All issues

Volume 75 (2018)
- Issue 6 Pages 475-
- Issue 5 Pages 387-
- Issue 4 Pages 293-
- Issue 3 Pages 241-
- Issue 2 Pages 103-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
Predecessor
Volume 75, Issue 6
Displaying 1-18 of 18 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Special Topic on Polyolefins
Commentary
-
Toshiaki TANIIKE2018 Volume 75 Issue 6 Pages 475-476
Published: November 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 22, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (257K)
Comprehensive Papers
-
Yosuke HARAUCHI, Takashi HOUKAWA, Satoru ADACHI, Kunihito ARAI, Taichi ...2018 Volume 75 Issue 6 Pages 477-485
Published: November 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 22, 2018
Advance online publication: August 30, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSCyclo-olefin polymer (COP) is a saturated hydrocarbon polymer having an alicyclic structure. Specific properties of COP, including high transparency, high purity, low moisture adsorption and low adsorption, enabled it to be utilized in various fields such as optical devices, display parts, pharmaceutical- and bio-use, and in the semi-conductor industry. In this report, we introduce the latest advancement of COP that meets market demand for higher performance. In optical uses, we developed a new COP applicable for thin lenses with reduced weld line, focusing on the viscosity curve of the polymer melts. In pharmaceutical packaging applications, it was verified that adsorption and aggregation of proteins were largely suppressed in the COP package, as compared with the case in the conventional glass package. Finally, we succeeded to develop a crystalline COP having higher heat resistance, by controlling the stereostructure of the polymer chain. View full abstractDownload PDF (3138K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3138K) -
Hiroshi TERAO, Takashi NAKANO, Seiichi ISHII, Terunori FUJITA2018 Volume 75 Issue 6 Pages 486-496
Published: November 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 22, 2018
Advance online publication: September 19, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe deployment of fluorinated moieties to engender electronic effects through non-covalent attractive interactions is a new concept for olefin polymerization catalysts, and was proposed to account for the unprecedented living polymerization mediated by certain catalysts bearing fluorine-containing ancillary ligands. This strategy is distinct from conventional approaches based on steric influences to control olefin polymerization processes. In this Perspective, the concept, generality and beneficial effects of applying non-covalent interactions to control polymerization reactions are discussed, with particular emphasis given to intramolecular C-H⋯F-C interactions between a fluorinated ligand and growing polymer chain. View full abstractDownload PDF (2356K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2356K) -
 Takumitsu KIDA, Yusuke HIEJIMA, Koh-hei NITTA2018 Volume 75 Issue 6 Pages 497-506
Takumitsu KIDA, Yusuke HIEJIMA, Koh-hei NITTA2018 Volume 75 Issue 6 Pages 497-506
Published: November 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 22, 2018
Advance online publication: October 09, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn situ Raman spectroscopy was performed to evaluate microscopic deformation behavior such as the load sharing of molecular chains and the molecular orientation for high-density polyethylene and isotactic polypropylene under uniaxial stretching. Below the α1 relaxation temperature, the compression stress is applied to the crystalline chains in the yielding region due to the macroscopic shrinkage with necking. Moreover, the crystalline chains orient in the 30–50° direction, suggesting that the molecular orientation of the crystalline chains is hindered by the excluded volume effect of the lamellar cluster units. On the other hand, above the α1 relaxation temperature, the crystalline chains immediately orient in the stretching direction after the yielding point and the stretching stress is applied on the crystalline chains. The enhancement of the molecular orientation of the crystalline chains is caused by the thermal activation of the molecular motion within the crystalline phase owing to the onset of α1 relaxation.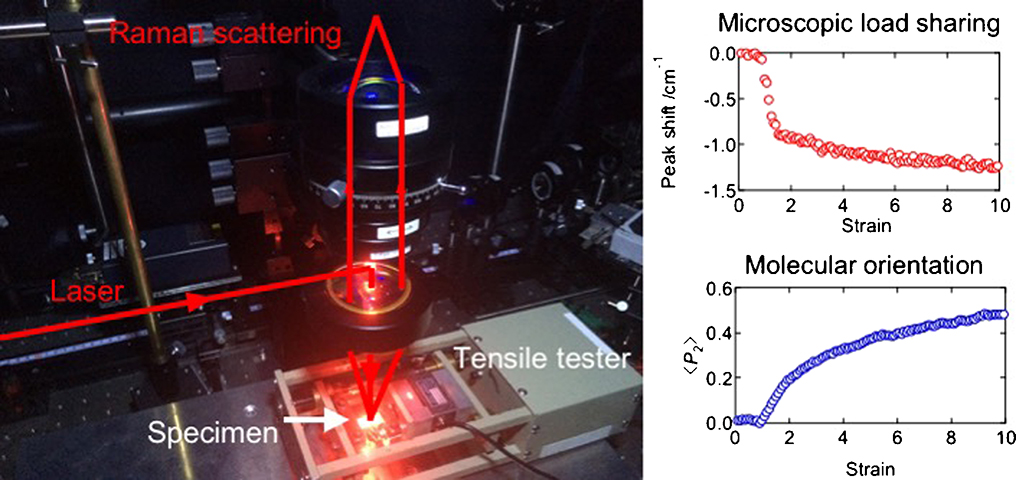 View full abstractEditor's pickDownload PDF (3462K)
