
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 Shinya Harusawa2020 年68 巻1 号 p. 1-33
Shinya Harusawa2020 年68 巻1 号 p. 1-33
発行日: 2020/01/01
公開日: 2020/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLNovel reactions using hetero-heavy atoms (P, S, Si, Se, and Sn) were developed and applied to the synthesis of biofunctional molecules and some medicine-candidates, in which the following items are covered. 1) Development of introduction of C1-unit using cyanophosphates (CPs). 2) Carbene-generation under neutral condition from CPs and its application to organic synthesis. 3) [3,3]Sigmatropic rearrangement-ring expansion reactions of medium-sized cyclic thionocarbonates containing a sulfur atom and their application to natural product synthesis. 4) Stereoselective synthesis of novel β-imidazole C-nucleosides via diazafulvene intermediates and their application to investigating ribozyme reaction mechanism. 5) Developments of novel histamine H3- and H4-receptor ligands using new synthetic methods involving Se or Sn atoms.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pickNovel reactions using hetero-heavy atoms (P, S, Si, Se, and Sn) were developed and applied to the synthesis of biofunctional molecules and some medicine-candidates. 1) Development of introduction of C1-unit using cyanophosphates (CPs). 2) Carbene-generation from CPs and its application to organic synthesis. 3) [3,3]Sigmatropic rearrangement-ring expansion reactions of medium-sized cyclic thionocarbonates containing a sulfur atom and their application to natural product synthesis. 4) Stereoselective synthesis of novel b-imidazole C-nucleosides via diazafulvene intermediates and their application to investigating ribozyme reaction mechanism. 5) Developments of novel histamine H3- and H4-receptor ligands using new synthetic methods involving Se or Sn atoms.
PDF形式でダウンロード (5209K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Yukihiro Itoh2020 年68 巻1 号 p. 34-45
Yukihiro Itoh2020 年68 巻1 号 p. 34-45
発行日: 2020/01/01
公開日: 2020/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLEnzymatic and post-translational modifications (PTMs) such as ubiquitination, acetylation, and methylation occur at lysine residues. The PTMs play critical roles in the regulation of the protein functions, and thus, various cellular processes. In addition, aberrations of the PTMs are associated with various diseases, such as cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. Therefore, we hypothesized that modulation of the PTMs and normalization of the PTM abnormalities could be useful as methods to control various cellular mechanisms and as a therapeutic strategy, respectively. To modulate the PTMs, we have focused on lysine-modifying enzymes and have pursued drug discovery researches on ubiquitination inducers, lysine deacetylase (KDAC) inhibitors, and lysine demethylase (KDM) inhibitors. For the identification of the modulators, we have used not only conventional drug design, such as structure-based drug design (SBDD) and ligand-based drug design (LBDD), but also “strategic chemistry approaches,” such as drug design based on enzyme catalytic mechanism. As a result, we have identified several modulators which have pharmacological effects in animal models or in cellular studies. In this review, focusing on the drug design based on enzyme catalytic mechanism, our drug discovery researches have been discussed.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pickBecause lysine modifications on proteins control various cellular processes and aberrations of the modifications are associated with various diseases, chemical modulation of lysine-modifying enzymes is interesting as a method to regulate the cellular functions or as a therapeutic strategy. Therefore, the author has identified some modulators of lysine-modifying enzymes. To find the modulators, the author has combined conventional drug design with “strategic chemistry approaches,” such as drug design based on enzyme catalytic mechanism. In this review, the author’s drug discovery studies are presented.
PDF形式でダウンロード (1855K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Dmitry Aminin, Sergey Polonik2020 年68 巻1 号 p. 46-57
発行日: 2020/01/01
公開日: 2020/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLOver the past decade, a number of new 1,4-naphthoquinones have been isolated from natural sources and new 1,4-naphthoquinones with diverse structural features have been synthesized. Cardioprotective, anti-ischemic, hepatoprotective, neuroprotective and some other new properties were found for these compounds; their role in protecting against neurodegenerative diseases has been established. Their anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and antitumor activities have been studied in more detail; new, previously unknown intracellular molecular targets and mechanisms of action have been discovered. Some compounds of this class are already being used as a medicinal drugs and some substances can be used as biochemical tools and probes for non-invasive detection of pathological areas in cells and tissues in myocardial infarction and neurodegenerative diseases using modern molecular imaging techniques.
