
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Youn-Bae Kang, Joo-Hyeok LeeArticle type: Note
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1665-1667
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLPhase equilibria of Fe–Al–Ti–O system is shortly reviewed, in particular for stability of oxide phases in equilibrium with liquid Fe alloy in dilute concentration. This system is relevant to Ultra Low Carbon steel with Ti alloying (Ti-ULC), often causing clogging of Submerged Entry Nozzle (SEN) during continuous casting. In order to predict stable oxides in the Ti-ULC steel, thermodynamic calculation using CALPHAD approach was employed. Previously available thermodynamic calculations were examined, and compared with available experimental data. A slight modification of thermodynamic modeling of previous investigation resulted in noticeable improvement for the prediction of stable phases by thermodynamic calculation. Significance of the present revision of the thermodynamic modeling is discussed in the view of nozzle clogging of Ti-ULC casting.
View full abstractDownload PDF (435K) Full view HTML
-
Cao Son Nguyen, Ko-ichiro Ohno, Takayuki Maeda, Kazuya KunitomoArticle type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1491-1498
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA wetting behaviour of Fe–C sample on carbonaceous materials has been extensively investigated to understand the liquid flow behaviour in lower part of blast furnace. The previous studies reported a large change in apparent contact angle in the initial contact period in the wetting between the Fe–C sample and the carbonaceous materials substrate. The carbon dissolution reaction and the interfacial morphology in the initial contact period would strongly affect the wetting behaviour in this period. To further understand the wetting behaviour between the Fe–C sample and the substrate, the effects of the carbon dissolution reaction on the wetting behaviour in the initial contact period must be considered. Fe-3.70, 4.26, 4.90 mass% C samples were fabricated using a high-frequency induction heating furnace under an inert gas atmosphere. The graphite substrate was made from 99.90% pure graphite powder using a hot press furnace under an argon gas atmosphere. The wetting behaviour of the graphite substrate with molten Fe–C sample is investigated using a sessile drop method with a molten sample injection and quenching systems. The results shown that the apparent contact angles significantly decreased from the initial apparent contact angle. The carbon concentration of the carbon-unsaturated Fe–C sample gradually increased and reached the saturation after the 300 s of contact. The formation of concave was observed and developed in the initial contact period due to the transfer of carbon atoms into the carbon-unsaturated Fe–C sample. The wetting behaviour was dependent on interfacial energy of solid-liquid phases before the formation of concave. After the formation of concave, the wetting behaviour dominantly depended on interfacial morphology change.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1775K) Full view HTML -
Moritoshi Mizutani, Tsunehisa Nishimura, Takashi Orimoto, Kenichi Higu ...Article type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1499-1508
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLH2 injection through the shaft into blast furnace (BF) is a potential option for a further reduction of CO2 emission from BF. H2 promotes reduction reaction of burden materials, but its influence on their reduction disintegration behavior remains unknown in detail. This study has investigated the influence on the iron ore sinter, self-fluxed and acid pellets and specified essential factors governing the reduction disintegration behavior.
Mass ratios of particles below 3 mm in size were measured as an index for reduction disintegration (RDI) after the reduction of burden samples applying the gas mixtures of CO–H2–CO2–N2 at 823 K. The reduced samples were observed by an optical-microscope and an electron probe micro-analyzer for evaluation of reaction mode. Further, using the measurement results, stress, strain energy and crack area generated during reduction were calculated and formation mechanism of cracks was examined.
RDI value of self-fluxed pellet increased under higher H2 condition (40%N2-20%H2-10%CO-30%CO2) and reached to 26 mass%. Such an increase was larger than expected from the standard RDI measure without H2. Sample observation revealed a fact that reaction mode governed RDI value, that is, disintegration worsened under the reduction with non-topochemical mode. The fact was explained by the calculation as an influence of crack formation and propagation. In a case of reduction with topochemical reaction, cracks generated in a concentric fashion. Meanwhile, reduction with non-topochemical reaction tended to generate cracks in radial direction, which causes pellet chipping and further degradation. Calculated crack areas showed good correlation with RDI values. The Crack area of non-toochemical reaction was more than double than that of topochemical reaction. This result indicates that disintegration does not much progress when crack area is less than the certain limit value, but it proceeds drastically when it exceeded the limit value.