View full abstractEditor's pickDownload PDF (3462K) -
 Daisuke TAKEUCHI, Shigenaga TAKANO, Yuriko CHIBA, Takashi IWAMURA, Koh ...2018 Volume 75 Issue 6 Pages 507-514
Daisuke TAKEUCHI, Shigenaga TAKANO, Yuriko CHIBA, Takashi IWAMURA, Koh ...2018 Volume 75 Issue 6 Pages 507-514
Published: November 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 22, 2018
Advance online publication: October 04, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDinuclear complex catalysts often show different catalytic bahavior compared to the corresponding mononulcear complex catalysts. Most of the previously reported dinuclear catalysts contain two mononuclear complexes connected by a flexible tether. Herein we report double-decker type dinuclear complex catalysts having two metal centers located on cyclic ligands in close proximity. They show a higher catalytic activity than the mononuclear analogue, and gave polymers with higher molecular weight. The dinuclear catalysts also promote copolymerization of olefins with various comonomers and gave copolymers with unique structures. It was also revealed that the dinuclear catalysts are stable at elevated temperature. View full abstractEditor's pickDownload PDF (1954K)
View full abstractEditor's pickDownload PDF (1954K) -
Bruce S. XIN, Naomasa SATO, Akio TANNA, Yasuo OISHI, Yohei KONISHI, Fu ...2018 Volume 75 Issue 6 Pages 515-526
Published: November 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 22, 2018
Advance online publication: October 03, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe investigated the copolymerization of ethylene and alkyl acrylates and found that a Ni complex containing the α-iminocarboxamide ligand can catalyze such copolymerization to form linear copolymers. Since this catalyst system needs low polymerization temperatures around 40°C because it lacks in high temperature tolerance, we further explored better Ni catalyst systems. We finally found that phosphinophenol-ligated neutral Ni complexes can catalyze copolymerization of ethylene and acrylates to produce highly linear copolymers at higher temperatures. By introducing methoxy groups into the ligand, we were able to improve the catalyst performance significantly in terms of catalyst activity, molecular weight of the copolymer, and acrylate content. View full abstractDownload PDF (3232K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3232K) -
Norio TOMOTSU, Masahiko KURAMOTO, Nobuhide ISHIHARA2018 Volume 75 Issue 6 Pages 527-542
Published: November 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 22, 2018
Advance online publication: October 24, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe authors had published a novel development of metallocene-based catalysts for the first time in 1985 that made it possible to synthesize syndiotactic polystyrene (SPS). Here, we review the structure and characteristics of SPS, which is a semi-crystalline engineering thermoplastic with a crystalline melting point of 270°C. Because of its crystalline nature, SPS has a high heat resistance, an excellent chemical and water/stream resistance. Furthermore, some mechanistic model for polymerization and stereo regulation as well as the factors which affect the activity and stereospecificity of the catalysts, are discussed. View full abstractDownload PDF (2250K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2250K) -
Kotohiro NOMURA, Hitomi HAYASHIBARA2018 Volume 75 Issue 6 Pages 543-550
Published: November 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 22, 2018
Advance online publication: August 21, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS(Imido)vanadium(V)-alkylidene complexes of type V(NR)(CHSiMe3)(OR′)(PMe3)2 [R = Ad, C6H5, 2,6-Me2C6H3, 2,6-Cl2C6H3; R′ = 2,6-Me2C6H3, 2,6-iPr2C6H3, 2,6-F2C6H3, C6F5, C6Cl5, C(CH3)(CF3)2, C(CF3)3] exhibited moderate to remarkable catalytic activities for ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP) of norbornene (NBE). In particular, V(N-2,6-Cl2C6H3)(CHSiMe3)(OC6X5)(PMe3)2 (X = F, Cl) demonstrated exceptionally high catalytic activities for ROMP of NBE and these complexes polymerize cis-cyclooctene. The catalytic activities increased upon increasing the temperature and the highest activity was observed at 120°C upon addition of small amount of PMe3. Cis-specific ROMP of NBE has been attained by V(CHSiMe3)(N-2,6-Cl2C6H3)[OC(CF3)3](PMe3)2, and the activity increased at high temperature with high cis specificity (98%) even at 80°C. This is the rare demonstration of thermally robust, highly cis-specific catalysts, which are apparently different from known molybdenum and ruthenium catalysts. View full abstractDownload PDF (3557K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3557K)