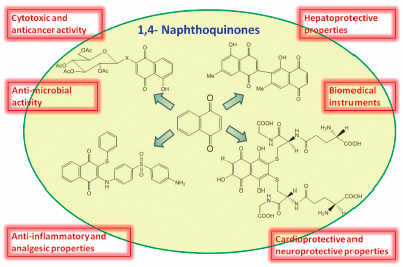 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1152K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1152K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Kongkai Zhu, Daohai Du, Rui Yang, Hongrui Tao, Hua Zhang2020 年68 巻1 号 p. 58-63
発行日: 2020/01/01
公開日: 2020/01/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/11/01ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) is an attractive drug target for anti-cancer treatment. Among the three core subunits (EZH2, EED and SUZ12) of PRC2, EZH2 is the catalytic subunit that methylates histone H3 lysine 27 (H3K27), while EED is the regulatory subunit. Besides the small-molecule inhibitors of EZH2, those targeting the protein–protein interaction (PPI) between EZH2 and EED have also been reported. Here, for the first time, we have identified the key residues that contributed most to the EED–EZH2 binding affinity by molecular mechanics Poisson–Boltzmann surface area (MM-PBSA) calculations based on the 200 ns molecular dynamics simulation. Moreover, we report the identification of two novel and potent small-molecule inhibitors (35 and 49) of EZH2–EED interaction (bottom interaction surface) by virtual screening and biological evaluations. Binding modes of the two identified molecules with EED were probed by molecular docking. Additionally, 35 and 49 displayed cellular antiproliferative activity against diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cancer cell line Toledo whose cell growth was driven by aberrant PRC2 activity. Our findings have provided structural insights for the design of novel EZH2–EED interaction inhibitors to regulate the activity of PRC2 complex.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1321K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1321K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Xiaoyan Han, Shumin Wang, Na Zhang, Liwen Ren, Xiaoyang Sun, Yali Song ...2020 年68 巻1 号 p. 64-69
発行日: 2020/01/01
公開日: 2020/01/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/11/08ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Invasive fungal disease constitutes a growing health problem and development of novel antifungal drugs with high potency and selectivity are in an urgent need. In this study, a novel series of triazole derivatives containing different ester skeleton were designed and synthesized. Microdilution broth method was used to investigate antifungal activity. Significant inhibitory activity of compounds 5c, 5d, 5e, 5f, 5m and 5n was evaluated against the Candida albicans (I), Candida albicans clinical isolate (II), Candida glabrata clinical isolate (I), and Candida glabrata (II) with minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC80) values ranging from 2 to 16 µg/mL. Notably, compounds 5e and 5n showed the best inhibition against Candida albicans (II), Candida glabrata (I), and Candida glabrata (II) at the concentrations of 2 and 8 µg/mL, respectively. Molecular docking study revealed that the target compounds interacted with CYP51 mainly through hydrophobic and van der Waals interactions. The results indicated that these novel triazole derivatives could serve as promising leads for development of antifungal agents.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1291K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1291K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Fumihiko Ogata, Takehiro Nakamura, Megumu Toda, Masashi Otani, Naohito ...2020 年68 巻1 号 p. 70-76
発行日: 2020/01/01
公開日: 2020/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録In this study, nickel–aluminium complex hydroxides at different molar ratios (nickel–aluminium = 1 : 2, 1 : 1, 2 : 1, 3 : 1, and 4 : 1, referred to as NA12, NA11, NA21, NA31, and NA41) were prepared, and their adsorption capability for chromium(VI) ion was investigated. Firstly, physicochemical characteristics (SEM images, X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns, specific surface area, amount of hydroxyl groups, and surface pH) of nickel–aluminum complex hydroxide were evaluated. The amount of chromium(VI) ion adsorbed onto NA11 (15.3 mg/g) was greater than that adsorbed onto the other adsorbents. This research elucidated that the amount of chromium(VI) ion adsorbed using nickel–aluminium complex hydroxide was related to the adsorbent surface properties (r = 0.818–0.875). Subsequently, the adsorbent (NA11) surface before and after adsorption of chromium(VI) ion was evaluated, and chromium energy (577 and 586 eV) detected after adsorption onto the NA11 surface. These results revealed that the NA11 surface properties were very important for the removal of chromium(VI) ion from aqueous solution. In addition, the effects of pH, contact time, and temperature on the adsorption of chromium(VI) ion were evaluated. We confirmed a high recovery percentage of chromium(VI) ion when using sodium hydroxide solution at 10–1000 mmol/L (approximately greater than 80%) in this experimental condition. Thus, NA11 is a promising adsorbent for the removal of chromium(VI) ion from aqueous solution.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1747K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1747K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Kazuyuki Kuramoto, Yuki Sawada, Naoki Ishibashi, Tomohiro Yamada, Take ...2020 年68 巻1 号 p. 77-90
Kazuyuki Kuramoto, Yuki Sawada, Naoki Ishibashi, Tomohiro Yamada, Take ...2020 年68 巻1 号 p. 77-90
発行日: 2020/01/01
公開日: 2020/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLNovel 3,5-dimethylpyridin-4(1H)-one scaffold compounds were synthesized and evaluated as AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activators. Unlike direct AMPK activators, this series of compounds showed selective cell growth inhibitory activity against human breast cancer cell lines. By optimizing the lead compound (4a) from our library, 2-[({1′-[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-2-methyl-1′,2′,3′,6′-tetrahydro[3,4′-bipyridin]-6-yl}oxy)methyl]-3,5-dimethylpyridin-4(1H)-one (25) was found to have potent AMPK activating activity. Compound 25 also showed good aqueous solubility while maintaining the unique selectivity in cell growth inhibitory activity.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pickThis paper describes that synthesis and evaluation of novel 3,5-dimethylpyridin-4(1H)-one scaffold compounds as indirect AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activators. Unlike direct AMPK activators, this series of compounds inhibited cell growth of MDA-MB-453 but not that of SK-BR-3. The initial structure optimization of the lead compound 4a led to the discovery of compound 4f with potent AMPK activation activity and poor aqueous solubility. By further optimizing 4f, promising compound 25 was found out as a potent AMPK activator with good aqueous solubility.
