All issues

Volume 75 (2018)
- Issue 6 Pages 475-
- Issue 5 Pages 387-
- Issue 4 Pages 293-
- Issue 3 Pages 241-
- Issue 2 Pages 103-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
Predecessor
Volume 75, Issue 2
Displaying 1-14 of 14 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Special Topic on Biomedical Polymers II
Comprehensive Papers
-
Yuji TERAMURA2018Volume 75Issue 2 Pages 103-115
Published: March 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 23, 2018
Advance online publication: January 11, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSince amphiphilic polymers carrying adhesive domains can be used for cell surface modification, they induce cell adhesion by acting as cell glues. For example, conjugation of single stranded DNA (ssDNA) or cell-penetrating peptide to poly(ethylene glycol)-conjugated phospholipid (PEG-lipid) made it possible to induce cell-cell attachment and cell-substrate attachment. These PEG-lipid derivatives are very convenient for this purpose because they are not taken up into cells and are localized on the cell surface, which means that the adhesive domains are displayed on the cell surface. In future our PEG-lipid derivatives will be useful for cell-based arrays for drug screening and high-throughput gene analyses, and pancreatic islet transplantation and regenerative medicine which require 3D tissue structures. View full abstractDownload PDF (1462K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1462K) -
Tsubasa YAMANOUCHI, Naoya KATSUYAMA, Yuki HIRUTA, Eri AYANO, Hideko KA ...2018Volume 75Issue 2 Pages 116-127
Published: March 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 23, 2018
Advance online publication: February 13, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDrug delivery system (DDS) is a technology that controls sustained release of medicines in the body and localized delivery to diseased tissues. Therefore, it is possible to keep the concentration of medicine at therapeutically effective concentrations for a long time and to reduce side effects. We have achieved controlled intracellular uptake, and release of medicines by nanocarriers modified with stimuli-responsive polymers based on poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), which undergoes a reversible phase transition in response to external temperature stimulation. In this article, we introduce our recent research on the design of temperature- and pH-responsive polymers, which enables selective intracellular uptake with external stimulation, and applications to DDS of an anti-tumor agent and siRNA by micelle and liposomes modified with those polymers.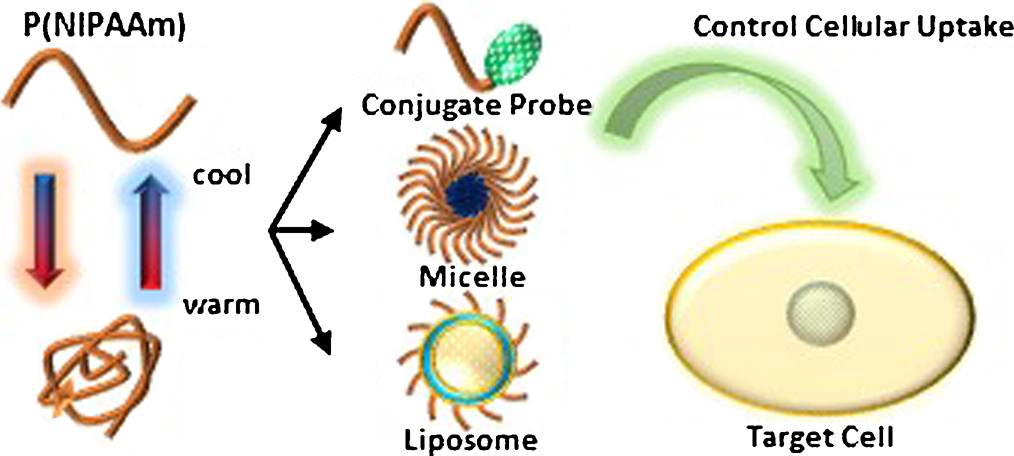 View full abstractDownload PDF (1465K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1465K) -
Naoko NAKAMURA, Tsuyoshi KIMURA, Akio KISHIDA2018Volume 75Issue 2 Pages 128-136
Published: March 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 23, 2018