View full abstractDownload PDF (2108K) Full view HTML -
Dongdong Zhou, Shusen Cheng, Ruixuan Zhang, Yan Li, Tian ChenArticle type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1509-1516
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
Advance online publication: July 11, 2017JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLWith the effective volume of the blast furnace is upsizing in recent years, the effective volume and the hearth diameter of largest blast furnace are reached to 5800 m3 and 15 m in China, respectively. The numbers of raceway zones are increased from one dozen to several dozens, the hearth uniformity and the activity become more important for large blast furnaces. The uniformity and activity of hearth are very crucial to produce the high quality hot metal and prolong the campaign life of blast furnace, it also could influence the stability state and operation indexes of a blast furnace. Currently, there is still no effective evaluation system for estimating whether the hearth is uniformity and activity or not. In this paper, the Uniformity Index and Activity Index in the peripheral direction and local regions were proposed to evaluate the hearth condition by measured the flame temperature of raceway zones in 2000 m3 and 2500 m3 blast furnaces. The established uniformity and activity evaluation system for blast furnace hearth, not only has academic value in understanding the formation of raceway zone and combustion mechanism, but also has tremendous application values to estimate work state of hearth and maintain a stable state of the blast furnace.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1585K) Full view HTML -
Keith Richard Vining, Jasbir Khosa, Graham J. SparrowArticle type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1517-1523
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
Advance online publication: August 22, 2017JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe effects of the operating parameters of the briquetting machine, feed moisture content and the addition of hydrated lime as a flux on the green and fired properties of briquettes produced from Australian iron ore fines were investigated to determine the best operating conditions for producing satisfactory briquettes.
The results confirmed earlier work that iron ore fines can be agglomerated by briquetting to produce a feed material suitable for a blast furnace. Feed moisture was found to be a critical operating parameter while machine operating parameters had secondary effects. The density of the green briquettes was found to depend on feed moisture content with higher density briquettes being produced with lower moisture contents. The strength of the green briquettes depended on the density of the green briquette. Feed moisture contents of 7.5–8.5 wt% resulted in a high yield of whole briquettes with densities of 3.40–3.45 g/cm3 and green strengths of 4.0–5.5 kgf.
The briquettes produced could be dried rapidly, potentially giving higher productivity values for production of briquettes compared with pellets. During briquette induration the green briquettes performed well. The basicity of the briquettes and the firing temperature had the most significant effect on the product quality. For firing temperatures of 1300–1350°C, and a basicity of 1.22, fired briquettes with good mechanical strength and reduction properties were obtained. Crush strengths ranged from 200 kgf to >450 kgf.
View full abstractDownload PDF (636K) Full view HTML -
Ataru Uchida, Yoshiaki Yamazaki, Shohei Matsuo, Yasuhiro Saito, Yohsuk ...Article type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1524-1530
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe effect of HPC (Hyper-coal), which was affected by the iron oxide, on coal particle adhesion during carbonization was investigated. X-ray diffraction analyses were carried out to obtain changes of iron oxide crystal structure on HPC with iron oxide addition during caking temperature. The promoted weight loss of HPC by the iron oxide during caking temperature was calculated from the weight losses by thermogravimetric analyses and gas concentrations by a gas chromatograph and a Karl Fischer titrator. Furthermore, to reveal the effect of iron oxide on coal particle adhesion at resolidification temperature, the yields of semi-coke with and without HPC/High Fluidity-HPC (HF-HPC)/Fe2O3/Fe3O4 were measured, the strength of the semi-coke samples was evaluated using diametral compression tests, and the adhesion of coal particles was evaluated using microstructure analyses. As a result, the promoted weight loss of HPC was increased by the catalysis of Fe2O3, and was decreased, when the Fe2O3 was reduced to Fe3O4, due to hydrogen atoms in the thermoplastic components of HPC. Thus, the strength of semi-coke with HPC increased. Furthermore, although the iron oxide affected the HPC, the adhesiveness of coal particles, which was an index of ferro-coke strength, was enhanced by HPC, and the adhesiveness of HF-HPC was higher than that of HPC. Therefore, the HPC decreased the chemical effect of iron oxide, and improved the adhesiveness.
