All issues

Volume 53, Issue 4
Displaying 1-25 of 25 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Fundamentals of High Temperature Processes
Regular Article
-
Masashi Nakamoto, Yoshikazu Tanaka, Shingo Tagaki, Toshihiro Tanaka, T ...2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 551-556
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLRecovery of Nd from used products is a crucial problem to be solved for a stable supply of Nd resource. In the present work, the use of two immiscible liquids, i.e. a Cu-rich phase and an Fe-rich phase, in an Fe–Cu–C system was regarded as one of the solutions for this purpose and the distributions of Nd between two immiscible liquids in an Fe–Cu–C system were measured. We found Nd is distributed in the Cu-rich phase more than in the Fe-rich phase in an Fe–Cu–C system and Nd is more concentrated at low temperatures than at high temperatures. In addition, the thermodynamic parameters for Nd were obtained based on the experimental results.View full abstractDownload PDF (506K) Full view HTML
Ironmaking
Regular Article
-
Tu Hu, Xuewei Lv, Chenguang Bai, Zhigang Lun, Guibao Qiu2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 557-563
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe effect of Fe–Si on the carbothermaic reduction of Panzhihua titanomagnetite concentrates were investigated under argon atmosphere by isothermal experiments at 1623 K and non-isothermal experiments in the temperature range from room temperature to 1723 K with a heating rate of 10 K/min, respectively. The morphology of reduced samples obtained by isothermal experiments was checked by scanning electron microscope. The results show that the addition of Fe–Si accelerates the carbothermic reduction rate of PTC. A part of silicon in the Fe–Si substitutes for carbon to participate the reduction of PTC. The addition of Fe–Si facilitates the nucleation and coalescence of metallic iron formed by reduction. A reaction mechanism for the carbothermic reduction of PTC with Fe–Si addition was proposed. The reduction process could be divided into three stages. In the first stage (lower than 1273 K), the solid phase reactions with carbon and silicon as reductants are dominant. The exdothermic reduction by silicon, to a certain extent, promotes the reduction of PTC. In the second stage (1273–1423 K), the rate of reduction by CO is much faster than that of reduction by silicon, resulting in little influence of Fe–Si on the reduction of PTC. In the final stage, the reduction by silicon markedly occurs again, which further facilitates the coalescence of metallic iron and the reduction of PTC.View full abstractDownload PDF (941K) Full view HTML -
Haoyan Sun, Xiangjuan Dong, Xuefeng She, Qingguo Xue, Jingsong Wang2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 564-569
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTitanomagnetite concentrate was reduced by graphite isothermally under argon gas in thermogravimetry system at 1373 to 1623 K. The influences of reductive conditions on the reduction and metallization degree including reduction temperature, reduction time and C/O molar ratio were studied. And the characteristics of reduced samples were analyzed by XRD, BES and EDS. Results shown that in the temperatures range of 1423 to 1623 K, initially the reduction proceeded rapidly and after 30 min only a slow increase in reduction was observed. The low reduction degree was owing to the high impurities oxides content such as magnesium oxide in titanomagnetite concentrate and the reduction and metallization degree increased with the C/O molar ratio until up to 1.0 at 1623 K. Above 1373 K, the reduction path is suggested as follow: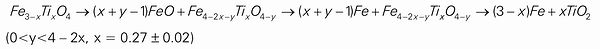 View full abstractDownload PDF (809K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (809K) Full view HTML -
Daisuke Noguchi, Ko-ichiro Ohno, Takayuki Maeda, Kouki Nishioka, Masak ...2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 570-575
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAs a fundamental study for clarifying the reduction phenomena of iron ore sinter in blast furnace, iron oxide (H) and quaternary calcium ferrite (Cf) were prepared and these kinetic behaviors at the final stage of reduction with CO–CO2 gas mixture were studied.Reduction rate increased with increasing reduction temperature. Moreover, it increased with increasing partial pressure of CO gas. Difference of reduction rate caused by gas composition is much larger than reduction temperature. From comparisons of weight loss curves, reduction rate of H samples was faster than that of Cf samples under the same or similar conditions.Reduction reaction of H and Cf samples proceeded topochemically at higher temperature (≥1100°C), and didn’t proceed topochemically at lower temperature (≤1000°C). Besides, the reduction reaction of samples with CO rich gas proceeded more topochemically. Structure of iron layer in H samples was affected by temperature and gas composition. On the other hand, structure of iron layer in Cf samples was almost the same in all experimental conditions.Reduction data were analyzed based on one interface unreacted core model, and chemical reaction rate content kc and effective diffusion coefficient in product layer De were determined. The values of kc show Arrhenius-type temperature dependency, and were approximately same tendency except for Cf samples with near equilibriums gas compositions. The values of De of H samples show the temperature and gas composition dependencies, and that of Cf samples were approximately constant in all experimental conditions.View full abstractDownload PDF (1738K) Full view HTML -
