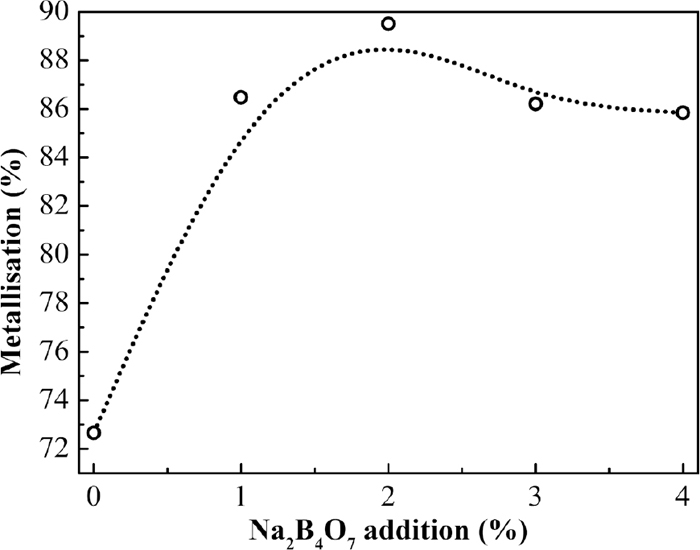
Volume 56, Issue 12
Displaying 1-30 of 30 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Ironmaking
Regular Article
-
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2113-2117
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Download PDF (790K) Full view HTML -
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2118-2125
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Advance online publication: October 20, 2016Download PDF (1288K) Full view HTML -
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2126-2131
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Advance online publication: October 18, 2016Download PDF (588K) Full view HTML -
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2132-2139
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Download PDF (1147K) Full view HTML -
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2140-2146
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Download PDF (1219K) Full view HTML -
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2147-2155
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Advance online publication: October 25, 2016Download PDF (1529K) Full view HTML -
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2156-2160
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Download PDF (675K) Full view HTML
Steelmaking
Regular Article
-
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2161-2170
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Advance online publication: October 15, 2016Download PDF (1867K) Full view HTML -
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2171-2180
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Advance online publication: November 08, 2016Download PDF (1245K) Full view HTML
Note
-
Article type: Note
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2327-2329
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Download PDF (362K) Full view HTML
Casting and Solidification
Regular Article
-
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2181-2190
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Advance online publication: November 12, 2016Download PDF (1654K) Full view HTML -
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2191-2198
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Download PDF (1471K) Full view HTML -
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2199-2207
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Advance online publication: October 20, 2016Download PDF (1581K) Full view HTML
Instrumentation, Control and System Engineering
Regular Article
-
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2208-2213
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Download PDF (952K) Full view HTML -
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2214-2223
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Download PDF (1003K) Full view HTML
Chemical and Physical Analysis
Regular Article
-
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2224-2227
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Download PDF (357K) Full view HTML -
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2228-2235
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Advance online publication: October 18, 2016Download PDF (538K) Full view HTML
Note
-
Article type: Note
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2330-2332
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Download PDF (620K) Full view HTML
Forming Processing and Thermomechanical Treatment
Regular Article
-
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2236-2242
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Advance online publication: October 27, 2016Download PDF (1129K) Full view HTML -
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2243-2249
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Advance online publication: October 25, 2016Download PDF (993K) Full view HTML -
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2250-2258
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Advance online publication: September 23, 2016Download PDF (2004K) Full view HTML -
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2259-2266
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Download PDF (1349K) Full view HTML
Surface Treatment and Corrosion
Regular Article
-
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2267-2275
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Advance online publication: October 27, 2016Download PDF (2284K) Full view HTML -
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2276-2283
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Download PDF (1843K) Full view HTML
Transformations and Microstructures
Regular Article
-
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2284-2289
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Download PDF (1265K) Full view HTML -
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2290-2297
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Download PDF (2820K) Full view HTML
Mechanical Properties
Regular Article
-
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2298-2303
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Download PDF (1428K) Full view HTML -
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2304-2312
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Download PDF (2811K) Full view HTML -
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2313-2319
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Download PDF (1283K) Full view HTML -
Article type: Regular Article
2016 Volume 56 Issue 12 Pages 2320-2326
Published: December 15, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: December 20, 2016
Advance online publication: October 22, 2016Download PDF (1361K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|