 Promoted relative weight loss of HPC by reduction reaction of iron oxide (HPC: Fe2O3 = 70: 30). Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (790K) Full view HTML
Promoted relative weight loss of HPC by reduction reaction of iron oxide (HPC: Fe2O3 = 70: 30). Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (790K) Full view HTML -
Jun Ishii, Ryota Murai, Ikuhiro Sumi, Yang Yongxiang, Rob BoomArticle type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1531-1536
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLReduction of CO2 emissions in blast furnaces is an important problem for the steel industry. Operating a blast furnace at lower CO2 levels requires a reduction in the amount of coke that is used to maintain gas permeability in the cohesive zone. Therefore, gas permeability in the iron-ore layer of the cohesive zone should be improved. In this study, gas permeability through a packed bed with liquid was measured using an experimental sponge ball packed bed as a model. The pressure drop of the sponge ball packed bed without liquid was proportional to the square of gas flow velocity. Furthermore, it was affected by the shrinkage ratio of particles. The pressure drop of the deformed packed bed with liquid was mostly affected by liquid that overflowed from the sponge balls into vacancies in the packed bed during the deformation process. This setup can simulate the phenomenon of rising pressure drop within sinter ore at the cohesive zone.
The effect of sponge ball arrangement was tested using sponge balls filled with much liquid and sponge balls with smaller amount of liquid. These sponge balls simulate gas permeability of the ore layer containing acid pellets and sintered ore in the cohesive zone. The results indicate that both the mixed arrangement and longitudinal arrangements are effective in maintaining higher gas permeability.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1225K) Full view HTML
-
Lingzhong Kong, Zhiyin Deng, Miaoyong ZhuArticle type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1537-1545
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
Advance online publication: July 25, 2017JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIndustrial and laboratory experiments were carried out to understand the formation and evolution mechanism of non-metallic inclusions in medium Mn steel during secondary steelmaking process. In industrial experiments, with the generation of dissolved Mg and Ca in liquid steel, the inclusions in liquid steel would transform along with the route of “Al2O3 inclusions → MgO·Al2O3 spinel inclusions → (Mn, Mg)O·Al2O3 spinel inclusions → CaO–MgO–MnO–Al2O3 system calcium aluminate inclusions”. (Mn, Mg)O·Al2O3 spinel with a high MnO content was found as a different type of inclusions compared with conventional Al-killed steel grades, and finally, the MnO content in calcium aluminate inclusions became very low. Laboratory experiments were employed to explain the generation of (Mn, Mg)O·Al2O3 spinel inclusions. It is found that the crystal structure of MgO·Al2O3 spinel phase would help the formation of (Mn, Mg)O·Al2O3 spinel inclusions, while Al2O3 inclusions can not react with dissolved Mn in steel to form (Mn, Mg)O·Al2O3 spinel inclusions, even the Mn content was around 5 mass% in steel. Consequently, (Mn, Mg)O·Al2O3 spinel inclusions formed after the formation of MgO·Al2O3 spinel inclusions in industrial practice.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1280K) Full view HTML -
Akifumi Harada, Akitoshi Matsui, Seiji Nabeshima, Naoki Kikuchi, Yuji ...Article type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1546-1552
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIt is well known that the formation of MgO·Al2O3 spinel-type inclusions is affected by the slag composition. To clarify the effect of the slag composition on the formation of spinel-type inclusions, laboratory-scale experiments were carried out in 30 kg-scale induction furnace. Changes in the composition of inclusions were investigated with different slag compositions. As the CaO/SiO2 and CaO/Al2O3 of the slag increased, spinel-type inclusions were observed, and the total Mg content and average composition of MgO in the inclusions were also higher. On the other hand, the total Mg content and average composition of MgO in inclusions decreased with decreasing CaO/SiO2 and CaO/Al2O3 of the slag, and most inclusions were Al2O3-type inclusions including a small amount of MgO. Based on the experimental results, a kinetic analysis was carried out using a calculation model to simulate the reactions between the molten steel, slag, refractory and inclusions in order to evaluate the effect of the slag composition on inclusions. The calculated results of the inclusion composition were in good agreement with the experimental results. In this experimental system, the total Mg content and spinel-type inclusions were suppressed due to a decrease in the activity of MgO in the slag and an increase in the oxygen activity at the interface between the molten steel and slag when the CaO/SiO2 and CaO/Al2O3 of the slag were lower. Therefore, the formation of spinel-type inclusions can be determined by the relationship between the MgO activity of the slag and the interfacial activity of oxygen.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1577K) Full view HTML
-
Peri Subrahmanya Srinivas, Anugrah Singh, Jose Martin Korath, Amiya Ku ...Article type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1553-1562
