
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Aoi Miyamoto, Takahiko Aoyama, Yoshiaki Matsumoto2017 年 65 巻 2 号 p. 121-126
発行日: 2017/02/01
公開日: 2017/02/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2016/12/01ジャーナル フリー HTMLA high-performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet spectrophotometry (HPLC-UV) method for the determination of meloxicam (MEL) and meloxicam metabolites (5′-hydroxy meloxicam (5-HMEL) and 5′-carboxy meloxicam (5-CMEL)) has been developed. After extraction of MEL, 5-HMEL, and 5-CMEL from rat plasma using Oasis HLB cartridges, the extracts were separated with a Luna C18 (2) 100 A column (5 µm, 4.6×150 mm, Phenomenex) using a mobile phase of 50 mM phosphate buffer (pH 2.15, solvent A) and acetonitrile (solvent B) at a flow rate of 0.8 mL/min in a linear gradient. The detection wavelength was 360 nm, and the internal standard (IS) was piroxicam. Each calibration curve was linear in the range of 40 to 1000 ng/mL (r2>0.999). The extraction rates of MEL, 5-HMEL, and 5-CMEL were greater than 86.9%. The intra- and inter-day accuracies were in the range of 95.0 to 119.0%, and the precision was 0.2 to 17.0%. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of the quantitative and qualitative measurement of meloxicam and each metabolite using an HPLC-UV method.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (567K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (567K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Sayuko Shiraishi, Tamami Haraguchi, Saki Nakamura, Dahong Li, Honami K ...2017 年 65 巻 2 号 p. 127-133
発行日: 2017/02/01
公開日: 2017/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe purpose of this study was to evaluate the taste-masking effects of chlorogenic acid (CGA) on bitter drugs using taste sensor measurements and surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis of CGA–drug interactions. Six different bitter drugs were used: amlodipine besylate (AMD), diphenhydramine hydrochloride (DPH), donepezil hydrochloride (DNP), rebamipide (RBM), diclofenac sodium (DCF) and etodolac (ETD). Taste sensor outputs were significantly inhibited by the addition of CGA to all drugs. The inhibition ratio of the taste sensor output decreased in the following order DPH>DNP>AMD≈DCF≈RBM≈ETD. The association rate constant (ka) for the interaction between drugs and CGA as evaluated by SPR measurement also decreased in the following order DPH>DNP>AMD>DCF≈ETD≈RBM. It was suggested that basic drugs (AMD, DNP, DPH) associate more easily with CGA than acidic drugs (DCF, RBM, ETD). The inhibition ratios (%) of the taste sensor output of bitter drugs caused by CGA and the association rate constants (ka) between the drugs and CGA were significantly correlated (rs=0.886, p<0.05, Spearman’s correlation test). Our findings suggest that the taste-masking effects of CGA are due to its direct association with the drugs. CGA may therefore be a useful taste-masking agent for basic drugs.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (928K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (928K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Shinya Yoshida, Yasuko Obata, Yoshinori Onuki, Shunichi Utsumi, Noboru ...2017 年 65 巻 2 号 p. 134-142
発行日: 2017/02/01
公開日: 2017/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLl-Menthol increases drug partitioning on the surface of skin, diffusion of drugs in the skin, and lipid fluidity in the stratum corneum and alters the rigidly arranged lipid structure of intercellular lipids. However, l-menthol is a solid at room temperature, and it is difficult to determine the effects of l-menthol alone. In this study, we vaporized l-menthol in order to avoid the effects of solvents. The vaporized l-menthol was applied to the stratum corneum or lipid models comprising composed of ceramides (CER) [EOS], the longest lipid acyl chain of the ceramides in the stratum corneum lipids that is associated with the barrier function of the skin; CER [NS], the shorter lipid acyl chain of the ceramides, and the most components in the stratum corneum of the intercellular lipids that is associated with water retention in the intercellular lipid structure of the stratum corneum; cholesterol; and palmitic acid. Synchrotron X-ray diffraction, differential scanning calorimetry, and attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analyses revealed that the lipid models were composed of hexagonal packing and orthorhombic packing structures of different lamellar periods. Taken together, our results revealed that l-menthol strongly affected the lipid model composed of CER [EOS]. Therefore, l-menthol facilitated the permeation of drugs through the skin by liquid crystallization of the longer lamellar structure. Importantly, these simple lipid models are useful for investigating microstructure of the intercellular lipids in the stratum corneum.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1893K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1893K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Jairo Quiroga, Yazmín Villarreal, Jaime Gálvez, Alejandro Ortíz, Braul ...2017 年 65 巻 2 号 p. 143-150
