
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Toshiyuki Wakimoto2023 年71 巻1 号 p. 1-8
発行日: 2023/01/01
公開日: 2023/01/01
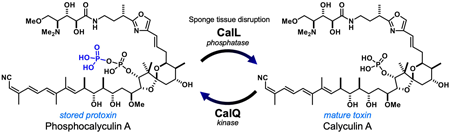
ジャーナル フリー HTMLMarine sponges are among the most primitive animals and often contain unique, biologically active compounds. Several of these compounds have played an important roles as pharmaceutical leads for anti-cancer drugs, such as halichondrin B, which led to the development of an anti-breast cancer drug. Some compounds with remarkable biological activities are accumulated in significantly high concentrations in the sponge. How and why the marine sponges produce and accumulate bioactive natural products are long-standing questions with both biochemical and ecological implications, since in sponges, the animal-microbe symbioses are presumed to be responsible for the biosynthetic machinery, consisting of efficient enzymes and regulatory systems for the specific biological activities of medicinally relevant natural products. In this review, I focus on the chemically rich Theonellidae family sponges and discuss the biosynthesis of bioactive peptides and polyketides. In particular, the biosynthetic pathway of calyculin A suggests that crosstalk between the sponge host and bacterial symbiont confers a chemical defense system on the immobile animal-microbe holobiont.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3215K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3215K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Mitsuhiro Wada2023 年71 巻1 号 p. 9
発行日: 2023/01/01
公開日: 2023/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLPDF形式でダウンロード (183K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Ryoko Tomita, Tadashi Hayama, Nao Nishijo, Rintaro Sogawa, Chisato Shi ...2023 年71 巻1 号 p. 10-14
発行日: 2023/01/01
公開日: 2023/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLIn this study, an HPLC analysis method using pre-column derivatization with 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate (AQC) was developed for the determination of o-phosphoethanolamine (PEA), which is a potential biomarker for the diagnosis of major depressive disorder, in human plasma sample. After PEA was derivatized with AQC under mild conditions, the obtained derivative was subjected to purification with a titanium dioxide-modified monolithic silica spin column (MonoSpin® TiO). The eluate from the MonoSpin® TiO was directly injected into an amide-type hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) column-equipped HPLC system, and the resulting derivative could be separated on the column under alkaline mobile phase conditions and subsequently detected fluorometrically at excitation and emission wavelengths of 250 and 395 nm, respectively. The limit of detection and limit of quantification for a 10 µL injection volume of PEA were 0.052 and 0.17 µM, respectively. The method was validated at 0.2, 1.0, and 5.0 nmol/mL levels in plasma sample, and the precision values were 2.0–6.6% as relative standard deviation and the correlation coefficient (r) of the calibration curve was 0.9995. Furthermore, applicability of this method was demonstrated by analyzing PEA levels in plasma samples from mental illness patients.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (481K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (481K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Tsutomu Kabashima, Nana Hamasaki, Keiko Tonooka, Takayuki Shibata2023 年71 巻1 号 p. 15-18
発行日: 2023/01/01
公開日: 2023/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLProlidase is the only enzyme capable of cleaving imidodipeptides containing C-terminal proline (Pro) or hydroxyproline and plays a crucial role in several physiological processes such as wound healing and cell proliferation. Here, we developed a new method to determine prolidase activity. This method is based on a novel fluorescence (FL) reaction selective for N-terminal glycine (Gly)-containing peptides using 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (3,4-DHPAA). The 3,4-DHPAA can selectively react with Gly–Pro, the substrate for prolidase, and the prolidase activity is measured by monitoring the decrease in FL intensities. The prolidase activities in fibroblasts and HeLa cells were successfully measured by the proposed method. Compared with classical Chinard’s method, our method does not require any caustic acids, pre-incubation to activate the enzyme, and heating for reaction with the detection reagent. The proposed method enables facile and specific measurement for biogenic prolidase activity.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (512K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (512K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Makoto Takada, Ichika Watanabe, Kazuya Naito, Junpei Mutoh, Yoshihito ...2023 年71 巻1 号 p. 19-23
発行日: 2023/01/01