Jian Xu, Shengli Wu, Mingyin Kou, Kaiping Du2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 576-582
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLNumerical simulation is considered to be an important method to study the inner characteristics of metallurgical processes, thus providing effective strategies for practical smooth operations. A three-dimensional full scale mathematical model considering mass, momentum, energy transfers and chemical reactions under steady state is developed in the present work to describe the characteristics inside the pre-reduction shaft furnace of COREX smelting reduction ironmaking process. The uneven gas and solid flow distributions in both radial and axial directions not only restrain the gas utilization but also cause the difference in the solid metallization between the center and near wall to reach as high as 0.4. Predicted by the established model, the CO–CO2–H2–H2O reducing gas with the temperature 1050–1100 K, the volume fraction of CO+CO2 around 70%, the ratio of CO to CO2 5–7, as low as possible H2O content, and the reasonably matched burden solid charging rate to control the top gas consumption per ton burden solid (TGC) in the range of 800–1000 Nm3/t, are the optimal operation conditions to further improve furnace efficiency.View full abstractDownload PDF (1164K) Full view HTML -
Masato Sugiura, Tomoyuki Nakagawa, Takashi Arima, Kenji Kato, Michitak ...2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 583-589
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLMany of the coke oven batteries in Japan have been in operation for about 40 years. These coke ovens tend to become obsolete, resulting in a production impediment such as increase in pushing force. This paper proposed an experimental expression named as a resistive index that describes resistance received by a pushed coke cake being in contact with an uneven coke oven wall. The resistive index is calculated based on the shape of the deformed oven wall. Linear relationship between a resistive index and a pushing force was experimentally verified by using a simulated part of a coke oven. The resistive index was applied to actually working aged coke ovens. A newly-developed diagnosis apparatus equipped with a 3D profile measurement system was utilized to acquire irregularity data of high-temperature coke oven walls. Here, correlation between the resistive index and the force development during pushing was also clearly confirmed. From these results, it was concluded that the resistive index enables to quantitatively assess the harmfulness of damaged coke oven walls from the standpoint of a rise in pushing force. The resistive index is available for evaluating the needs and preferentiality of maintenance of damaged coke oven.View full abstractDownload PDF (1008K) Full view HTML -
Tatsuya Kon, Shungo Natsui, Shigeru Ueda, Ryo Inoue, Tatsuro Ariyama2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 590-597
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe liquid dripping under the cohesive zone influences gas flow and permeability in the lower part of the blast furnace, and it is closely related to blast furnace productivity and operational stability. Especially, liquid distribution and hold-up in the coke packed bed can be mentioned as important phenomena regarding the liquid dripping. Although these phenomena are influenced by the structure of the packed bed and the physical properties of the melt, numerical analysis of blast furnace based on melt properties is difficult. Therefore, in this research, the influence of the physical properties of the melt on liquid flow distribution and hold-up phenomena was studied by modeling the liquid flow in a packed bed and performing numerical analysis based on Moving Particle Semi-implicit (MPS) method, which is one of the particle methods. The results of the analysis clarified the fact that the viscosity of the liquid is the controlling factor for dynamic hold-up, and solid-liquid wettability is the controlling factor for static hold-up.View full abstractDownload PDF (916K) Full view HTML
Note
-
Chris Petrich, Martin Arntsen, Hamid Dayan, Rune Nilsen2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 723-725
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDownload PDF (297K) Full view HTML
Steelmaking
Regular Article
-
Zhangfu Yuan, Yan Wu, Hongxin Zhao, Hiroyuki Matsuura, Fumitaka Tsukih ...2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 598-602
