
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Lin-jiao Wang, Wei Xi, Xiao-lan Yuan, Xiao-hua Yang2023 年 71 巻 12 号 p. 846-851
発行日: 2023/12/01
公開日: 2023/12/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/10/03ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Dapagliflozin (DAPA), sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor, is used to treat Type 2 diabetes. In this study, a highly sensitive and selective analytical method based on ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry (UHPLC-HRMS) was established and validated for the determination of DAPA in rat plasma. The separation of DAPA and internal standard (DAPA-d5) were performed on a reversed-phase ACQUITY UPLC® BEH C18 column (100 × 3.0 mm, 1.7 µm). The mobile phase is composed of 0.1% formic acid in water (solvent A) and methanol (solvent B) in gradient elution. Under the negative ion mode, full MS/dd-MS2 was adopted to collect data via Q-Orbitrap. DAPA was effectively separated from matrix backgrounds within 10 min, and DAPA in plasma showed a good linear relationship in the range of 10–10000 µg/L. The determination coefficient (R2) was 0.9987, and the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) was 10 µg/L. The precision and accuracy were all less than 10%, and the extraction recovery of DAPA was 86.16–96.06% from plasma. This study offered an efficient separation and quantification method for DAPA. The improved and validated method succeeded in evaluating the pharmacokinetics of DAPA in rat plasma samples after a single oral administration of 1 mg/kg.
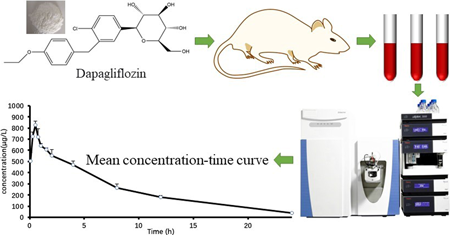 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (649K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (649K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Xing He, Dongmei Li, Tianqing Chen2023 年 71 巻 12 号 p. 852-858
発行日: 2023/12/01
公開日: 2023/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Porcine acellular dermal matrix (pADM) is known to accelerate wound healing. However, the underlying molecular mechanism remains unclear. This study aimed to investigate the effects of pADM on wound healing and its underlying mechanisms. HaCaT cells were treated with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) or pADM, and the appropriate treatment concentration was determined using the cell counting kit-8 and flow cytometry. Cell migration was assessed using a Transwell assay and scratch test. Inflammation was evaluated using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Western blotting was performed to measure the levels of protein kinase B (AKT) pathway-related proteins. The results showed that H2O2 inhibited cell viability and induced apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner. pADM promoted cell migration and decreased the levels of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in H2O2-treated HaCaT cells. Moreover, pADM rescued the downregulation of phosphorylated (p)-AKT and p-mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) induced by H2O2. LY294002, a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor, abrogated migration and anti-inflammatory response caused by pADM. In conclusion, pADM promotes cell migration and inhibits inflammation by activating the AKT pathway under oxidative stress. These findings support the use of pADM for post-traumatic therapy and reveal a novel underlying mechanism of action.
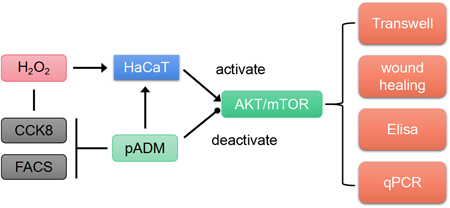 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5070K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5070K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Shota Kawai, Shunsuke Takashima, Masafumi Ando, Sayaka Shintaku, Shige ...2023 年 71 巻 12 号 p. 859-878
発行日: 2023/12/01
公開日: 2023/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLHurler syndrome, a type of Mucopolysaccharidosis type I, is an inherited disorder caused by the accumulation of glycosaminoglycans (GAG) due to a deficiency in lysosomal α-L-iduronidase (IDUA), resulting in multiorgan dysfunction. In many patients with Hurler syndrome, IDUA proteins are not produced due to nonsense mutations in their genes; therefore, readthrough-inducing compounds, such as gentamycin, are expected to restore IDUA proteins by skipping the premature termination codon. In the present study, we synthesized a series of chromenopyridine derivatives to identify novel readthrough-inducing compounds. The readthrough-inducing activities of synthesized compounds were examined by measuring cellular IDUA activities and GAG concentrations in Hurler syndrome patient-derived cells. Compounds with a difluorophenyl group at the 2-position of chromenopyridine, a cyclobutyl group at the 3-position, and a basic side chain or basic fused ring exhibited excellent readthrough-inducing activities. KY-640, a chromenopyridine derivative with a tetrahydroisoquinoline sub-structure, increased the cellular IDUA activities of patient-derived cells by 3.2-fold at 0.3 µM and significantly reduced GAG concentrations, and also significantly increased enzyme activity in mouse models, suggesting its therapeutic potential in patients with Hurler syndrome.