公開日: 2023/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLAn assay using HPLC with fluorescence (FL) detection method for monitoring native FL of tocilizumab (TCZ) in human serum combined with extremely simple and rapid pretreatment without any antigen-antibody reaction was developed. Good separation of TCZ was achieved within 13 min on a Presto FF-C18 column (100 × 4.6 mm i.d., 2 µm). Simple pretreatment with acetonitrile containing primary and secondary alkylamines having longer than C3 in the alkyl chain removed immunoglobulin G subclass 1 and TCZ could be recovered selectively. The spiked calibration curve of TCZ in human serum showed good linearity in the range of 40–1000 µg/mL (r > 0.997). The lower limit of quantitation (S/N = 10) of the TCZ was 19.7 µg/mL. The accuracy was within 103.5–114.9%, and the intra- and inter-day precisions as relative standard deviations were less than 5.3 and 7.8% (n = 5), respectively. The recovery of TCZ was 42.2 ± 3.4% (n = 3). The TCZ in pretreated sample was confirmed to be stable for 6 h (>95%) at room temperature and 24 h (>95%) at 4 °C. The proposed method is considered extremely superior to the previous methods in terms of time requirement for analysis. Therefore, the developed method may be more useful than conventional methods in urgent situations, such as confirming therapeutic efficacy of cytokine-release syndrome by 2019 coronavirus disease.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (574K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (574K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Koichi Saito, Miki Takase, Yuka Yasumura, Rie Ito2023 年71 巻1 号 p. 24-30
発行日: 2023/01/01
公開日: 2023/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録We have developed a fluorescence detection-liquid chromatography (HPLC-FL) method that involves sample pretreatment by solid-phase dispersive extraction (SPDE) and solid-phase fluorescence derivatization for the simple and rapid analysis of methamphetamine (MA) in urine. This method uses a reversed-phase polymeric solid-phase gel to clean up analytes in SPDE, followed by fluorescence derivatization with 9-fluorenylmethyl chloroformate (FMOC) in the solid-phase. The optimal conditions for SPDE and solid-phase fluorescence derivatization were obtained when J-SPEC PEP was used as the solid-phase gel and 0.5 mmol/L FMOC in 50 mmol/L borate buffer solution (pH 10) was used as the fluorescence derivatization reagent. The recovery experiment of MA in urine yielded a clean chromatogram with no interfering peaks, demonstrating the validity of our method; the recoveries were 83.6% when spiked at a low concentration level (100 ng/mL) and 80.7% when spiked at a high concentration level (1000 ng/mL). Compared with the conventional liquid-phase method, the reaction product (FMOC-MA) of solid-phase fluorescence derivatization had higher stability. Reaction rate constants were calculated by changing the temperature conditions, and physicochemical parameters, including activation energy and activation entropy involved in the degradation reaction, were obtained from the Arrhenius plot and analyzed thermodynamically. Taken together, our results suggest that the HPLC-FL method with SPDE and solid-phase fluorescence derivatization for sample pretreatment provides a simple and rapid means of analyzing MA in urine samples.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1057K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1057K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
 Hiroki Ohnari, Eiji Naru, Osamu Sakata, Yasuko Obata2023 年71 巻1 号 p. 31-40
Hiroki Ohnari, Eiji Naru, Osamu Sakata, Yasuko Obata2023 年71 巻1 号 p. 31-40
発行日: 2023/01/01
公開日: 2023/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Intercellular lipids fill the interstices of corneocytes and serve a barrier function. The amount of transdermal water evaporation varies depending on the packing structure of intercellular lipids, as this structure is important for maintaining barrier efficacy. This packing structure consists of a mixture of crystals (orthorhombic and hexagonal) and liquid crystals (fluid phase), and the proportion of these phases is thought to affect barrier function. However, there have been no methods to visualize the actual distribution of the domains formed by packing structure in intercellular lipids. In this study, the planar distribution of intercellular lipid structures was determined using focal plane array (FPA)-based Fourier transform (FT) IR imaging analysis of stratum corneum cell units obtained by grid stripping. The lipid composition of ceramides was revealed by electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (ESI-MS/MS)-based shotgun lipidomics. The distribution of domains formed by packing structures and the lipid composition of ceramides was compared in skin with high- or low-transepidermal water loss (TEWL). The orthorhombic proportion was lower in high-TEWL skin than in low-TEWL skin. ESI-MS/MS-based shotgun lipidomics analysis showed that the alpha-hydroxyceramide content in the low- and high-TEWL groups differed regarding the distribution of fatty acid chain lengths. The evaluation of stratum corneum cell units using FPA-based FTIR imaging is an innovative technology that can visualize the distribution of domains formed by intercellular lipid-packing structures. Increased proportions of alpha-hydroxyceramide subclasses such as alpha-hydroxy-sphingosine ceramide and alpha-hydroxy-phytosphingosine ceramide were associated with a reduced proportion of the orthorhombic packing structure domain.
 抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
抄録全体を表示Editor's pickThe packing structure of intercellular lipids in the stratum corneum plays a pivotal role in the skin’s barrier function. The distribution of the packing structure domain is not well understood. The authors collected human stratum corneum cell samples by grid stripping and performed focal plane array-based Fourier transform infrared imaging analysis. The result suggested the distribution of packing structure domain was not uniform, and that the proportion of orthorhombic packing domain was lower in barrier-deficient skin with high transdermal water loss. Authors discussed the relationship between the distribution of packing structure domain and ceramide composition and its chain length.
PDF形式でダウンロード (3643K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Koko Tanaka, Rieko Saito, Maki Matsuhama, Seiko Miyazaki2023 年71 巻1 号 p. 41-51
Koko Tanaka, Rieko Saito, Maki Matsuhama, Seiko Miyazaki2023 年71 巻1 号 p. 41-51
発行日: 2023/01/01
公開日: 2023/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Globalization of pharmaceutical supply chains has expanded and manufacturers are required to manufacture products in compliance with the pharmacopoeial standards used in all exporting countries/regions to ensure product quality. International harmonization has been facilitated by the Pharmacopoeial Discussion Group consisting of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia, the United States Pharmacopeia, and the European Pharmacopoeia. However, since the pharmacopoeias have been developed individually under the regulatory framework of each country/region, differences exist between these pharmacopoeias. When using pharmacopoeias, an understanding of common pharmacopoeial rules is essential. Clarifying the similarities and differences in the General Notices of the pharmacopoeias widely referenced worldwide is considered valuable for those already using one or two of them to access the remaining pharmacopoeias. In this study, we compared the existence of items and the contents described in the General Notices of the three pharmacopoeias to clarify the differences. Investigation of the existence of items revealed that more than 70% of the 105 items in General Notices in the three pharmacopoeias were in the entire pharmacopoeias (for Japan, including Japanese laws and notifications). Furthermore, investigating contents revealed that approximately 20% of the 105 items have some differences such as numerical values and test conditions. However, it was shown that most of the items did not have major differences. It is expected that the three pharmacopoeias will be utilized simultaneously by understanding the similarities and differences shown in this study.
 抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
抄録全体を表示Editor's pickWith the globalization of pharmaceutical supply chains, manufacturers are required to manufacture products in compliance with the pharmacopoeial standards used in all exporting countries/regions to ensure product quality. However, since pharmacopoeias have been developed individually under the regulatory framework of each country/region, the structures and contents are unique. When using pharmacopoeias, an understanding of General Notices is essential because they list general rules applied to the entire pharmacopoeia. The authors compared the existence of items and the contents in the General Notices of the pharmacopoeias in Japan, the United States, and Europe comprehensively and revealed their similarities and differences.