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLWetting experiments in two cases have been carried out to measure the wettability between molten slag and MgO–C refractories. Especially, the variations of wettability with time are taken into consideration in this paper. The spread diameter increased significantly and the slag height decreased with the increase of the time from 0 to 237 s at 1783 K. While the spread diameter changed slowly, and reached the steady state from 300 to 500 s. More specifically, the fitting formulae for diameter, height, area of the slag as a function of time have been determined. Moreover, the interfacial characteristics of the non-melting slag and MgO–C refractories and of the wetting slag and MgO–C refractories were investigated to further explain the wettability in two cases.With the help of the wetting experiment, adhesion and protection mechanism was demonstrated. It could optimize the slag splashing process and give guides to the increase of the converter lining life, which can make the contribution to the promotion of technological transformation and innovation of the steel industry.View full abstractDownload PDF (673K) Full view HTML -
Ville-Valtteri Visuri, Mika Järvinen, Petri Sulasalmi, Eetu-Pekka Heik ...2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 603-612
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA process model was proposed by Järvinen and co-authors for modelling the side-blowing decarburisation stage of the Argon-Oxygen Decarburisation (AOD) process. Here, a new model for the reduction stage has been derived and coupled with the earlier-developed model. The model considers mass-transfer controlled reversible reactions between the steel bath and the top slag. The effect of emulsification phenomena on the total reaction area and on the mass and heat transfer characteristics have been taken into account. The effects of various additions on the mass and heat balance have also been considered. The paper is divided into two parts: Part I presents the derivation of the model, while Part II considers validation of the model with full-scale production data from a 150 t AOD converter at Outokumpu Stainless Oy, Tornio Works, Finland.View full abstractDownload PDF (633K) Full view HTML -
Ville-Valtteri Visuri, Mika Järvinen, Jari Savolainen, Petri Sulasalmi ...2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 613-621
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA process model was proposed by Järvinen and co-authors for modelling the side-blowing decarburisation stage of the Argon-Oxygen Decarburisation (AOD) process. In Part I, a new mathematical model was derived for the reduction stage and coupled with the decarburisation model developed earlier. This paper, Part II, considers the validation of the model for the reduction stage with full-scale production data from a 150 t AOD converter in operation at Outokumpu Stainless Oy, Tornio Works, Finland. The results indicate that the model can accurately predict the end composition of the steel bath. Moreover, the model can be used to study rate phenomena during the reduction stage. Model predictions suggest that the reduction rate of chromium oxides is controlled initially by mass transfer of silicon onto the reaction surface and later by the diffusive mass transfer of chromium oxides in the slag droplets. Sensitivity of the model predictions to different initial bath temperatures, blowing times, ferrosilicon particle sizes and ferrosilicon feed rates was studied.View full abstractDownload PDF (928K) Full view HTML -
Simon N. Lekakh, David G. C. Robertson2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 622-628
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLControl of melt flow in steelmaking processes is important for technology optimization and product quality. To overcome the difficulty of making measurements in actual steelmaking vessels (furnace, ladle, tundish, or mold), both physical modeling (water models) and CFD simulations have been used extensively for melt flow visualization. However, it is not easy to interpret the results of either type of model study, because it is difficult to determine which flow pattern is best by only visual inspection. In this article, a new approach is proposed for the analysis of the melt flow in metallurgical vessels after obtaining residence time distributions from CFD simulation or physical experiments (RTDCFD or RTDmodel). In this analysis the melt flow is assumed to be in a combined reactor (CR) system consisting of a combination of three basic unit reactors: “plug flow”, “perfect mixer”, and “recirculated volume”. An inverse simulation is used to define the volumes of the unit reactors and the melt flow rate between them by fitting the RTDCR curve to the RTDCFD or RTDmodel curves. The effectiveness of the suggested approach is demonstrated for tundish applications; however, it could also be used for melt flow analysis in other steelmaking processes.View full abstractDownload PDF (1450K) Full view HTML -
Inclusion Formation and Interfacial Reactions between FeTi Alloys and Liquid Steel at an Early StageManish Marotrao Pande, Muxing Guo, Bart Blanpain2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 629-638