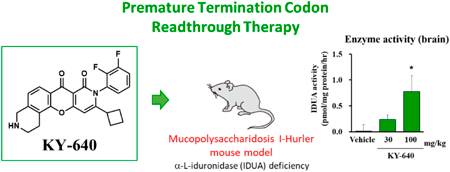 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1501K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1501K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Kohei Tsuji, Takuya Kobayakawa, Takahiro Ishii, Nobuyo Higashi-Kuwata, ...2023 年 71 巻 12 号 p. 879-886
発行日: 2023/12/01
公開日: 2023/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録In the development of anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) drugs, its main protease (Mpro), which is an essential enzyme for viral replication, is a promising target. To date, the Mpro inhibitors, nirmatrelvir and ensitrelvir, have been clinically developed by Pfizer Inc. and Shionogi & Co., Ltd., respectively, as orally administrable drugs to treat coronavirus disease of 2019 (COVID-19). We have also developed several potent inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro that include compounds 4, 5, TKB245 (6), and TKB248 (7), which possesses a 4-fluorobenzothiazole ketone moiety as a reactive warhead. In compounds 5 and TKB248 (7) we have also found that replacement of the P1-P2 amide of compounds 4 and TKB245 (6) with the corresponding thioamide improved their pharmacokinetics (PK) profile in mice. Here, we report the design, synthesis and evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors with replacement of a digestible amide bond by surrogates (9–11, 33, and 34) and introduction of fluorine atoms in a metabolically reactive methyl group on the indole moiety (8). As the results, these compounds showed comparable or less potency compared to the corresponding parent compounds, YH-53/5h (2) and 4. These results should provide useful information for further development of Mpro inhibitors.
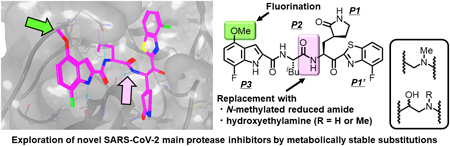 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1810K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1810K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Shohei Nakamura, Mai Jinno, Momoka Hamaoka, Ayumi Sakurada, Takatoshi ...2023 年 71 巻 12 号 p. 887-896
Shohei Nakamura, Mai Jinno, Momoka Hamaoka, Ayumi Sakurada, Takatoshi ...2023 年 71 巻 12 号 p. 887-896
発行日: 2023/12/01
公開日: 2023/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLDirect compression is a tableting technique that involves a few steps in non-demanding manufacturing conditions. High strength and rapid disintegration of tablet formulations were previously achieved through the addition of cellulose nanofibers (CNFs), which have recently attracted attention as a high-performance biomass material. However, CNF addition results in greater variation in tablet weight and drug content, potentially due to differences in particle size between CNF and other additives. Herein, we used pulverized CNF to evaluate the effect of CNF particle size on the variation in tablet weight and drug content. Tablet formulations consisted of CNF with different particle sizes (approximately 100 µm [CNF100] and 300 µm [CNF300], at 0, 10, 30, or 50%), lactose hydrate, acetaminophen, and magnesium stearate. Ten powder formulations with different particle sizes and CNF concentrations were prepared; thereafter, the tablets were produced using a rotary tableting press with a compression force of 10 kN. The variation in weight and drug content as well as the tensile strength, friability, disintegration time, and drug dissolution of tablets were evaluated. CNF100 addition to the tablets reduced the weight and drug content variation to a greater extent than CNF300 addition. Using CNF300, we produced tablets of sufficient strength and short disintegration time. These properties were also achieved with CNF100 addition. Our findings suggest that adding CNF of small particle size to the tablet formulation can reduce the variation in weight and drug content while maintaining high strength and short disintegration time.