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLVortexing in continuous slab casting mould is a complex inter-related phenomenon of multiphase fluid flow which can entrain mould powder and deteriorate the end product quality. In this contribution, a 0.4-scale water model has been employed to investigate the interactive effects of the operational parameters including, partial clogging of SEN ports, water flow rates, submerged entry nozzle (SEN) immersion depth and air flow rates. Operating conditions like higher values of air flow rates and deeper submergence depth of the SEN are found to reduce vortex frequencies. At higher air flow rates, bubbles emerging from the SEN port would have higher diameter and hence higher terminal velocity. Also, at higher air flow rates, volume fraction in the vicinity of the SEN is high. Raising larger bubbles with high volume fraction and high terminal velocities, during their interaction with the liquid flow streams approaching the meniscus, would reduce the horizontal velocity components to very low values. As a consequence, the shearing effect between the liquid streams fast approaching the SEN would be decreased, leading to reduction in vortex frequencies. The bubble rising pattern along with the upper circulation loop is found to vary with the SEN submergence depth. At deeper submergence depth, larger fraction of gas bubbles traversing along the upper recirculation loop would reach to a point which is very close to the SEN and escape into atmosphere from there. On contrary, this point of contact between gas bubbles and the meniscus is comparatively away from the SEN at shallow submergence depths. As known, vortices are formed in the vicinity of the SEN where the shearing effect is the maximum. In case of deeper submergence depth, the ascending gas bubbles interact with the swirling and reduce the shearing effect and hence the vortex formation. These findings of the current study are important in controlling the mould powder entrainment through vortexing.
View full abstractDownload PDF (998K) Full view HTML
-
Kenta Sakane, Kazuaki WagatsumaArticle type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1563-1566
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe objective of this paper is to suggest a new method for obtaining an in-depth profile with better precision in 13.56-MHz radio-frequency (RF) glow discharge - optical emission spectrometry. For this purpose, a phenomenon regarding self-bias voltage in the RF plasma is focused on. The self-bias voltage is induced near the RF-loaded electrode, enabling sample atoms to be sputtered from it into the plasma. A bias current can be introduced through the electric circuit including the plasma body, by connecting an external electric device with the glow discharge lamp. The amount of the bias current would change the characteristics of the plasma for atomic emission spectrometry. When higher bias current flows, the resulting plasma extended in the whole area of the glow discharge lamp, including both the electrodes and grounded housing of the lamp, thus making the plasma unstable. However, an exposure to such a plasma could remove gaseous species, which would be entrained when the sample was exchanged, from interior parts of the lamp. This effect contributed to better response of the emission signal just after the discharge was ignited. Depth profiles of a nickel-electroplated steel plate were measured in RF-GD-OES, to investigate the effect of the bias-current introduction.
 Depth profiles of a nickel-electroplated steel plate with or without a pre-discharge for 20 s at a bias current of 50 mA. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (555K) Full view HTML
Depth profiles of a nickel-electroplated steel plate with or without a pre-discharge for 20 s at a bias current of 50 mA. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (555K) Full view HTML
-
Yan Peng, Ming Zhang, Jian-Liang Sun, Yang ZhangArticle type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1567-1576
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
Advance online publication: July 28, 2017JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe model of the roll system vibration is usually limited to a one-dimensional or two-dimensional translation. In reality, however, the roll system also has a rotation behavior due to the uneven force distribution on the roll body. So the vibration, especially in rolling the wide steel strip, should perform a swing behavior, which consists of rotation and translation. In this paper, the experiment phenomena of plant vibration are analyzed, and the influences of roll system vibration on the rolling process are studied. A swing dynamic model of roll system is established considering the dynamic characteristics of the hot rolling process, the uneven force distribution on the roll body, and the coupling relationship between the horizontal and vertical vibration of the work roll. Through the numerical simulation, the natural characteristics of roll system swing are analyzed, the vibration responses of roll system swing are simulated with the arc tooth gear meshing impact force, and the stability of roll system is studied.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1340K) Full view HTML -
Tao Sun, Jian-ping LiArticle type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1577-1585
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
