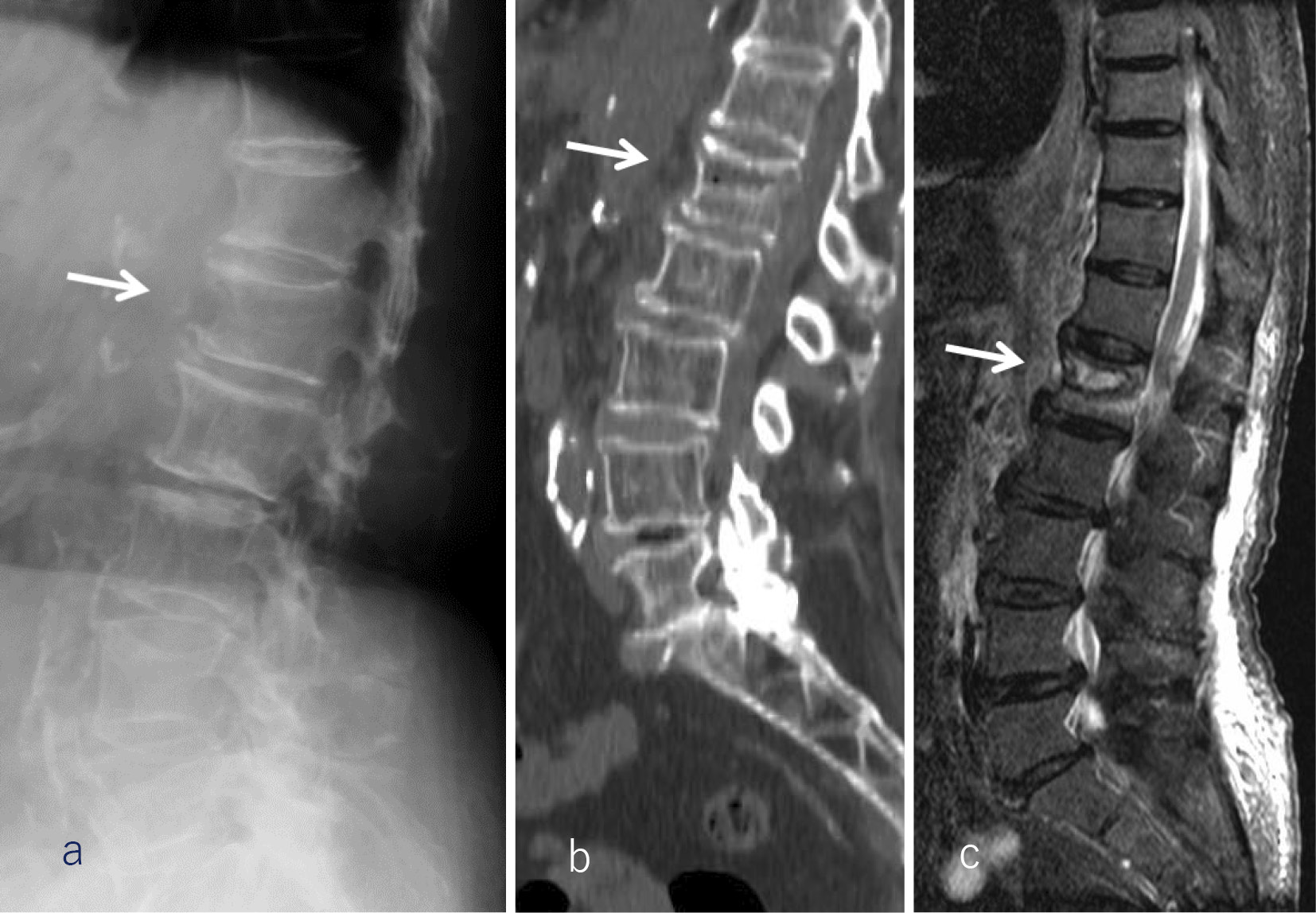
Volume 11, Issue 12
Displaying 1-18 of 18 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Editorial
-
2020Volume 11Issue 12 Pages 1316
Published: December 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2020
Download PDF (265K) -
2020Volume 11Issue 12 Pages 1317
Published: December 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2020
Download PDF (250K)
Original Article
-
2020Volume 11Issue 12 Pages 1318-1322
Published: December 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2020
Download PDF (870K) -
2020Volume 11Issue 12 Pages 1323-1328
Published: December 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2020
Download PDF (1135K) -
2020Volume 11Issue 12 Pages 1329-1332
Published: December 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2020
Download PDF (712K) -
2020Volume 11Issue 12 Pages 1333-1338
Published: December 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2020
Download PDF (1177K) -
2020Volume 11Issue 12 Pages 1339-1345
Published: December 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2020
Download PDF (2116K) -
2020Volume 11Issue 12 Pages 1346-1348
Published: December 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2020
Download PDF (606K) -
2020Volume 11Issue 12 Pages 1349-1352
Published: December 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2020
Download PDF (808K) -
2020Volume 11Issue 12 Pages 1353-1356
Published: December 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2020
Download PDF (630K) -
2020Volume 11Issue 12 Pages 1357-1361
Published: December 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2020
Download PDF (780K) -
2020Volume 11Issue 12 Pages 1362-1368
Published: December 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2020
Download PDF (1634K) -
2020Volume 11Issue 12 Pages 1369-1373
Published: December 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2020
Download PDF (969K) -
2020Volume 11Issue 12 Pages 1374-1379
Published: December 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2020
Download PDF (1054K)
Case Report
-
2020Volume 11Issue 12 Pages 1380-1385
Published: December 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2020
Download PDF (1438K) -
2020Volume 11Issue 12 Pages 1386-1391
Published: December 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2020
Download PDF (1190K) -
2020Volume 11Issue 12 Pages 1392-1397
Published: December 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2020
Download PDF (1547K) -
2020Volume 11Issue 12 Pages 1398-1402
Published: December 20, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2020
Download PDF (1828K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|