Original Papers
-
Ryo TANAKA, Takayuki YAMASHITA, Naoki TONOKO, Yuushou NAKAYAMA, Takesh ...2018 Volume 75 Issue 6 Pages 551-556
Published: November 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 22, 2018
Advance online publication: July 30, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe effects of phenols and silanols as a modifier of trialkylaluminum-depleted modified methylaluminoxane (dMMAO) were investigated in the living propylene polymerization using fluorenylamido-ligated titanium complex–dMMAO catalyst system. The addition of phenols with electron withdrawing groups increased the turnover frequency (TOF) of the catalyst, while the addition of non-substituted phenol and monosilanol had a negative effect on the TOF. These results indicate that the Lewis acidity of aluminoxane was enhanced by the modification with electron deficient phenoxides. The decrease of the stereoregularity of the obtained polypropylene accompanied by the increase of TOF supported this interpretation. These findings could be extended to explain the cocatalytic behavior of MMAO supported onto silica. View full abstractDownload PDF (970K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (970K) -
Sosuke KUDO, Miru HIRAHARA, Hitoshi OGIHARA, Hideki KUROKAWA2018 Volume 75 Issue 6 Pages 557-563
Published: November 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 22, 2018
Advance online publication: October 02, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSPolyethylene blend (PEB) was synthesized by polymerization of ethylene using a combined catalyst system consisting of [R-N=C(CH3)-C(CH3)=N-R, R: 2,6-(CH3)2Ph]Ni(II) and {2,6-[R-N=C(CH3)]C5H3N, R: 2,6-(CH3)2Ph}Fe(III) immobilized into fluorotetrasilicic mica interlayers. When the ethylene polymerization was performed using the combined catalyst system, the PEB having multiple melting peaks (107, 126, and 135°C) was formed. Both, the average number molecular weight (Mn) and the polydispersity index of the PEB, showed an intermediate value obtained by each of the catalysts alone (Mn = 4.4 × 104, PDI = 9.8) compared to the values [Ni(II)-based catalyst, Mn = 8.5 × 104, PDI = 3.7; Fe(III)-based catalyst, Mn = 3.7 × 104, PDI = 12.5]. The co-polymerization of ethylene/1-hexene afforded the PEB consisting of high-density polyethylene and linear low-density polyethylene including butyl branches. View full abstractDownload PDF (2151K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2151K)
Notes
-
Kei NISHII, Shigetaka HAYANO, Yasuo TSUNOGAE, Yuushou NAKAYAMA, Takesh ...2018 Volume 75 Issue 6 Pages 564-569
Published: November 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 22, 2018
Advance online publication: August 27, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialSiMe2(η1-C13H8)(η1-tBuN)TiMe2(thf) (1; C13H8 = fluorenyl, thf = tetrahydrofuran) was synthesized and characterized by 1H, 13C, DEPT NMR, and single crystal X-ray analysis. The catalyst system composed of the complex 1 and modified methylaluminoxane (MMAO) exhibits the characteristics of a quasi-living polymerization of 1-hexene in toluene at −30°C, producing a syndiotactic-rich polymer with a relatively narrow molecular weight distribution (Mw/Mn = 1.36). Moreover, this catalyst system is also capable of promoting the quasi-living copolymerization of 1-hexene with norbornene at room temperature, yielding random copolymers with narrow molecular weight distributions. The quasi-living nature of the catalyst allows the synthesis of syndiotactic-rich poly(1-hexene)-block-poly(1-hexene-ran-norbornene) diblock copolymers. View full abstractDownload PDF (1637K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1637K) -
Masayoshi SAITO, Toshiya UOZUMI, Toshihiko SUGANO, Takuo KATAOKA, Riic ...2018 Volume 75 Issue 6 Pages 570-575
Published: November 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 22, 2018