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTitanium is usually added to the liquid steel in the form of ferroalloys with varying Ti concentrations. These titanium sources also contain Al, Ca and O as the main impurities. In the present work, three different titanium sources, namely, pure Ti and two commercially produced Ti alloys i.e. FeTi70 and FeTi35 are studied. The Ti or FeTi was brought in contact with the liquid iron using the suction method, for a predetermined time and quenched. The reaction zone between the liquid Fe and the titanium source was subjected to microstructural investigation. The high Ti concentration region obtained in a pure Ti–Fe reaction couple, the inclusion formation in liquid iron after coming in contact with FeTi70 and the evolution of existing inclusions in FeTi35 after coming in contact with liquid iron have been studied. The present study has helped in understanding the influence of impurities from the Ti source on the dissolution behavior and the inclusion formation. On the basis of this study, it can be concluded that the Ti rich regions formed after the introduction of pure Ti could modify the existing alumina inclusions in liquid steel, the impurities in FeTi70 contribute to the inclusion formation depending upon the availability of O while FeTi35 introduces inclusions to the liquid steel.View full abstractDownload PDF (4082K) Full view HTML
Casting and Solidification
Regular Article
-
Toshiaki Mizoguchi, Yoshiyuki Ueshima, Masaaki Sugiyama, Kazumi Mizuka ...2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 639-647
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAlumina clusters extracted from molten steel and from a cast slab at our plant were analyzed by SEM and TEM. It was found that a small amount of liquid FeO could accelerate the clustering of alumina inclusions in aluminum-killed steel because of the strong liquid-capillary negative pressure of liquid FeO. The sources of the FeO are most likely oxygen contamination from ferroalloy additives, residual steel adhering to the refractory surfaces of ladles and vessels, and air entrainment.View full abstractDownload PDF (2622K) Full view HTML -
Masahito Hanao2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 648-654
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLCrystallization of mold flux was observed with confocal laser microscope. Crystallization temperature, CCT curve and crystallization rate were evaluated from the observed images. The evaluated results were compared between two kinds of mold flux, and influence of basicity on crystallization rate was discussed. Crystallization temperature increased with basicity. Crystallization rate also increased with basicity, but its dependency on cooling rate was differed by basicity. The difference could be explained by the viscosity of mold flux at crystallization temperature. Crystallization rate has clear relation to the viscosity at crystallization temperature, and the rate increased with decrease of the viscosity. Two kinds of mold flux were unified in this relationship. Crystallization is controlled with basicity in terms of not only equilibrium but also kinetics through viscosity.View full abstractDownload PDF (1605K) Full view HTML -
Zibing Hou, Guoguang Cheng, Fang Jiang, Guoyu Qian2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 655-664
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn order to investigate the compactness degree of longitudinal section of the outer columnar grain zone in continuous casting billet, a Cellular Automaton-Finite Element coupling model was first developed. After validation, the solidification structures of billet under different conditions were simulated. The compactness degree of longitudinal section of billet is evaluated by the grain number in the same area. Because the widths of the columnar grain zone of billet under different conditions are different, the same zone was chosen for comparison and the zone was named as outer columnar grain zone. Thereafter, the compactness degree of longitudinal section of the outer columnar grain zone is found to be decreased with the increase of superheat, and increased slightly with the increase of casting speed, and decreased slightly with the increase of mould cooling intensity. Meanwhile, the corresponding compactness degree is increased with the increase of maximum nucleation density, and decreased with the increase of mean nucleation undercooling, and also decreased with the increase of dendrite growth velocity. Moreover, it is shown that the compactness degree of longitudinal section of the outer columnar grain zone in continuous casting billet is closely related to the average temperature gradient of the solidification process of the outer columnar grain zone, i.e., the former will be decreased when increasing the latter. This phenomenon can be probably attributed to two features that the established model has considered the preferential growth direction and new nucleation cores in the solidification front of the columnar grains.View full abstractDownload PDF (2689K) Full view HTML -
Lejun Zhou, Wanlin Wang, Juan Wei, Boxun Lu2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 665-672
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAn investigation was conducted to study the effects of Na2O and B2O3 on heat transfer behavior of low fluorine mold flux for casting medium carbon steels by using Single Hot Thermocouple Technique (SHTT) and an advanced Infrared Emitter Technique (IET) in this paper. Results suggested that crystalline layer thickness, crystalline fraction and interfacial thermal resistance of the mold flux increased with the addition of Na2O, while they decreased with the increase of B2O3. Besides, the initial crystallization temperature and steady state heat flux reduced with the addition of Na2O, and they were getting higher with the addition of B2O3. Those results obtained in this research can provide fundamental guidance for designing new type of low fluorine or fluorine free mold fluxes for casting medium carbon steels.View full abstractDownload PDF (1423K) Full view HTML