Advance online publication: February 20, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDecellularized tissues have broad applications as implantable biomaterials and/or biological scaffolds for tissue repair. They show good clinical performance. Decellularized tissue is the extracellular matrix (ECM) that can be obtained by several techniques. Decellularized tissue characteristics, such as shape, structure, mechanical properties, and biological activity, are strongly affected by the decellularization protocol. The orthotopic implantation of decellularized tissues, a common procedure, typically induces cell infiltration and ECM reconstruction resulting in tissues that resemble the source tissues. The ectopic implantation of decellularized tissues results in reconstruction that is either adapted to the implantation site or to the decellularized tissue source. In this study, the differences between methods are discussed. In addition, new methods aimed at extending the applications of decellularized tissues are discussed, particularly methods that confer novel functions to decellularized tissues by polymer complexing, such as devices that link native tissues with artificial materials using decellularized tissue as an intermediate. View full abstractDownload PDF (1140K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1140K) -
Chie KOJIMA2018Volume 75Issue 2 Pages 137-142
Published: March 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 23, 2018
Advance online publication: February 05, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSLysine has two amino groups and one carboxylic acid group. Polylysines with linear and dendritic structures have been produced. Polylysine is widely used as a coating material for cell substrates as well as a nanoplatform for conjugating some compounds such as thermosensitive elastin-like peptide (ELP). The association of dendritic polylysines with poly(glycolic acid) fibers was lower and unstable, compared with linear polylysine. However, more hippocampal neurons adhered to dendritic polylysine. The ELP-grafted linear polylysine exhibited a lower phase transition temperature than the ELP-grafted dendritic polylysine. The ELP-grafted linear polylysine formed an α-helix when it was heated. It is likely that the flexibility in linear polylysines affected their functions as a biomaterial. View full abstractDownload PDF (800K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (800K) -
 Kenichi NAGASE, Teruo OKANO, Hideko KANAZAWA2018Volume 75Issue 2 Pages 143-154
Kenichi NAGASE, Teruo OKANO, Hideko KANAZAWA2018Volume 75Issue 2 Pages 143-154
Published: March 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 23, 2018
Advance online publication: February 16, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSProtein drugs and therapeutic cells are among promising current and future therapies for patients. The importance of these proteins and cells has increased in the clinical field, and protein and cell purification methods, without losing their potency or biological activity, are urgently needed. We prepared thermoresponsive polymer brushes as a new protein and cell separation tool because interactions between the polymer brushes and targeted proteins