Advance online publication: August 27, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn the commercial production of polypropylene, MgCl2-supported TiCl4 catalyst, containing a phthalate compound as an electron donor, has been widely used, so far. It is well-known that catalyst performance depends strongly on the adsorption state of the phthalate compound on magnesium chloride. Therefore, we prepared several catalysts with different catalyst preparation conditions and phthalate compounds, and analyzed the state of phthalate compound contained therein with solid 13C NMR. When the correlation between the relaxation time of the carbonyl group in the catalyst and the catalyst performance was investigated, it was found that a catalyst exhibiting a shorter relaxation time showed higher polymerization activity. View full abstractDownload PDF (1685K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1685K)
Regular Topics
Review Articles
-
Yuki NAGAO2018 Volume 75 Issue 6 Pages 576-587
Published: November 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 22, 2018
Advance online publication: July 10, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSHighly proton-conductive polymers have attracted the attention of many researchers to be used in energy conversion devices, sensors, catalysts, actuators and others. From the viewpoint of the scientific history for developing highly proton-conductive polymers, one fundamental approach is based on the strategy of phase-segregated structures of polymers with strong acid groups. Understanding the relation between the structure and proton transport property is fundamentally important, but this attempt has often been hampered in many highly proton-conductive polymers like Nafion because of the lack of structural information derived from such amorphous or amorphous-like polymers. In this article, a new approach to enhance the proton conductivity of polymer thin films by an interface is reviewed. The author introduces suppressed proton conductivity in the Nafion thin films and then specifically examines the proton conductivity enhancement by orienting the polymers. As a related topic, highly proton-conductive organized polyimide thin films with a lyotropic liquid-crystal phase is demonstrated. The proton conductivity is enhanced by improved molecular ordering and the in-plane molecular orientation. View full abstractDownload PDF (4570K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (4570K)
Original Papers
-
Kiyomi OKADA, Wang LONG, Masahiro OHSHIMA2018 Volume 75 Issue 6 Pages 588-596
Published: November 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 22, 2018
Advance online publication: July 26, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe have studied the change in the higher order structure of polypropylene (PP)/cellulose nanofiber (CNF) composites, which have been developed in recent years, after annealing at 100°C. We found the following: CNFs suppress β crystal growth of PP in the oriented state, but do not suppress β crystal growth of PP without orientation. The amount of CNFs controls the size and orientation of PP crystals. CNFs increase the onset value of melting and crystallization. In the thermal annealing process, CNFs suppress changing of the onset value of melting, and prevent the growths of PP crystals. PP/CNF composite samples keep their shape even after thermal oxidative deterioration. As the result of the tensile testing, CNF limits elongation and increases yield stress of PP composites. View full abstractDownload PDF (4896K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (4896K) -
Yuji NISHIKAWA, Hiroto ITOH, Isao NODA, Takeshi HASEGAWA2018 Volume 75 Issue 6 Pages 597-606
Published: November 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 22, 2018
Advance online publication: August 30, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSPreviously, a pulse-induced ring down dynamic compression ATR step scan time-resolved FT-IR system had been developped by us. To obtain a basic analytical understanding of the present method, further studies have been carried out using a high density polyethlene film. Dynamic compression difference ATR spectra of the CH2 stretching vibration regions (2917–2847 cm−1) have been explored. As compared with spectral simulations based on a Fresnel multiple reflection model in the same region, the effect of the refractive index is revealed in therelative intensity of CH2 symmetric and anti-symmetric stretching vibrational bands. We have further found that obtained dynamic difference spectra are including many overtone signals, which are not involved in the original ring down compression signals generated among piezo electric actuator, inertia, and visco-elastic materials. Since the results are considered to be related to detecting non-linear components of molecular (functional) dipole moments, we suggest that this method is providing a potentially new mode of non-linear spectroscopy. View full abstractDownload PDF (4687K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (4687K) -
