
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
[in Japanese]2023Volume 23Issue 8 Pages 414
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (450K)
-
Yasuyuki SETO2023Volume 23Issue 8 Pages 415-421
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis review provides an overview of milk protein from a nutritional function perspective. Milk is known as a calcium-rich food, but it is also a food that contains good-quality protein. Milk proteins are broadly classified into caseins and whey proteins. Caseins forms a unique structure called casein micelle in milk and plays an important role in transporting calcium phosphate, which is essential for bone growth in infants. On the other hand, whey proteins contains many types of proteins. The major components are β-lactoglobulin, α-lactalbumin, bovine serum albumin, lactoferrin, and lactoperoxidase and many of them also have some role in the growth of infants. In addition, proteins that are not major components but have unique functions have been discovered, such as milk basic protein (MBP). Furthermore, milk proteins have interesting characteristics in digestion and absorption. Whey proteins have a firm structure and are rapidly passed through the stomach to be broken down and absorbed in the intestinal tract. Casein, on the other hand, coagulates in the stomach and is slowly broken down and absorbed. Due to these differences in digestion and absorption, protein synthesis initiates quickly and keep for a long time when milk is consumed.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (679K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (679K) -
Yoshiharu TAKAYAMA2023Volume 23Issue 8 Pages 423-429
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSLactoferrin is a glycoprotein found in mammalian exocrine secretions, including milk and tears. It has a three-dimensional structure similar to that of transferrin (serotransferrin), an iron transport protein in blood plasma. Lactoferrin binds two ferric ions per molecule with high affinity, making the protein a strong iron scavenger. The iron-depriving ability combined with a direct bactericidal and immunomodulating activity contributes its host defense function. Furthermore, animal and human studies indicate that oral administration of lactoferrin improve glucose homeostasis and ameliorate their metabolic and diabetic phenotypes. At the cellular level, lactoferrin attenuated adipogenic differentiation of preadipocytes and reduced lipid accumulation by inducing lipolysis in mature adipocytes. In hepatocytes and adipocytes, LDL receptor-related protein-1 (LRP-1) is involved in cellular uptake of lactoferrin and activation of intracellular signaling pathways in response to lactoferrin.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1471K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1471K) -
Satoshi HIGURASHI2023Volume 23Issue 8 Pages 431-438
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSBreastmilk is considered the best source of nutrition for the healthy growth and development of infants. Breastmilk contains many bioactive substances, including those whose functions have not been yet known. The numerous unknown benefits of breastmilk are being researched all over the world. In order to improve the formula fed to infants as an alternative to breastmilk, it is necessary to carefully understand the composition and function of breastmilk. Therefore, we have conducted nationwide breastmilk surveys at about 30-year intervals. This review focuses on the history of our studies and describes the findings of our ongoing breastmilk survey.
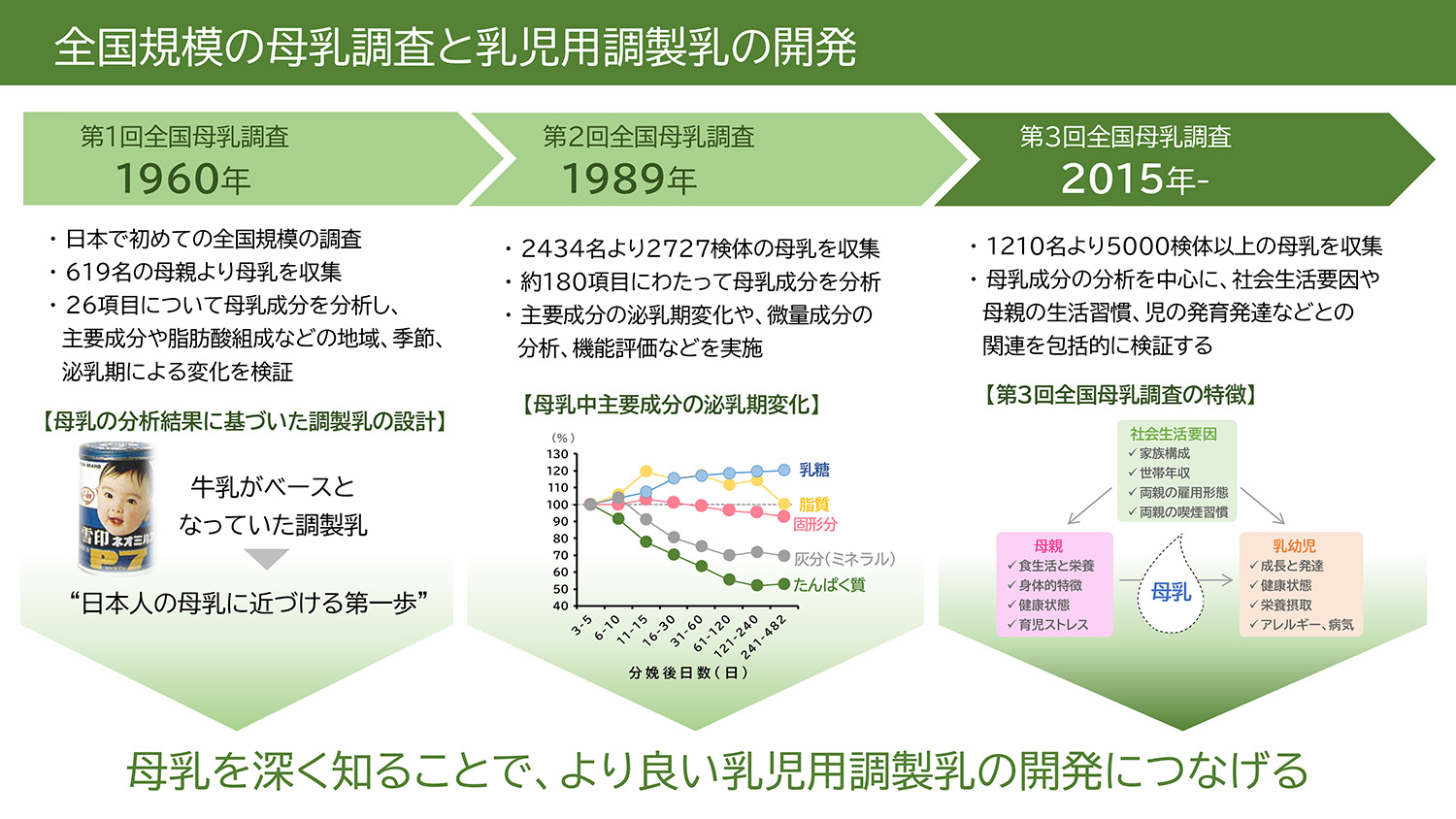 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (873K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (873K) -
Nobuya SHIRAI, Risa ARAKI, Yoshiharu TAKAYAMA2023Volume 23Issue 8 Pages 439-445
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSMilk fat is a major component of milk solids, and remains stable as emulsion of lipid particle, named milk fat globular membrane (MFGM). The predominant lipid components of MFGM are triglycerides and phospholipids. Additionally, MFGM contains lipid derivatives (sterols and carotenoids) and vitamins. Dairy foods are widely recognized as healthy sources of protein, calcium and fat-soluble vitamins. However, many dietary guidelines recommend reducing intake of saturated fats, abundantly found in milk fats, to decrease the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), especially coronary heart disease (CHD). In this review, we introduce recent animal and human studies investigating the effect of individual components of milk fat on prevention of metabolic dysfunction or chronic disease derived from metabolic dysfunction, such as CVD and type 2 diabetes.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (877K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (877K)
-
Tsunehiro Aki2023Volume 23Issue 8 Pages 456-459
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (465K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|