and cells can be modulated by changing the external solution temperature without using other agents that might contaminate these biologics or disrupt their function. Using these new thermoresponsive polymer brushes, a variety of different bio-separations have been performed by simple temperature changes in aqueous solutions. The present review describes the recent achievement in bioseparation using thermoresponsive polymer brushes. View full abstractDownload PDF (1884K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1884K) -
Tsuyoshi KIMURA, Naoko NAKAMURA, Yoshihide HASHIMOTO, Shimon SAKAGUCHI ...2018Volume 75Issue 2 Pages 155-163
Published: March 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 23, 2018
Advance online publication: February 08, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSCell separation is a powerful tool in life science research and clinical use. Various methods for cell separation have been developed. In this paper, we describe two cell separation methods using surface immobilizing antibodies via dissociation molecules. As one method, acrylic acid was grafted on the surface in order to inhibit non-specific cell adhesion and the antibody was immobilized via desthiobiotin-avidin interaction. Cells were selectively captured through antibody-antigen interaction and released by addition of biotin-modified polymer due to the exchange reaction of desthiobiotin and biotin. For the second method, the surface was modified by grafting poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-arylic acid) and the antibody was immobilized via double strand DNA. Cells were adhered on the surface at 37°C and detached by 4°C incubation with remaining cells that interacted with the surface via antibody-antigen interaction. The adhered cells were released by DNase treatment. These results suggest that cells can be selectively captured and collected by using the surface that immobilizes an antibody via dissociation molecules.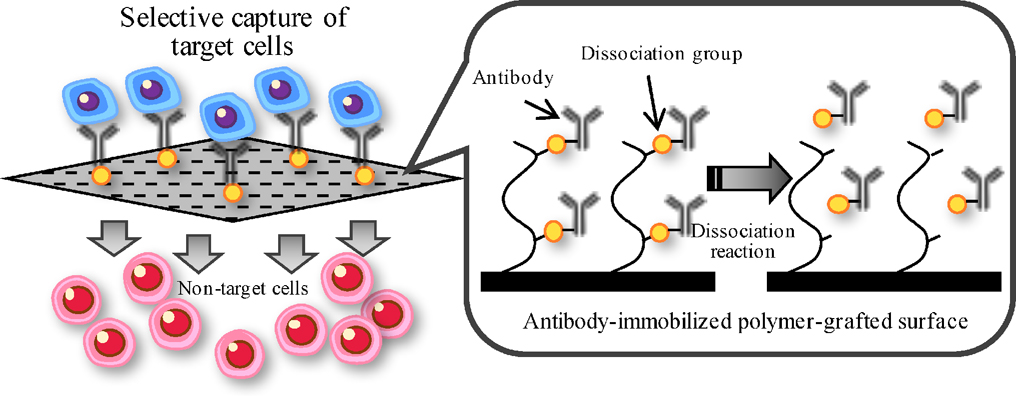 View full abstractDownload PDF (1232K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1232K) -
Aira MATSUGAKI, Takayoshi NAKANO2018Volume 75Issue 2 Pages 164-173
Published: March 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 23, 2018
Advance online publication: January 16, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSOrdered structures in constituent materials govern their functions, sometimes much more than their amount would suggest. The crystallographic texture of apatite with a hexagonal lattice structure dominates the mechanical properties of bone more than bone mass. However, obtaining an appropriate anisotropic microstructure during the bone regeneration process remains a big challenge. A powerful strategy for the control of structural development of newly formed bone is required in bone tissue engineering, in order to realize functional bone tissue regeneration. We developed essential strategies for control of bone matrix anisotropy by using biomedical materials involving polymeric, metallic and other related materials. View full abstractDownload PDF (2130K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2130K) -