Advance online publication: August 22, 2017JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe warm rolling process with heated rolls for AZ31 sheets was proposed instead of normal hot rolling process without roll heating. Experimental study showed that the quality of rolled sheets was sensitive to the outlet temperatures which need well control during rolling process. In the paper, a computational model combining a finite element method (FEM) with a mathematical model was developed to predict the outlet temperature during the warm rolling of AZ31 alloy sheets. The accuracy of the FEM model was verified by rolling experiments with various process parameters. Numerous thermo mechanical finite element simulations were carried out to obtain a database relation between process parameters and out let temperature. The process parameters were rolls and sheet heated temperatures, rolling speed, initial sheet thickness and thickness reduction. The mathematical model was obtained based on regression of the database. The model gave satisfactory results when comparing the predictions and FEM simulation results. A comprehensive validation of the prediction model is presented by new set of designed experiments. In the explored process window, a good correlation was found with an error on the outlet temperature lower than 10°C. The proposed method in this paper was suitable for outlet temperature control by rolling schedule design during the warm rolling process of AZ31 sheet with heated rolls.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1513K) Full view HTML -
Kevin Mark Banks, Alison Susan Tuling, Dannis Rorisang Nkarapa MaubaneArticle type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1586-1594
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe roughing conditions required to avoid local heterogeneous regions in the final microstructure of high temperature processing (HTP) Nb linepipe steels have been investigated for quasi-compact strip production (CSP) conditions. The influence of strain sequence, rolling temperatures and Mn content on recrystallisation and carbonitride precipitation before and after roughing were studied using laboratory simulation, mathematical modelling and transmission electron microscopy. The roughing conditions necessary to avoid the formation of local heterogeneous regions have been established for HTP steels with an initial grain size of 850 µm. Low Mn Nb–Ti steels experience more sluggish recrystallisation kinetics and are more vulnerable to forming local heterogeneous regions during roughing. To prevent local heterogeneous regions if finishing commences at 900°C, sufficient effective strain is necessary to produce a bulk softened fraction of at least 0.55 in each of the first two roughing passes. If finishing commences at 1000°C, slow air cooling from roughing provides additional time for recrystallisation to go to completion and so prevent the occurrence of local heterogeneous regions. Maintaining the strand temperature as high as possible prior to the commencement of roughing encourages recrystallisation. A roughing start temperature of 1100°C, as opposed to 1075°C, significantly reduces the risk of forming local heterogeneous regions. For the conditions tested, no correlation between softening fraction and carbonitride precipitate characteristics was found. Thus, the influence of Nb on austenite recrystallisation is expected to be due to either solute drag or solute clustering.
View full abstractDownload PDF (3333K) Full view HTML -
Chao Liu, Anrui He, Yi Qiang, Defu Guo, Jian ShaoArticle type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1595-1602
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
Advance online publication: July 28, 2017JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn order to quantify the effect of volume changes due to temperature drop and phase transformation on hot rolling deformation behavior of non-oriented electrical steel and make up for the deficiency of traditional austenitic rolling model, mathematical models derived from experiments are established, and programmed to subroutines to be incorporated into the coupled temperature-displacement strip model. The calculated results of temperature field, phase field and stress field are then transferred into the rolls-strip coupling model to participate in rolling process. The results indicate that the temperature deviation along strip width direction can lead to an obvious transverse transformation difference. When only the volume change due to temperature drop is considered, the strip shows completely elastic “tensile stress in the edge, compressive stress in the middle”, and the central thickness and quadratic crown of strip are increased slightly. When the volume changes due to temperature drop and phase transformation are both considered, the unexpected “secondary plastic deformation” is produced and the reverse distribution form of internal stress is presented, which significantly decrease the thickness and quadratic crown of strip. However, due to the average effect of tensile stress and compressive stress, both volume changes contribute little to the total roll force.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1497K) Full view HTML
-
Tu Hu, Xuefeng Liao, Jie Li, Jinhui Peng, Libo Zhang, Li Yang, Zhaogan ...Article type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1603-1608