発行日: 2017/02/01
公開日: 2017/02/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2016/11/25ジャーナル フリー HTMLA series of pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridines were prepared by a microwave-assisted aza-Diels–Alder reaction between pyrazolylformimidamides 1 and β-nitrostyrenes 2 in toluene as the solvent. This procedure provides a simple one-step and environmentally friendly methodology with good yields for the synthesis of these compounds. All compounds were tested for antifungal activity against two clinically important fungi Candida albicans and Cryptococcus neoformans. Within the compounds of the series bearing a –CH3 group on the carbon C-3 of the azole ring (3a–e), the compound without a substituent on the p′-phenyl ring (3a), showed the best activity against both fungi, followed by the p′-Br-phenyl (3c). Within the compounds of the series bearing a tert-butyl group in the carbon C-3 of the azole ring (3f–j), the non-substituted p′-compound (3f) was the most active one, followed by (3h) (p′-Br substituted) that showed the best activity against both fungi. The remaining compounds of this sub-series (3g, i, j) showed similar moderate activities. The antifungal activity of the compounds of the series was found to be correlated with a higher log P and a lower dipole moment in the more active compounds.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (858K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (858K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Sayuko Shiraishi, Tamami Haraguchi, Saki Nakamura, Honami Kojima, Ikuo ...2017 年 65 巻 2 号 p. 151-156
発行日: 2017/02/01
公開日: 2017/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe purpose of the study was to evaluate suppression of the bitterness intensity of bitter basic drugs by chlorogenic acid (CGA) using the artificial taste sensor and human gustatory sensation testing and to investigate the mechanism underlying bitterness suppression using 1H-NMR. Diphenhydramine hydrocholoride (DPH) was the bitter basic drug used in the study. Quinic acid (QNA) and caffeic acid (CFA) together form CGA. Although all three acids suppressed the bitterness intensity of DPH in a dose-dependent manner as determined by the taste sensor and in gustatory sensation tests, CFA was less effective than either CGA or QNA. Data from 1H-NMR spectroscopic analysis of mixtures of the three acids with DPH suggest that the carboxyl group, which is present in both QNA and CGA but not CFA, interact with the amine group of DPH. This study showed that the bitterness intensity of DPH was suppressed by QNA and CGA through a direct electrostatic interaction with DPH as confirmed in 1H-NMR spectroscopic analysis. CGA and QNA may therefore be useful bitterness-masking agents for the basic drug DPH.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (549K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (549K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Atsushi Nakashima, Tomohisa Izumi, Kazutomi Ohya, Keita Kondo, Toshiyu ...2017 年 65 巻 2 号 p. 157-165
Atsushi Nakashima, Tomohisa Izumi, Kazutomi Ohya, Keita Kondo, Toshiyu ...2017 年 65 巻 2 号 p. 157-165
発行日: 2017/02/01
公開日: 2017/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLIn this study, we developed highly dispersible polylactic glycolic acid (PLGA) copolymer microparticles (MRPs) in aqueous fluid. A solution containing both dissolved aripiprazole as a model drug and PLGA were spray-dried to make MRPs. The resultant MRPs were further co-processed with water-soluble additives and a surfactant to improve their dispersion behavior. The granules containing MRPs and additives, termed granulated microparticles (G-MRPs) were prepared by a newly established drop freeze-drying technique. The physicochemical properties of MRPs and G-MRPs were evaluated as a long-acting release depot injectable. The MRPs were spherical particles with diameters of approximately 1 to 20 µm and strongly assembled to one another in the aqueous phase, forming large aggregations. In contrast, the G-MRPs were spherical granules with diameters of approximately 200 to 400 µm that displayed a microparticles-in-granule structure in which small MRPs were embedded in the porous matrix inside the granules. When the G-MRPs were placed in water, the porous matrix base was immediately dissolved, and each embedded MRP was individually released, thus inducing monodispersion and significantly improved dispersibility. The excellent dispersibility was attributed to the water-soluble porous network structure mainly composed of D-mannitol and the steric hindrance effects derived from the polymeric molecular chains. These properties may give rise to the excellent passage of PLGA microparticles through needles for use in depot formulation suspensions. A crystalline evaluation of the G-MRPs suggested that the drug and PLGA molecularly interacted and that their thermodynamic stability was improved.