PDF形式でダウンロード (1752K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Koji Wada, Masuo Goto, Kuo-Hsiung Lee, Hiroshi Yamashita2023 年71 巻1 号 p. 52-57
発行日: 2023/01/01
公開日: 2023/01/01
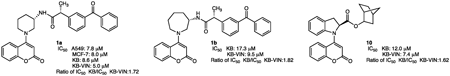
ジャーナル フリー HTMLChemotherapy refers principally to the use of small molecules to treat cancer, and natural product derivatives have been main sources of clinically using anticancer drugs. While the coumarin skeleton does not inhibit cell growth, its derivatives are often active, and numerous coumarins have been examined for antiproliferative activity against human cancer cell lines. In this study, 16 novel coumarin derivatives (1, 1a–5a, 1b, 2b, 6b, 7b, 8–13) with attached N-heterocycles, including aminopyrrolidine, aminopiperidine, aminoazepane, and indoline, were prepared and ultimately esterified or amidated with alcohols or amines, respectively. All synthesized N-heterocycles containing coumarin derivatives with alcohols, amines, and carboxylic acids were assessed for antiproliferative activity against several human cancer cell lines, containing triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) as well as a P-glycoprotein (P-gp) overexpressing multidrug-resistant (MDR) KB subline KB-VIN. Five coumarin derivatives (3a–5a, 12, 13) showed no effect (IC50 >40 µM) against all tested cell lines. In contrast, derivative 1a showed broad-spectrum activity against four cell lines, while 1b and 10 were nearly twice as selective for KB-VIN cells as the parent KB. The coumarin derivatives 1a, 1b, and 10 were optimal for antiproliferative activity in this study and could provide a new avenue for overcoming MDR tumors. Derivatives 1a, 1b, and 10 showed MDR cell-selective antiproliferative activity, indicating that N-heterocycle-coumarins exert previously unexplored bioactivity with selective action on MDR cancer cells.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (484K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (484K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Hidetomo Yokoo, Seiji Tanaka, Eiichi Yamamoto, Genichiro Tsuji, Yosuke ...2023 年71 巻1 号 p. 58-63
Hidetomo Yokoo, Seiji Tanaka, Eiichi Yamamoto, Genichiro Tsuji, Yosuke ...2023 年71 巻1 号 p. 58-63
発行日: 2023/01/01
公開日: 2023/01/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2022/10/27ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Understanding the characteristics of crystal polymorphism of active pharmaceutical ingredients and analyzing them with high sensitivity is important for quality of drug products, appropriate characterization strategies, and appropriate screening and selection processes. However, there are few methods to measure intra- and intermolecular correlations in crystals other than X-ray crystallography, for which it is sometimes difficult to obtain suitable single crystals. Recently, solid-state NMR has been recognized as a straightforward method for measuring molecular correlations. In this study, we selected ranitidine hydrochloride, which is known to exist in two forms, 1 and 2, as the model drug and investigated each form using solid-state NMR. In conducting the analysis, rotating the sample tube, which had a 1-mm inner diameter, increased the solid-state NMR resolution at 70 kHz. The 1H–14N dipolar-based heteronuclear multiple quantum coherence (D-HMQC) analysis revealed the intermolecular correlation of Form 1 between the N atom of the nitro group and a proton of the furan moiety, which were closer than those of the intramolecular correlation reported using single X-ray crystal analysis. Thus, 1H–14N D-HMQC analysis could be useful for characterizing intermolecular interaction in ranitidine hydrochloride crystals. In addition, we reassigned the 13C solid-state NMR signals of ranitidine hydrochloride according to the liquid-state and multiple solid-state NMR experiments.
 抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
抄録全体を表示Editor's pickIt is important to develop new analytical methods for crystal polymorphs as one of the characterizations of active pharmaceutical ingredients. In this study, advanced solid-state NMR (SSNMR) methods were developed to investigate crystal polymorphs of the model drug ranitidine hydrochloride, which is known to exist in two forms, Form 1 and Form 2. 1H-14N dipolar-based heteronuclear multiple quantum coherence analysis revealed an intermolecular correlation of ranitidine hydrochloride Form 1. In addition, the multiple SSNMR experiments resulted in the reassignment of the 13C SSNMR signals for each form of ranitidine hydrochloride.