Chemical and Physical Analysis
Regular Article
-
Shigeo Sato, Kazuaki Wagatsuma, Mikio Ishikuro, Eui-Pyo Kwon, Hitoshi ...2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 673-679
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe dislocation characteristics and subgrain size of cold-drawn pearlitic steels with different carbon compositions were analyzed using X-ray diffraction line profile analysis to determine the work-hardening mechanism, with particular focus on microstructural deformation resulting from the rotation of pearlitic colonies. Modified Williamson—Hall and modified Warren—Averbach methods, which use multiple diffraction profiles, were applied to evaluate the microstructural parameters of the ferrite phase. Although the dislocation density increased with an increase in the drawing strain, the subgrain size was almost constant up to a strain of about 0.7. It was also shown that the higher carbon composition in the pearlitic steels contributes to the refinement of subgrains of the ferrite phase and the accumulation of dislocations. Moreover, the single-line profile analysis was performed for the cementite powder, which was prepared by electrolytic extraction from the steel specimens. The thickness of the cementite lamellae decreased with increasing drawing strain, indicating that the decomposition of the cementite phase occurred at the low strain level of 0.7. On the basis of these microstructural parameters, the strengthening mechanism as a function of the strain level is discussed.View full abstractDownload PDF (1229K) Full view HTML
Forming Processing and Thermomechanical Treatment
Regular Article
-
Hamed Mirzadeh, Abbas Najafizadeh2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 680-689
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe hot deformation behavior of a 17-4 PH stainless steel was investigated by compression tests. The typical single-peak dynamic recrystalization (DRX) behavior and also a transition state between single and multiple peak (cyclic) behaviors were seen in the resultant flow curves. The application of constitutive equations for determination of hot working constants was critically discussed. As a result, the deformation activation energy and the stress multiplier in the hyperbolic sine equation were determined as 337 kJ/mol and 0.011, respectively. The Zener-Hollomon parameter (Z) exponents for peak stress and peak strain based on the power relationships were determined as 0.18 and 0.11, respectively. The normalized critical stress and strain for initiation of DRX were respectively found to be 0.89 and 0.47. The prior austenite grain boundaries (PAGB) were revealed by electrolytic etching of the martensite in order to study the microstructure of hot deformed samples. Significant grain refinement occurred as a result of necklace DRX mechanism. The average dynamically recrystallized grain size was related to Z and peak stress by power equations with exponents of –0.25 and –1.24, respectively. A DRX map was developed to show the effect of deformation conditions on the occurrence of DRX and on the final grain size.View full abstractDownload PDF (1999K) Full view HTML -
Yukio Takashima, Toshiki Hiruta2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 690-697
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLUniversal rolling of channel sections has various advantages in both productivity and product quality. However, research on deformation in channel universal rolling appears to be inadequate. In particular, the effect of rolling conditions such as thickness reductions on deformation behavior is still unknown. To investigate the influence of rolling conditions in detail, a model rolling experiment and finite element analyses of channel universal rolling were conducted. The results showed that flange spread displays a linear relationship against the reduction balance, which was defined as the difference of the flange and web thickness strains. Similar linear behaviors of the flange depth and bulge height against the reduction balance were also demonstrated. The results of a non-steady-state finite element simulation showed that the friction force between the flange inside surface and the horizontal roll side surface caused asymmetric flange deformation, decreasing flange depth and increasing bulge height. The results of this research indicate the importance of the reduction balance for controlling flange deformations, and in particular, for reducing bulge height. Finally, the suitable range of the reduction balance considering other phenomena was discussed.View full abstractDownload PDF (1298K) Full view HTML
Welding and Joining
Regular Article
-
Arshad Alam Syed, Andreas Pittner, Michael Rethmeier, Amitava De2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 698-703