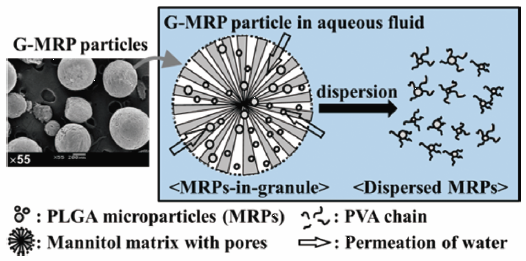 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pickIn this article, injectable products composed of biocompatible and biodegradable poly-lactic glycolic acid copolymer (PLGA) microparticles are described. In order to improve the dispersibility of MRPs in injection solutions, MRPs were subjected to a secondary processing, i.e., the drop freeze-drying technique. The suspension with MRPs and water-soluble additives were rapidly dripped into liquid nitrogen in the form of droplets. The resultant frozen particles were freeze-dried to prepare spherical granules containing multiple MRPs (Granulated-MRPs). When the G-MRPs were placed in water for injection, the porous matrix base was immediately dissolved, and each embedded MRPs were individually released, thus inducing monodispersion and significantly improved dispersibility. The granular products could be automatically filled into the pre-filled syringes and may give rise to the excellent passage of PLGA MRPs through needles for use in depot injected formulation as a ready-to-use.
PDF形式でダウンロード (3812K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Yeongbin Lee, Prakash Thapa, Seong Hoon Jeong, Mi Hee Woo, Du Hyung Ch ...2017 年 65 巻 2 号 p. 166-177
発行日: 2017/02/01
公開日: 2017/02/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2016/11/30ジャーナル フリー HTMLEven though experimental designs are becoming popular especially for conventional dosage forms, limited studies have been performed to optimize formulations of orally disintegrating films (ODFs). This study aimed to evaluate sildenafil citrate-loaded ODFs for a controlled release with hydroxypropyl methylcellulose as a film-forming polymer. A factorial design was utilized for optimization with three control factors: ethanol ratio, plasticizer ratio, and the type of plasticizer. Tensile strength, disintegration time, water contact angle, and thickness were chosen as responses. For optimization, water contact angle, disintegration time, and thickness were minimized, while the tensile strength was maximized. Based on the conditions, optimal formulations were achieved for each type of plasticizer. Evaluation of desirability indicated that the response values were close to the target. When these optimal formulations were validated, the optimal solutions and target values were similar with small biases. The formulations were characterized using scanning electron microscopy, differential scanning calorimetry, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, surface pH, in vitro dissolution, and drug release simulation with a mathematical modeling. After the drug was homogenously dispersed throughout the film, the crystalline form of the drug provided strong hydrogen bonds between the drug and the film components. Moreover, it showed a controlled drug release profiles that were well matched with simulated results. This study suggests that the optimized films may present a better alternative to conventional tablets for the treatment of male erectile dysfunction.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2983K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2983K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Yang Zhou, Yu-Shun Yang, Xiao-Da Song, Liang Lu, Hai-Liang Zhu2017 年 65 巻 2 号 p. 178-185
発行日: 2017/02/01
公開日: 2017/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLFatty acid synthesis (FAS) is an essential metabolism during the whole growth and development process of the bacterial. Several key enzymes which involved in this biosynthetic pathway have been considered as useful targets for the development of new antibacterial agents. Among them, β-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthase III (FabH) is the most magnetic target, since it is central to the initiation of fatty acid biosynthesis and is highly conserved of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Following the previous researches, Schiff-based derivatives with dioxygenated rings and N-heterocycle were synthesized in succession, and their biological activities as potential FabH inhibitors were evaluated in this paper. Among these 15 compounds, compound 2E exhibited the best antibacterial activities with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values 1.56–3.13 mg/mL against the tested bacterial strains and showed the most powerful Escherichia coli (E. coli) FabH inhibitory activities with IC50 of 2.1 µM. Also the conceivable binding conformation of placing compound 2E into the E. coli FabH active site was affirmed docking simulation.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (637K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (637K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Masafumi Dohi, Wataru Momose, Kazunari Yamashita, Tadashi Hakomori, Sh ...2017 年 65 巻 2 号 p. 186-193
発行日: 2017/02/01