PDF形式でダウンロード (2961K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Naohiro Oshima, Honoka Kume, Takayoshi Umeda, Haruki Takito, Mitsutosh ...2020 年68 巻1 号 p. 91-95
発行日: 2020/01/01
公開日: 2020/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLMagnolia Flower is a crude drug used for the treatment of headaches, toothaches, and nasal congestion. Here, we focused on Magnolia kobus, one of the botanical origins of Magnolia Flower, and collected the flower parts at different growth stages to compare chemical compositions and investigate potential inhibitory activities against interleukin-2 (IL-2) production in murine splenic T cells. After determining the structures, we examined the inhibitory effects of the constituents of the bud, the medicinal part of the crude drug, against IL-2 production. We first extracted the flower parts of M. kobus from the bud to fallen bloom stages and analysed the chemical compositions to identify the constituents characteristic to the buds. We found that the inhibitory activity of the buds against IL-2 production was more potent than that of the blooms. We isolated two known compounds, tiliroside (1) and syringin (2), characteristic to the buds from the methanol (MeOH) extract of Magnolia Flower. Moreover, we examined the inhibitory activities of both compounds against IL-2 production and found that tiliroside (1) but not syringin (2), showed strong inhibitory activity against IL-2 production and inhibited its mRNA expression. Thus, our strategy to examine the relationship between chemical compositions and biological activities during plant maturation could not only contribute to the scientific evaluation of medicinal parts of crude drugs but also assist in identifying biologically active constituents that have not yet been reported.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1205K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1205K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Tran Thi Hong Hanh, Nguyen Thi Thuy My, Pham Thi Cham, Tran Hong Quang ...2020 年68 巻1 号 p. 96-99
発行日: 2020/01/01
公開日: 2020/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Chemical investigation of the aerial parts of Andrographis paniculata resulted in isolation of nine compounds, including a new ent-labdane diterpenoid, andrographic acid methyl ester (1), a new chalcone glucoside, pashanone glucoside (5), and seven known metabolites, andrograpanin (2), andrographolide (3), andropanolide (4), andrographidine A (6), andrographidine F (7), 6-epi-8-O-acetyl-harpagide (8), and curvifloruside F (9). Their chemical structures were elucidated based on comprehensive analyses of the spectroscopic data, including NMR and MS. Among the isolated compounds, andropanolide exerted cytotoxicity toward LNCaP, HepG2, KB, MCF7, and SK-Mel2 carcinoma cells, with IC50 values ranging from 31.8 to 45.9 µM. In addition, andropanolide significantly inhibited the overproduction of nitric oxide (NO) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages, with an IC50 value of 13.4 µM.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (469K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (469K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Makoto Anraku, Daisuke Iohara, Hajime Takada, Takafumi Awane, Jun Kawa ...2020 年68 巻1 号 p. 100-102
Makoto Anraku, Daisuke Iohara, Hajime Takada, Takafumi Awane, Jun Kawa ...2020 年68 巻1 号 p. 100-102
発行日: 2020/01/01
公開日: 2020/01/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/10/29ジャーナル フリー HTMLEuglena gracilis EOD-1, a microalgal strain, produces large quantities of paramylon, a class of polymers known as β-1,3-glucans and has been reported to function as a dietary fiber and to improve the metabolic syndrome including obesity. However, despite its importance, the morphometric analysis of paramylon has not been conducted so far. In this study, we attempted to observe the detailed three-dimensional structure of paramylon by focused ion beam/scanning electron microscopy (FIB/SEM). Paramylon samples were fixed and three-dimensional image reconstruction and segmentation of the image stack were created using computer software (Amira v6.0.1, FEI). The results indicated that the inside of paramylon particles (diameter: 5 µm, thickness: 3 µm) was comprised of a dense structure with no evidence of the presence of large pores and gaps, although a small 100 nm crack was observed. The specific surface area of paramylon particles measured by the Brunauer–Emmet–Teller (BET) method, was not as large as activated charcoal, but similar to those of plant starches, indicating that the cholesterol-lowering effect of paramylon cannot be simply attributed to its adsorption ability. The FIB/SEM method was found to be useful for elucidating the internal structure of small solid particles.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pickEuglena gracilis EOD-1, produces large quantities of paramylon, has been reported to function as a dietary fiber. However, the morphometric analysis of paramylon has not been conducted so far. The authors attempted to observe the detailed three-dimensional structure of paramylon by FIB/SEM. The inside of paramylon particles was comprised of a dense structure with no evidence of the presence of large pores and gaps. The specific surface area of paramylon particles was not as large as activated charcoal, but similar to those of plant starches, indicating that the cholesterol-lowering effect of paramylon cannot be simply attributed to its adsorption ability.
PDF形式でダウンロード (3418K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|