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLHigh peak temperature and continuous deposition of electrode droplets in the weld puddle inhibit real-time monitoring of thermal cycles and bead dimensions in gas metal arc welding. A three-dimensional numerical heat transfer model is presented here to compute temperature field and bead dimensions considering a volumetric heat source to account for the transfer of arc energy into the weld pool. The heat source dimensions are analytically estimated as function of welding conditions and original joint geometry. The deposition of electrode material is modeled using deactivation and activation of discrete elements in a presumed V-groove joint geometry. The computed values of bead dimensions and thermal cycles are validated with the corresponding measured results. A comparison of the analytically estimated heat source dimensions and the corresponding numerically computed bead dimensions indicate that the former could rightly serve as the basis for conduction heat transfer based models of gas metal arc welding process.View full abstractDownload PDF (575K) Full view HTML
Transformations and Microstructures
Regular Article
-
Hiroyuki Y. Yasuda, Kouki Fukushima, Keiji Kouzai, Taisuke Edahiro2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 704-708
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLStrength and damping capacity of Fe–Al alloys doped with different amounts of Ni were examined. Fe–Al alloys with an appropriate amount of Ni doping exhibited yield stress higher than 1 GPa and internal friction of above 0.032. In these alloys, the NiAl phase with the B2 structure densely precipitated in the Fe–Al matrix, satisfying the cube-on-cube orientation relationship. The precipitation of NiAl resulted in high strength, which was associated with the difference in primary slip systems between the NiAl precipitates and the Fe–Al matrix. Moreover, the internal friction measured under an external magnetic field showed low values, suggesting that Fe–Al alloys with the NiAl precipitates demonstrated magneto-mechanical damping caused by the irreversible motion of magnetic domain walls. The Al concentration in the Fe–Al matrix became appropriate for damping properties by the precipitation of NiAl, resulting in an increase in the internal friction of the alloy.View full abstractDownload PDF (611K) Full view HTML
Note
-
Tze-Yang Yeh, Ren-Kae Shiue, Chenchung Steve Chang2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 726-728
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDownload PDF (656K) Full view HTML
Mechanical Properties
Regular Article
-
Kazuto Kawakami, Tooru Matsumiya2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 709-713
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLHydrogen trap state by cementite in ferrite was investigated by ab-initio calculations. The calculated trap energy at cementite interstitial was 33 kJ/mol and that at the interface of cementite/ferrite was 39 kJ/mol. The calculated activation energy of the migration over the stable interstitial sites is 55 kJ/mol. Considering calculated zero point vibration energy, the trap energy at cementite interstitial becomes 41 kJ/mol and the activation energy becomes at least 59 kJ/mol. The low temperature peak at about 400 K in Thermal Desorption Spectrum (TDS) of cementite reported by other researchers is considered to correspond to the trap site at the cementite/ferrite interface. Since the interstitial trap site in cementite is not effective because of the high diffusion barrier at low temperature, the higher temperature peak at about 500 K in the TDS is considered to correspond to the migration energy from the defects such as grain boundaries in cementite introduced by deformation.View full abstractDownload PDF (857K) Full view HTML -
Yu Matsumoto, Kenichi Takai, Mikiyuki Ichiba, Takahisa Suzuki, Tsukasa ...2013 Volume 53 Issue 4 Pages 714-722
Published: 2013
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2013
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLImprovement of the surface layer as well as the microstructure has been needed to develop high-strength steels, since delayed fracture cracks initiate in the surface layer. In the present study, two approaches were taken to reduce the delayed fracture susceptibility of tempered martensitic steel with tensile strength of 1450 MPa. One was by increasing the Si content, which was intended to improve the microstructure. The other was by a surface-softening treatment, which was for improving the surface layer. Delayed fracture susceptibility was evaluated by conducting constant strain rate tensile tests (tensile tests) and constant load tests in a NH4SCN aqueous solution. It was found that increasing the Si content from 0.2 mass% to 1.88 mass% prevented intergranular fracture and reduced delayed fracture susceptibility. One reason for this improvement is that the Fe3C particle size on prior-γ grain boundaries and in the matrix decreases with increasing Si content, which implies that Si stabilizes dislocation structures. When the surface strength of surface-softened steel specimens was lowered to 1150 MPa, delayed fracture susceptibility was reduced further. This is attributed to not only a reduction of the Vickers hardness of the surface layer but also a reduced hydrogen concentration at the surface layer. The rearrangement and annihilation of dislocations and also the spheroidizing and coarsening of Fe3C particles at the surface layer subjected to a high tempering temperature lead to a reduction of the hydrogen concentration at the surface layer.View full abstractDownload PDF (2295K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|