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe preparation of coating material of welding electrode from marine placer via carbothermic reduction was systematically investigated. Four stages were observed in the carbothermic reduction of marine placer–coal mixture. The release of the volatiles in coal occurred at the first stage (≤600°C), and the solid–solid reduction and gas–solid reduction occurred at the second (600–960°C) and third stages (960–1350°C), respectively. The reduction rate of iron oxide at the third stage was higher than that at the second stage because of the high carbon gasification rate. A slowdown in the total mass loss at approximately 1350°C occurred at the fourth stage. X-ray diffraction patterns show that the reduction process of the marine placer exceeded 1100°C and can be written as: FeTiO3→FeTi2O5→Fe+TiO2. The quality index of the reduced ilmenite was evaluated in terms of the TiO2 and FeO content. The TiO2 content gradually increased as the reduction temperature increased from 1000°C to 1300°C, and the reduction time exerted lesser influence than temperature. The FeO content initially decreased rapidly and then exhibited a downward trend that became slower after 120 min with increasing reduction time. The TiO2 index could be achieved easily because of the high TiO2 content of the raw material. The FeO content could reach 8.45% after reduction at 1300°C for 180 min, which exceeded the technical requirement of 9%.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1101K) Full view HTML
-
Motoaki Morita, Kengo Kishihara, Shinichi Motoda, Norimitsu Koga, Tada ...Article type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1609-1616
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLCopper oxide (Cu-oxide) electrodes were produced by the vacuum deposition of pure copper on a stainless steel substrate, followed by oxidation in air between 150 and 550°C. The potentials and durability of the Cu-oxide electrodes under xenon light irradiation were evaluated, and the effects of the microstructure on the electrode performance were discussed. The photocatalytic effect of a p-type semiconductor in a Cu-oxide electrode was confirmed for all treatment temperatures. Electrodes oxidized at 150°C showed a very weak photocatalytic effect because the main phase of the thin film comprised amorphous Cu. The potentials of the electrodes oxidized at 450 and 550°C shifted to more than 230 mV (SCE) after light irradiation but they immediately decreased to 100 mV (SCE) due to the self-corrosion (photo-corrosion) of CuO. The electrodes oxidized at 250 and 350°C retained their photocatalytic activities at irradiation time of more than 24 h. The initial potentials of the electrodes oxidized at 250 and 350°C are 100 mV (SCE) and 280 mV (SCE), respectively. The potential of the electrode oxidized at 250°C increased with time because Cu2O, which was the initial main phase of the electrode, was oxidized to CuO by a surface reaction during irradiation. In the electrode oxidized at 350°C, the photo-excited electrons and the photo-generated holes hardly reacted with the electrode surface by the interactions between the Cu-oxide film and the passive film of stainless steel substrate. The electrode exhibited the best performance in terms of potential and durability during the light irradiation.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1440K) Full view HTML -
Qiang Yue, Long Zhang, Jia Wang, Hui Kong, Li ZhouArticle type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1617-1624
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThis paper presents the results of fluid flow and dynamic behavior of dross in a hot-dip coreless galvanizing process by performing water modeling experiments and numerical simulations. NaCl aqueous solutions and plastic particles were employed as model fluid and top and bottom dross, respectively. The velocity distributions of the fluid were measured with the help of an Acoustic Doppler Velocimeter (ADV) for the strip speeds from 1.0 m/s to 2.7 m/s. The results from both water modeling experiments and numerical simulations showed that the flow in the bath is very complex and is determined by the strip speed, which is also a key factor for the distribution of top and bottom dross distribution in the bath. In the water modeling experiments applying the ADV at different strip speeds, some swirling flow which may drive the dross to the strip was observed on the surface of the bath, as well as inside the bath. And the swirling flow on the surface was disappeared when the strip speed was increased to 2.0 m/s. Consequently, high strip speed is favorable for the strip to avoid the dross adhering problem. In addition, bottom dross distribution was also investigated by using plastic particles. The results illustrate that bottom particles distribution is highly determined by the strip speed. Remarkably, more intensive flow driven by much higher strip speed (2.3 m/s) may roll up the bottom particles into the bath. This gives higher possibilities for the strip to cause surface quality problem.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1688K) Full view HTML
-
Kunio ItoArticle type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1625-1630
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDetails of the Potts-MC-type simulation model modified to reduce computing time were explained and effects of parameters to control anti-freezing of the structure, orientation-relation-dependent migration rate and energy of boundaries as well as orientation-relation-dependent migration rate of triple lines on the elementary structural development process were presented. Some topological characters of the structures observed by the modified method were then compared with earlier reported ones. Most of them coincided with the earlier reported results. The critical grain size has been found to coincide with the topological mean grain size. The transition probabilities of grains between topological classes in the shortest elapsed time are reported for the first time; they suggest that the steady state topological grain size distribution could exist for only a short period.