Yoshikatsu AKIYAMA, Teruo OKANO2018Volume 75Issue 2 Pages 174-186
Published: March 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 23, 2018
Advance online publication: February 13, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn this review, we focus on the progress of temperature-responsive cell culture surface (TRCS), which is a poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PIPAAm) grafted surface, since the first report of temperature-responsive surfaces. We also show that the optimization of the grafted nano-scaled PIPAAm layer is essential to express temperature dependent cell attachment/detachment. Also, we describe the technologies required to readily fabricate cell sheets and TRCS in the near future, which are quantitative methods for cell adhesion/detachment processes from TRCS by using micro fluidic technique and a facile method for preparation of TRCS. View full abstractDownload PDF (1320K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1320K)
Original Papers
-
Eri NAKATSUKA, Sachiro KAKINOKI, Yoshiaki HIRANO2018Volume 75Issue 2 Pages 187-194
Published: March 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 23, 2018
Advance online publication: February 23, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe amide functionality in the 2,5-diketopiperazine ring forms intermolecular hydrogen bonds between adjacent molecules that enable 2,5-diketopiperazines to form regulated higher-order supermolecular structures that are important in surface and coating engineering. In this study, we synthesized a cyclic(D-Tyr-D-Phe) peptide for the purpose of evaluating its self-assembly on glass or SUS316L, and the peptide’s potential use in the design of antibacterial surfaces. A self-assembling 2,5-diketopiperazine nanostructure was observed and evaluated by atomic force microcopy (AFM). Cyclic(D-Tyr-D-Phe) formed a rod-like nanostructure on a glass surface. Compared to the synthetic H-D-Tyr-D-Phe-OH absorbed surface and the original material surfaces, self-assembling cyclic(D-Tyr-D-Phe) has the potential for antibacterial activity when adsorbed on surfaces. Finally, cyclic(D-Tyr-D-Phe) peptide did not show cell toxicity activity. The self-assembled cyclic(D-Tyr-D-Phe) has potential for use in the design of biomedical device surfaces with antibacterial activity.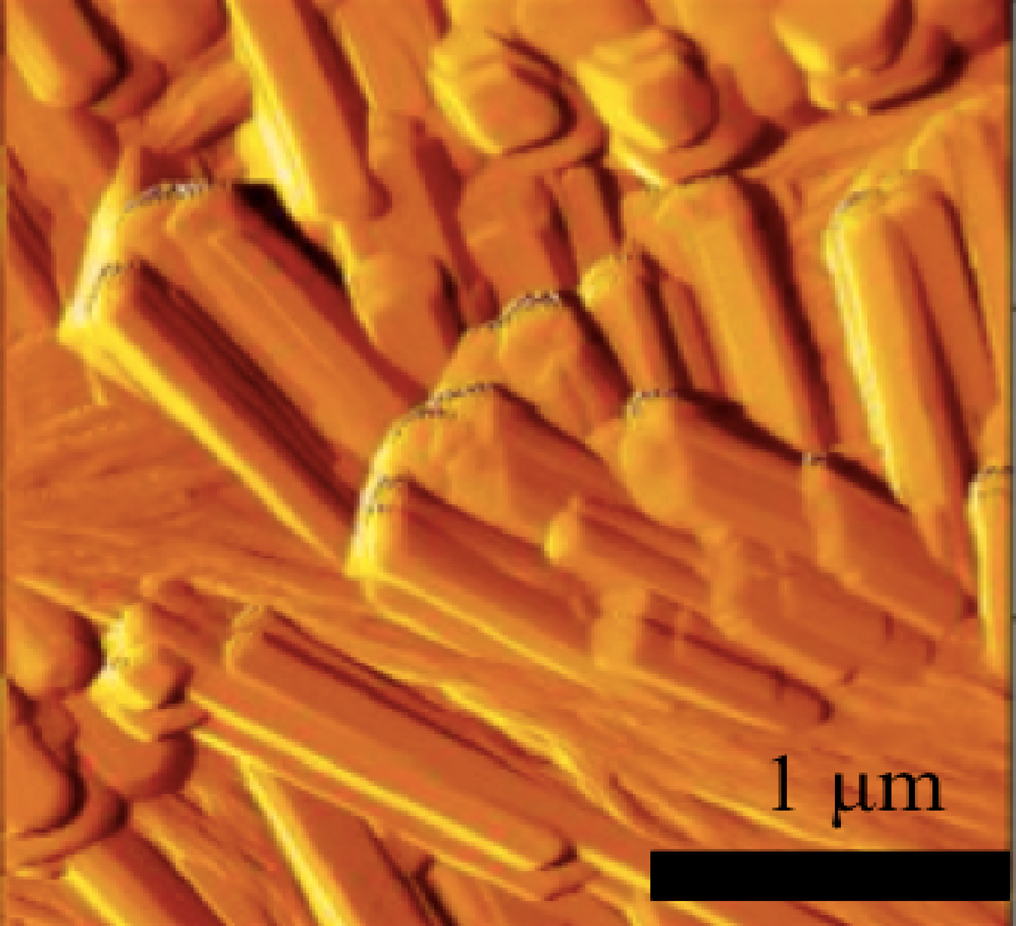 View full abstractDownload PDF (824K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (824K) -
Kazutoshi IIJIMA, Ayami SUZUKI, Mineo HASHIZUME2018Volume 75Issue 2 Pages 195-202
Published: March 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 23, 2018