PDF形式でダウンロード (1123K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Hirotaka Murase, Jeongsu Lee, Yosuke Taniguchi, Shigeki Sasaki2023 年71 巻1 号 p. 64-69
Hirotaka Murase, Jeongsu Lee, Yosuke Taniguchi, Shigeki Sasaki2023 年71 巻1 号 p. 64-69
発行日: 2023/01/01
公開日: 2023/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録In nucleic acid drug discovery, it is extremely important to develop a technology to understand the distribution in target organs and to trace the degradation process in the body in order to optimize the structure and improve the efficiency of the clinical trial process. Since nucleic acid drugs are essentially metabolically degraded into numerous fragments, labeling at the internal position is preferable to that at the terminus. Due to the high molar specific activity of tritium, various approaches for tritium-labeling have been studied for nucleic acid drugs. Nevertheless, a generally-applicable method for tritium labeling of the internal position of a nucleic acid has not been established. In this study, we have demonstrated a new and efficient method for site-specific tritium labeling of the cytosine base at a predefined internal position in nucleic acid drugs. This method was developed by the chemical modification of the cytosine 4-amino group with the pyridinyl vinyl keto group by the functionality-transfer reaction using the reactive oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN), followed by reduction with NaBT4. Applicability to a variety of chemical structures, such as 5-methyl cytosine, 2′-O-methyl, 2′-fluoro ribose derivatives, Locked/Bridged nucleic acid (LNA/BNA) derivatives, as well as phosphorothioate bonds, has been evidenced using nine oligoribonucleic acid (ORN) substrates. It has been clearly demonstrated that this method is an excellent method for tritium-labeling of nucleic acid with an average conversion efficiency of 74%, an average isolated labeling yield of 60%, and an average specific activity of 61 GBq/mmol. This method is expected to contribute to the preclinical absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion (ADME) studies of nucleic acid drug candidates.
 抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
抄録全体を表示Editor's pickIn nucleic acid drug discovery, it is extremely important to develop a technology to understand the distribution in target organs and to trace the degradation process in the body. In this study, the authors have demonstrated a new and efficient method for site-specific tritium labeling of the cytosine base at a predefined internal position in nucleic acid drugs. This method was developed by the chemical modification of the cytosine 4-amino group, followed by reduction with sodium tetratritioboranuide. Tritium-labeled nucleic acid drug candidates may be used for the preclinical ADME studies.
PDF形式でダウンロード (1467K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Kengo Banshoya, Makoto Shirakawa, Yuhzo Hieda, Masatoshi Ohnishi, Yuhk ...2023 年71 巻1 号 p. 70-73
発行日: 2023/01/01
公開日: 2023/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録In this study, we developed a water-soluble complex-hydrogel viscosity-controlled formulation of amphotericin B (AmB). AmB is insoluble in water, but borax makes it soluble by forming a complex with AmB. Borax also forms complexes with poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) to produce viscous hydrogels. Furthermore, boric acid interacts with mucin expressed in corneal epithelial cells. Accordingly, by utilizing these properties of borax simultaneously, we prepared a water-soluble AmB complex-hydrogel with poly(vinyl alcohol)/borate (PVA-B-AmB), which is suitable for eye drops. PVA-B-AmB was easily prepared by simply mixing aqueous AmB solution dissolved in borax, PVA solution, and water. The 11B-NMR results suggested that PVA-B-AmB existed by bonding PVA and AmB via boronic acid. PVA-B-AmB (gel ratio = 0.55) has a viscosity of 18.3 ± 0.5 mPa·s and is suitable for ophthalmic formulations. This formulation exhibited sustained release of AmB of approximately 45% at 24 h. It was also shown that this formulation interacts with mucin. These results suggest that PVA-B-AmB can be used as a water-soluble AmB preparation suitable for ophthalmic use.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (639K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (639K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Takuya Iwasaki, Ryosuke Uchiyama, Kazuto Nosaka2023 年71 巻1 号 p. 74-77
発行日: 2023/01/01
公開日: 2023/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLPropan-1,3-diol (PD) and propan-1,2-diol (propylene glycol, PG) are very similar compounds because their structures, safety data, and anti-microbial activities are almost the same. Actually, both compounds are made up of three carbon atoms and two hydroxyl groups. Regarding their safety, they do not have serious hazard data for animals, and LD50 values (in rats) of both are similar. As for the anti-microbial activity, minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values of both PD and PG are approximately 10% (v/v). In this study, we used the preservatives-effectiveness test (PET) to evaluate the anti-microbial activities of PD and PG, because both compounds are used in cosmetics as preservatives. The results indicated that PD was more effective as an anti-microbial agent compared with PG, and the effect of PD was marked against Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images showed that the membrane of Escherichia coli was injured by PD and PG, but the damage by PD was more marked. The damage of the cell membrane may be the cause of high anti-microbial activity of PD in PET. These results suggest that PD has greater potential as a preservative, and PD should be recommended as an additive for food and medicine.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2169K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2169K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|