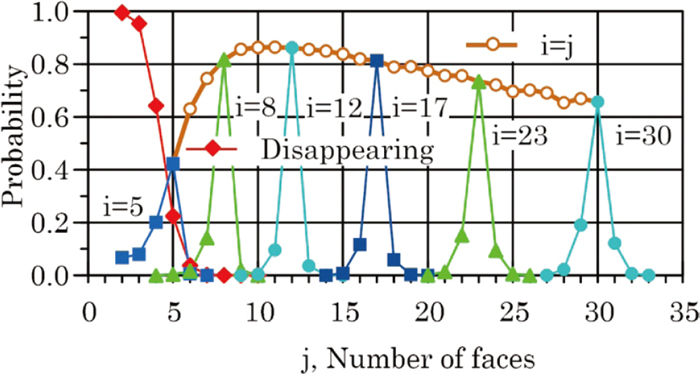 Transition probability of the number of faces of a grain from i to j in a single systematical MC step. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1559K) Full view HTML
Transition probability of the number of faces of a grain from i to j in a single systematical MC step. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1559K) Full view HTML -
Kunio ItoArticle type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1631-1636
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA method to simulate crystallographic texture development using a small computer is presented. The growth behavior of a specified grain embedded in previously prepared matrix grains, for which the energy and mobility of grain boundaries as well as the mobility of triple lines depended on the relation between the orientations of the embedded and matrix grains, was first observed by a modified Potts-Monte Carlo-type three-dimensional grain growth simulation model. A specimen investigated using a single simulation corresponded to part of the mother specimen, and hence, was sufficiently small to be handled by a personal computer. The texture development in the mother specimen was then statistically estimated from results obtained by varying the size of embedded grains. The orientation-relation-dependent mobility of triple lines was found to substantially influence the texture change developed by the orientation-relation-dependent energy of grain boundaries.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1196K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1196K) Full view HTML -
Yong Zhao, Yanhui Sun, Xiaobin Li, Fangyuan SongArticle type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1637-1644
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
Advance online publication: July 25, 2017JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe characteristics of the γ↔δ phase transformations were observed on the surface of duplex stainless steels with different nitrogen concentrations by the Ultra High Temperature Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (UHT-CSLM). The effects of the nitrogen content on the phase transformations are discussed based on the experimental results and thermodynamic calculations. It is found that the migration of the δ/γ IB is the main form of the phase transformation and leads to the continuous decline and final disappearance of the retained γ-phase during the γ→δ phase transformation in the high nitrogen steel (N1) and low nitrogen steel (N2). During the δ→γ phase transformation, the γ-cells prefer to precipitate along the δ/δ GBs and develop into the δ-ferrite matrix with finger-like or sword-like patterns. Then the γ-cells also nucleate in the δ-grains with a sword-like pattern and the growing speed in the longitudinal direction is much faster than that in the lateral direction. More importantly, the high nitrogen content can hinder the migration of δ/γ IBs during the γ→δ transformation and also promote the nucleation and growth of γ-phase during the δ→γ transformation by increasing both the starting and finishing temperatures of the phase transformation. Interestingly, the original δ/δ GB which is covered by the precipitation of γ-phase during the δ→γ transformation will reappear first at the same position by the moving of δ/γ IBs during the γ→δ transformation, but it is unstable and migrates fast with further heating.
View full abstractDownload PDF (2371K) Full view HTML
-
Ying Qin, Jin-Yu Lu, Shi CaoArticle type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1645-1651
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
Advance online publication: July 28, 2017JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLConcrete filled tube (CFT) columns have been increasingly used as the load-bearing systems in engineering applications. The fact that the CFT column has steel plate restrained by infilled concete and the availability of high strength structural steel leads to the application of thin steel plates in CFT columns. However, this gives rise to the local instability problem of thin steel plates under axial loadings. Furthermore, most of the studies on the local buckling of steel plates in contact with concrete reported in the literature were concerned with the cases where the four edges of the steel plate were assumed to be clamped or simply supported. This cannot reflect the real state of steel plate in CFT columns, where the unloaded edges of steel plate is more appropriate to be regarded as elastically restrained. This paper presents an analytical study of local buckling of steel plates in CFT columns. The steel plate, subjected to uniform axial compression, is assumed to be elastically rotationally restrained along loaded and unloaded edges. The approximate solution is obtained by Rayleigh-Rize method. The solution of rotationally restrained plates is verified by comparing with available experimental and theoretical data in the literature. Good agreement is found between them for local buckling stress of the steel plate. This research provides basis for capacity design of CFT columns under axial compression.