Hirokazu YANO, Masakazu NISHIYAMA, Sadayoshi HAYASHI, Kazuki KUDO, Hid ...2018 Volume 75 Issue 6 Pages 607-612
Published: November 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 22, 2018
Advance online publication: August 07, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA novel self-doped water-soluble conducting polymer (S-PEDOT) was synthesized by oxidative polymerization of 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene (EDOT) having an alkylsulfonate side chain. The S-PEDOT was completely dissolved in water. The weight average molecular weight (Mw) and molecular weight distribution were 22,400 g/mol and 15.4, respectively. The S-PEDOT was the paracrystalline polymer with the degree of crystallinity (Xc) and crystallite size (D100) of 68.2% and 7.1 nm, respectively. According to the values of sheet resistance (Rs = 1670~201 Ω/□) and total light transmittance (TT = 94.2~69.2%) of the S-PEDOT films with different thicknesses (d = 33~158 nm), the figure-of-merit (FOM) as a transparent electrode was found to be 4.1. It was also found that the electrical conductivity of the S-PEDOT film attained values as high as 315 S/cm. View full abstractDownload PDF (2531K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2531K) -
Shuta HARA, Sei KUREBAYASHI, Shuto WATANABE, Shigeru SHIMIZU, Hiroki I ...2018 Volume 75 Issue 6 Pages 613-618
Published: November 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 22, 2018
Advance online publication: October 04, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSemi-crystalline cast-films, referred to as mix-PLA(HFIP) and mix-PLA(CHL), respectively, were prepared by casting hexafluoro-2-propanol (HFIP) and chloroform (CHL) solutions of a mixture of an equal weight of poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA) and poly-D-lactic acid (PDLA). Before annealing, the crystal phase of mix-PLA(HFIP) consists of crystals of PLLA or PDLA (α-crystal) as a major constituent and stereocomplex of PLLA and PDLA (sc-crystal) as a minor constituent, while mix-PLA(CHL) consists of sc-crystals only. After annealing at 200°C, however, α-crystals of mix-PLA (HFIP) have disappeared and only sc-crystals were observed in mix-PLA(HFIP) as well as in mix-PLA(CHL). The size of sc-crystal domains of mix-PLA(HFIP), thus structured, has been found to be larger than that of mix-PLA(CHL). This might be the reason why mix-PLA(HFIP) films are opaque, while mix-PLA(CHL) films are transparent. View full abstractDownload PDF (2921K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2921K)
Short Communications
-
Saori TSUCHIYA, Seiichi FURUMI2018 Volume 75 Issue 6 Pages 619-624
Published: November 25, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 22, 2018
Advance online publication: September 11, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSColloidal crystals (CCs) have received tremendous interest because the highly ordered self-assembly of microparticles leads to the facile fabrication of 3D-photonic crystals. So far, there have been many reports on CC films fabricated with non-luminescent microparticles such as polystyrene (PS) or silica. This situation motivated us to synthesize luminescent PS microparticles by encapsulating organic dyes for the application to novel optoelectronic devices. In this communication, we report the successful preparation of luminescent PS microparticles encapsulating two kinds of organic dyes through emulsion polymerization in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate. When the luminescent PS microparticles were synthesized at an appropriate molar concentration of the organic dyes, the uniform CC films exhibited unique optical properties of not only Bragg reflection, but also with efficient white-light emission under illumination with UV light. As an extension of our findings, we could observe clear white-light emission from a flexible CC film of the luminescent PS particles self-assembled on a PET sheet. View full abstractDownload PDF (1932K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1932K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|