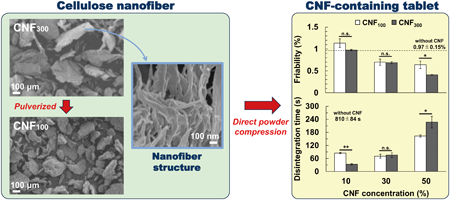 抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
抄録全体を表示Editor's pickWhile the addition of cellulose nanofiber (CNF) to tablet formulations during direct compression has attracted increasing attention as a means for enhancing tablet strength and disintegration, they are also known to increase the variation in tablet weight and drug content. This study evaluated the effect of pulverized CNF on the variation in tablet weight and drug content. The pulverized CNF reduced both weight and drug content variation to a larger extent than untreated CNF. Further, either CNF achieved sufficient tablet strength and short disintegration time. Thus, the authors provided evidence that CNF is useful as a multifunctional additive.
PDF形式でダウンロード (3434K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Kazunori Miwa, Yan Guo, Masayuki Hata, Yoshinori Hirano, Norio Yamamot ...2023 年 71 巻 12 号 p. 897-905
Kazunori Miwa, Yan Guo, Masayuki Hata, Yoshinori Hirano, Norio Yamamot ...2023 年 71 巻 12 号 p. 897-905
発行日: 2023/12/01
公開日: 2023/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Virtual screening with high-performance computers is a powerful and cost-effective technique in drug discovery. A chemical database is searched to find candidate compounds firmly bound to a target protein, judging from the binding poses and/or binding scores. The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-Cov-2) infectious disease has spread worldwide for the last three years, causing severe slumps in economic and social activities. SARS-Cov-2 has two viral proteases: 3-chymotrypsin-like (3CL) and papain-like (PL) protease. While approved drugs have already been released for the 3CL protease, no approved agent is available for PL protease. In this work, we carried out in silico screening for the PL protease inhibitors, combining docking simulation and molecular mechanics calculation. Docking simulations were applied to 8,820 molecules in a chemical database of approved and investigational compounds. Based on the binding poses generated by the docking simulations, molecular mechanics calculations were performed to optimize the binding structures and to obtain the binding scores. Based on the binding scores, 57 compounds were selected for in vitro assay of the inhibitory activity. Five inhibitory compounds were identified from the in vitro measurement. The predicted binding structures of the identified five compounds were examined, and the significant interaction between the individual compound and the protease catalytic site was clarified. This work demonstrates that computational virtual screening by combining docking simulation with molecular mechanics calculation is effective for searching candidate compounds in drug discovery.
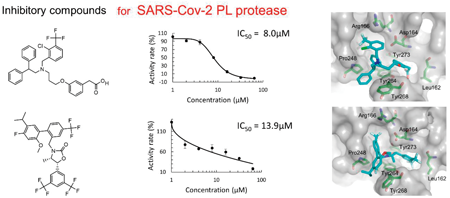 抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
抄録全体を表示Editor's pickComputational screening is a powerful technique for drug discovery today. In this work, a virtual screening was performed to find SARS-Cov-2 PL protease inhibitors, utilizing a chemical database consisting of approved and investigational drugs. A key issue for successful virtual screening is the accuracy of computational predictions for the binding pose and score of each compound to the target. The authors applied their original software program, Chem. Pharm. Bull., 2017, 65, 461, for calculating the score. Their approach identified five inhibitory compounds against the PL protease. The inhibitory activities were evaluated by an enzymatic assay with the FRET technique.
PDF形式でダウンロード (5051K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Haruka Shinotsuka, Naoya Mizutani, Shohei Aikawa, Go Kimura2023 年 71 巻 12 号 p. 906-908
発行日: 2023/12/01
公開日: 2023/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLDrug taste, which affects palatability, influences drug adherence. Sensory masking may be used to confound bitter tastes in drugs with other tastes and flavors; however, evaluation of sensory masking is difficult because of the existence of multiple tastes. In this study, a new two-bottle choice test was performed in rats to evaluate bitterness masking and determine the drug-to-sweetener ratio that significantly improves palatability. Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim were used as model bitter drugs, and sucralose was used as sweetener. The addition of sucralose and trimethoprim at a 0.13 : 1 ratio resulted in the greatest improvement in preference. This method is a useful new technique for evaluating the palatability of drug formulations.
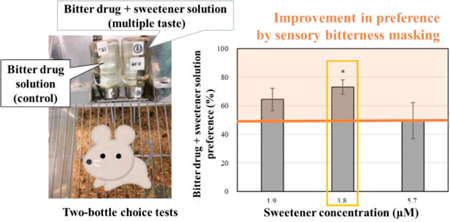 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (365K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (365K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|