View full abstractDownload PDF (329K) Full view HTML -
Kenichi Koide, Toshirou Anraku, Akihiro Iwase, Hiroyuki InoueArticle type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1652-1656
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLFatigue crack growth testing was carried out on Type304 stainless steel (Type304SS) at room temperature (RT) in mixed gasses controlled to various pressure levels of up to 70 MPa in order to measure changes in embrittlement sensitivity due to hydrogen partial pressure. At PH2 less than 3 MPa, as hydrogen partial pressure decreases, the crack growth rate (da/dN) of Type304SS decreased, and at PH2=5×10−5 MPa (50 Pa), it was 2.8 times higher than that in the air. The hydrogen partial pressure whose da/dN equals the rate in the air, which is the lower limit critical hydrogen partial pressure, was not observed. On the other hand, at PH2=3 MPa or higher, the da/dN reached approximately 20 times higher than in the air. There was an upper limit of the da/dN which no longer increases after hydrogen partial pressure reaches a certain level. From a conservative judgment, it is able to plan the fatigue life considering the da/dN at PH2=3 MPa as the upper limit; approximately 20 times higher than in the air.
View full abstractDownload PDF (732K) Full view HTML
-
Yasutaka Kuwahara, Hiromi YamashitaArticle type: Regular Article
2017 Volume 57 Issue 9 Pages 1657-1664
Published: September 15, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 20, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDischarging phosphorus through wastewaters into waterbodies holds potential risks of eutrophication and adverse effects on aquatic organisms. On the other hand, phosphorus is an indispensable element needed for all life forms and plant growth, while phosphate rock reserves available are anticipated to be depleted in the near future. Herein, we report phosphate removal from aqueous solution using a calcium silicate hydrate (CSH) adsorbent prepared from blast furnace slag (BF slag), a high-volume byproduct produced in iron-making industry. A high-surface-area CSH was synthesized through a facile two-step dissolution-precipitation method under controlled conditions (at 373 K and pH 11.0) using BF slag as a sole metal source. Adsorption experiments demonstrated that the slag-made CSH showed a maximum phosphorus adsorption capacity of 53.1 P-mg/g under standard adsorption conditions (pH 7.0 and 298 K), which was 73 times greater than that of BF slag. Owing to the presence of abundant Ca2+ species reactive with phosphate ions, the adsorbent showed excellent phosphorus adsorption performances in a broad range of conditions, particularly even from low-concentrated phosphate solutions and under a wide range of pH conditions. Kinetic analysis demonstrated that the adsorption of phosphate onto slag-made CSH adsorbent can be well fitted with pseudo-second-order kinetic model and Freundlich adsorption isotherms. This study demonstrates that the CSH synthesized from BF slag can be used as a promising adsorbent for efficient bulk wastewater treatment and phosphorus recovery.
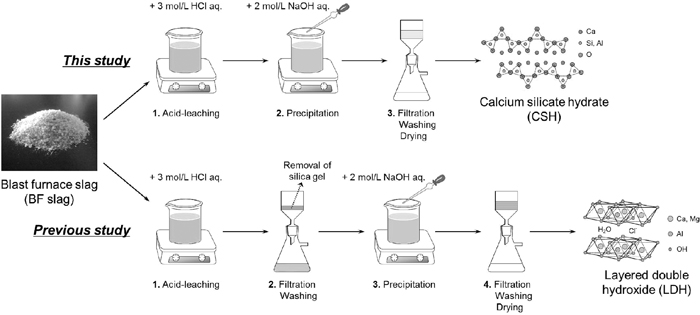 Comparison of synthetic procedures for calcium silicate hydrate (CSH) and layered double hydroxide (LDH) from BF slag. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1445K) Full view HTML
Comparison of synthetic procedures for calcium silicate hydrate (CSH) and layered double hydroxide (LDH) from BF slag. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1445K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|