Advance online publication: February 06, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSComposite films consisting of polysaccharide films, made of polyion complex of chondroitin sulfate C and chitosan, and supporting materials, polyethylene terephthalate (PET) sheets and silk mesh, were prepared by utilizing hot press techniques. Both composite films with PET sheet and silk mesh maintained their self-supporting properties even after immersion in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and their polysaccharide parts showed similar swelling behavior to original polysaccharide films. The PET sheets of the PET-supported films were detachable after adhering their polysaccharide parts to other substrates. In the silk mesh-supported films, methylene blue used as a model drug was loaded and released from the polysaccharide part of the film. View full abstractDownload PDF (1318K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1318K) -
Kenta HATAGUCHI, Masaki TAKAHASHI, Katsuki YAMORI, Michinori KARIKOMI, ...2018Volume 75Issue 2 Pages 203-211
Published: March 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 23, 2018
Advance online publication: February 05, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSFor use as a drug carrier for oral administration, polyglycolic acid (PGA) gels were prepared from PGA polymer by ring opening addition with pyromellitic dianhydride as a linking agent and transesterification with multi-branched polyethylene glycol as a crosslinking agent. The swelling degree and hydrolyzability of the resulting PGA gels were investigated by changing crosslinking structure and PGA introduction rate. Moreover, methylene blue as a basic dyestuff and acid black as an acidic dyestuff were loaded as dummy drugs in the resulting PGA gels, and their releasing behavior in human digestive organs was evaluated in simulated gastric and small-intestinal fluids. The PGA gels respond to changes in pH and easily hydrolyze and thus are found to be effective as drug carriers for oral administration. View full abstractDownload PDF (1158K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1158K)
Regular Topics
Comprehensive Papers
-
Kiyomi OKADA, Shun MUROGA, Masahiro OHSHIMA2018Volume 75Issue 2 Pages 212-220
Published: March 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 23, 2018
Advance online publication: February 06, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe propose an analytical method to evaluate the dispersion of additives in polymers using FT-IR spectroscopic imaging. Averaging filters with various window sizes were intentionally applied to imaging data measured with high resolution. The window size dependent coefficients of variance (CV) were calculated to evaluate the dispersion state in each sample. CVs in an ideally dispersed sample will be flat, on the other hand, less-than-ideal dispersions will show a steep CV curve.
Our proposed method was validated by applying the method to imaging data of polypropylene (PP)/ cellulose nanofiber (CNF) composite, which recently have been attracting a great attention due to their excellent characteristics. One of the dominant factors determining performance of a PP/CNF composite, e.g., Young’s modulus, tensile strength, is the dispersibility of CNF in PP. The PP/CNF composites prepared by different mixers were measured by FT-IR spectroscopic imaging and evaluated by our proposed method. A significant difference among samples was observed in the