公開日: 2017/02/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2016/12/06ジャーナル フリー HTMLManufacturing the solid dosage form of an orally administered drug requires lubrication to enhance manufacturability, ensuring that critical quality attributes such as disintegration and dissolution of the drug product are maintained during manufacture. Here, to evaluate lubrication performance during manufacture, we used terahertz attenuated total reflection (THz-ATR) spectroscopy to detect differences in the physical characteristics of the lubricated powder. We applied a simple formulation prepared by blending granulated lactose as filler with magnesium stearate as lubricant. A flat tablet was prepared using the lubricated powder to acquire sharp THz-ATR absorption peaks of the samples. First, we investigated the effects of lubricant concentration and compression pressure on preparation of the tablet and then determined the effect of the pressure applied to samples in contact with the ATR prism on sample absorption amplitude. We focused on the differences in the magnitudes of spectra at the lactose-specific frequency. Second, we conducted the dynamic lubrication process using a 120-L mixer to investigate differences in the magnitudes of absorption corresponding to the lactose-specific frequency during lubrication. In both studies, enriching the lubricated powder with a higher concentration of magnesium stearate or prolonging blending time correlated with higher magnitudes of spectra at the lactose-specific frequency. Further, in the dynamic lubrication study, the wettability and disintegration time of the tablets were compared with the absorption spectra amplitudes at the lactose-specific frequency. We conclude that THz-ATR spectroscopy is useful for detecting differences in densities caused by a change in the physical properties of lactose during lubrication.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1640K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1640K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Kengo Hanaya, Kazuaki Matsumoto, Yuta Yokoyama, Junko Kizu, Mitsuru Sh ...2017 年 65 巻 2 号 p. 194-199
発行日: 2017/02/01
公開日: 2017/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLLinezolid (1) is an oxazolidinone antibiotic that is partially metabolized in vivo via ring cleavage of its morpholine moiety to mainly form two metabolites, PNU-142300 (2) and PNU-142586 (3). It is supposed that accumulation of 2 and 3 in patients with renal insufficiency may cause thrombocytopenia, one of the adverse effects of linezolid. However, the poor availability of 2 and 3 has hindered further investigation of the clinical significance of the accumulation of these metabolites. In this paper, we synthesized metabolites 2 and 3 via a common synthetic intermediate, 4; this will encourage further exploration of events related to these metabolites and lead to improved clinical use of linezolid.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (493K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (493K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Meiying Ao, Yong Chen2017 年 65 巻 2 号 p. 200-203
発行日: 2017/02/01
公開日: 2017/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLBeta-cyclodextrin (β-CD) has been applied as drug/food carriers or potential drugs for treating some diseases. Most recently, some evidence indicated that methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MβCD) and 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (2-HPβCD), two major derivatives of β-CD, may inhibit atherogenesis, implying that cyclodextrins also can be potential drugs for treating atherosclerosis. It is well known that modification (e.g. oxidation) of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is one of the most critical steps of atherogenesis. Lipoxygenase, an enzyme able to be expressed by atherosclerosis-related vascular cells, is generally regarded as a possible in vivo agent of LDL oxidation. In this study, the effects of MβCD on LDL oxidation induced by lipoxygenase were investigated by measuring the electrophoretic mobility, conjugated diene formation, malondialdehyde (MDA) production, and amino group blockage of LDL. We found that the lipids depleted from LDL by MβCD could be oxygenated more readily by lipoxygenase whereas the lipoxygenase-induced oxidation of the remaining lipid-depleted LDL decreased. The data imply that MβCD has an inhibitory effect on lipoxygenase-induced LDL oxidation and probably helps to inhibit atherogenesis.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (941K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (941K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Nguyen Hai Dang, Nguyen Dinh Chung, Ha Manh Tuan, Nguyen Tuan Hiep, Ng ...2017 年 65 巻 2 号 p. 204-207
発行日: 2017/02/01
公開日: 2017/02/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2016/12/03ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録A phytochemical fractionation of a methanol extract of Ophiopogon japonicus tubers led to the isolation of a new homoisoflavanone, homoisopogon A (1), and three new homoisoflavanes, homoisopogon B–D (2–4). Their chemical structures were elucidated by mass, NMR, and circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopic methods. Homoisopogon A (1) exhibited potent cytotoxicity against human lung adenocarcinoma LU-1, human epidermoid carcinoma KB, and human melanoma SK-Mel-2 cancer cells with IC50 values ranging from 0.51 to 0.66 µM.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (391K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (391K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|