curves of CV against the window size. The PP/CNF sample mixed by a narrower clearance of a kneader, which is subjected to better mixing, showed a gentle slope of CV. The PP/CNF sample mixed by wider clearance, in contrast, showed a steep slope of CV. It was therefore confirmed that the curve of CV against the window size of the averaging filter were obtained in response to the dispersion state of each composite. We have shown that our proposed method is effective to evaluate the dispersion state of polymer composites.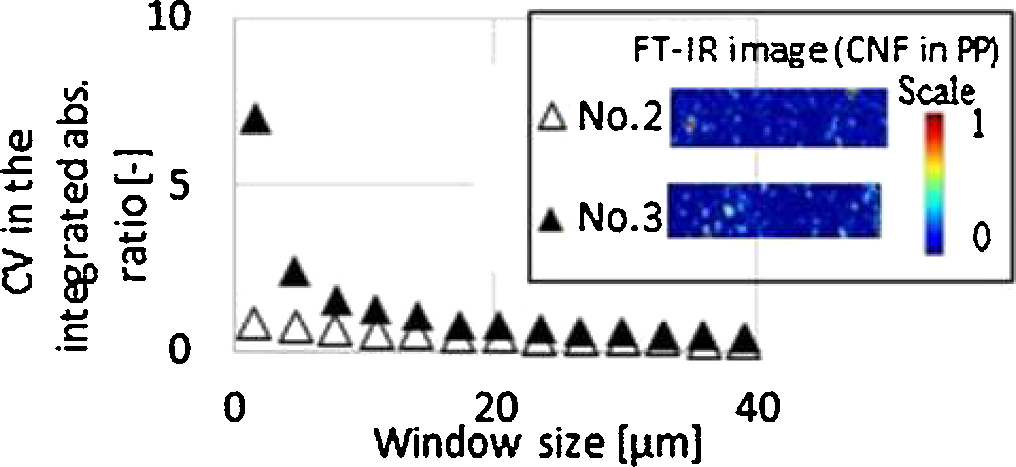 View full abstractDownload PDF (1146K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1146K)
Original Papers
-
Shigeki HIKASA, Kouichi KOUKA2018Volume 75Issue 2 Pages 221-231
Published: March 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 23, 2018
Advance online publication: December 28, 2017JOURNAL FREE ACCESSFor high density polyethylene (HDPE)/filler composites, incorporation of filler particles influences the impact fracture behavior. The influence of test temperature on the impact modification effect of a filler was investigated by the instrumented Charpy impact test. In the case that the matrix HDPE showed brittle fracture behavior in the impact test because of low test temperature or low impact strength, filler incorporation decreased the impact strength slightly. On the other hand, in the case that the matrix HDPE showed ductile fracture behavior in impact test because of high test temperature or high impact strength, filler incorporation significantly increased impact strength. View full abstractDownload PDF (1394K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1394K) -
Atsuyuki NOWAKI, Takafumi OUCHI, Kentaro MATSUMOTO, Takayuki TSUKEGI, ...2018Volume 75Issue 2 Pages 232-239
Published: March 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 23, 2018
Advance online publication: February 21, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn order to develop flame-retardant composite materials from biomass and commodity plastics, bamboo powder (BP) including micro fibers/whiskers and polypropylene (PP) were blended with some kinds of flame-retardants: mixed metal hydroxides, aromatic phosphate, and expandable graphite (EG). As a result, in BP/PP/flame-retardant composites, EG effectively functioned as an excellent flame-retarding agent to achieve class V-0~V-1 of the UL94 specification. Moreover, to improve mechanical properties of BP/PP/EG (40:40:20 wt/wt/wt) composite, maleic anhydride-modified polypropylene (MAPP) was added as a compatibilizer. Fabricated BP/PP/EG/MAPP composites showed higher values of tensile modulus, flexural strength, and flexural modulus by 209, 104, and 146%, respectively, than original PP when MAPP was added at 1 wt% only. Therefore, the biomass/PP composites balanced the excellent flame-resistance and improved the mechanical properties were achieved.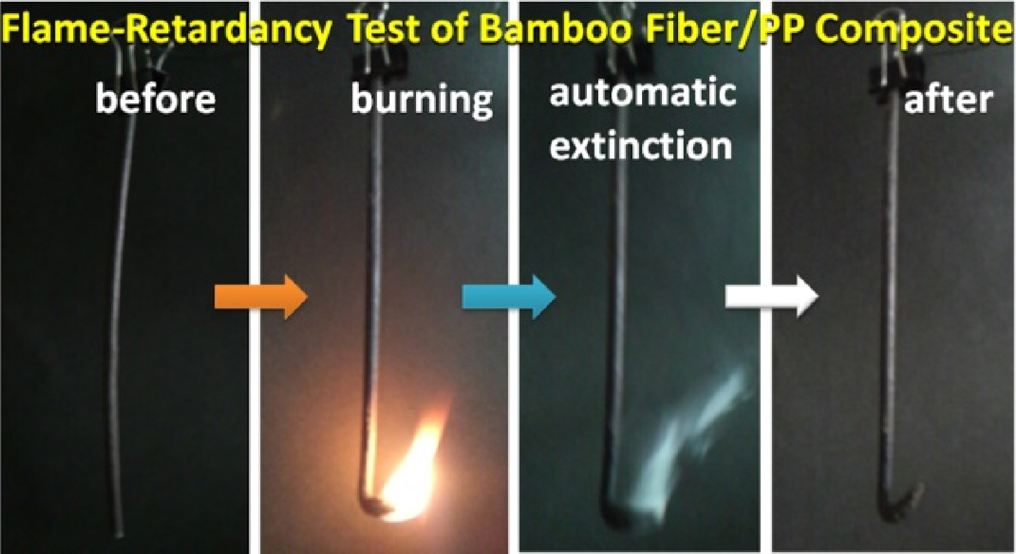 View full abstractDownload PDF (894K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (894K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|