
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2024 年 110 巻 5 号 p. Contents-
発行日: 2024/04/01
公開日: 2024/04/01
ジャーナル オープンアクセスPDF形式でダウンロード (1237K) -
2024 年 110 巻 5 号 p. Editorial-
発行日: 2024/04/01
公開日: 2024/04/01
ジャーナル オープンアクセスPDF形式でダウンロード (203K)
-
井川 大輔, 土肥 勇介, 松井 貴, 山本 哲也, 深田 喜代志, 角 広行, 下山 泉原稿種別: 論文
2024 年 110 巻 5 号 p. 395-403
発行日: 2024/04/01
公開日: 2024/04/01
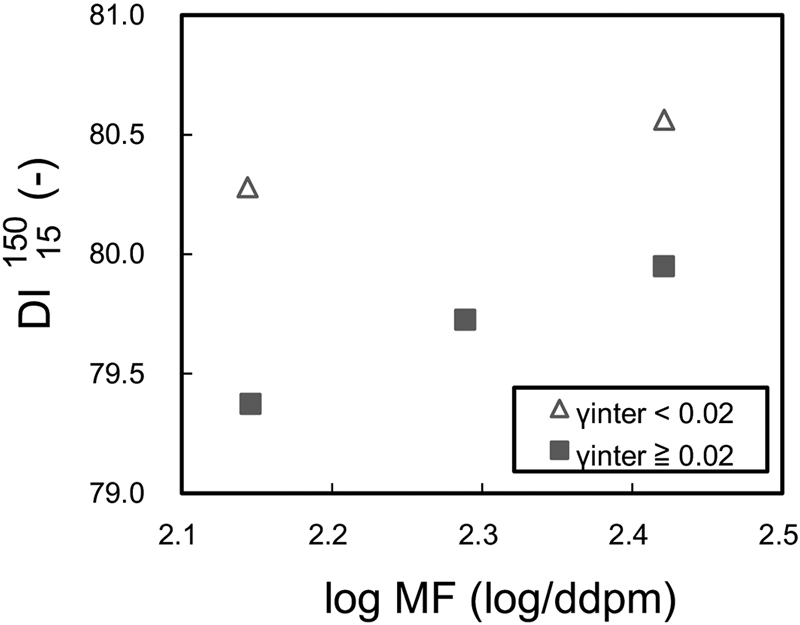
[早期公開] 公開日: 2024/01/23ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLIn our previous paper, a new measurement method for the coal adhesion property called “surface tension of semi-coke” was devised. The surface tension of a semi-coke sample obtained by heat treatment of a coal sample at 500°C was measured as a unique adhesion property. Conventionally, it has been thought that adhesion is dominant under a low MF (Gieseler maximum fluidity) condition. Moreover, it is important for effective coal utilization to develop a technique that enables production of high strength coke under low MF conditions, which has been thought to deteriorate coke strength. However, in the previous paper, the effect of surface tension on coke strength was investigated only under a single MF condition without changing the level of MF.
In this paper, the effects of surface tension on coke strength under adhesion dominant conditions (low MF and high TI (total inert content)) were investigated. As a result, it was found that the effect of surface tension on coke strength was significant when MF was low or TI was high. Therefore, it is considered that high strength coke can be produced even under low-grade conditions (low MF or high TI) by controlling surface tension. Finally, based on the results, the concept of the conventional MOF diagram was extended. This technique enables effective selection and utilization of coal resources.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2729K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2729K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
千葉 雅樹, 見澤 謙佑, 谷本 久典, 熊谷 正芳, 佐藤 成男, 川又 透, 鈴木 茂原稿種別: 論文
2024 年 110 巻 5 号 p. 404-413
発行日: 2024/04/01
公開日: 2024/04/01
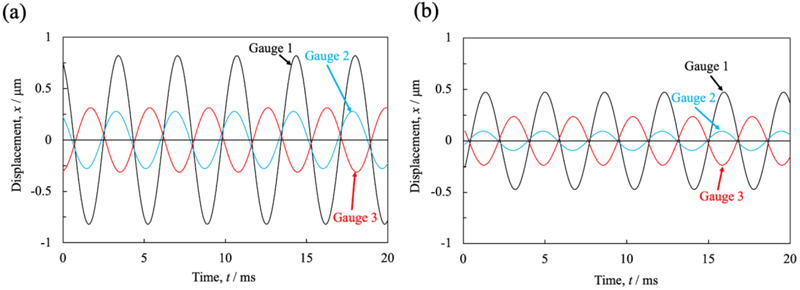
[早期公開] 公開日: 2024/02/09ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLTo understand the mechanism of vibration energy harvesting using magnetostrictive Fe-Ga alloys, the dynamic strains at different locations of a U-shaped device during vibration were simulated. In the simulations, the previous results for location-dependent strain in the vibration experiments were fitted with trigonometric functions. The results show that the amplitude and phase of the strain vary with location, and that the electromagnetic force is generated at different locations. Since magnetic induction is thought to occur due to an external magnetic field, the magnetic domain structure near the cube orientation of Fe-Ga alloy single crystals was observed using a Kerr effect microscope. As a result, Bloch magnetic domain structures with different contrasts of brightness and darkness were observed depending on the applied magnetic field. It was shown that striped magnetic domains were dominant when the applied magnetic field was small, while lancet magnetic domains oriented to the magnetic field appeared with transverse straight supplementary domains as a magnetic domain under a saturated magnetic field. The domain patterns in one direction magnetic fields were not necessarily the same as those observed in the opposite direction. This indicates that Fe-Ga alloy single crystals are used as a core for vibrational energy harvesting. Also, the motion of magnetic walls is thought to play an important role in the vibrational properties of the material, and inhomogeneous elastic strain associated with magnetic domains evolves microscopically in single crystals.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3177K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3177K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
相原 巧, 森貞 好昭, 潮田 浩作, 釜井 正善, 宮内 貴章, 長谷川 慎一, 藤井 英俊原稿種別: 論文
2024 年 110 巻 5 号 p. 414-425
発行日: 2024/04/01
公開日: 2024/04/01
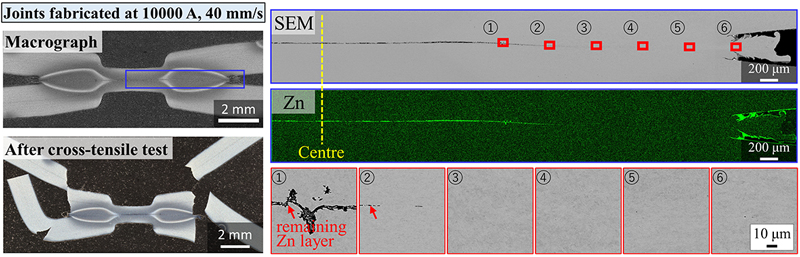
[早期公開] 公開日: 2024/02/22ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLThe microstructural evolution and tensile properties of joints fabricated by the newly developed cold spot joining (CSJ) method were investigated using galvannealed DP 780 MPa steel sheet. The novel solid-state joining method called CSJ is proved to make the joining interface plastically deformed under high pressure and appropriate current by expelling Zn-Fe coated layer, resulting in the sound joints with strong interface. Joints exploiting CSJ method were made focusing on the effects of the pressing speed and current level. Microstructural observations of the joints revealed that the lower pressing speed increases the interface temperature. In addition, the increase in the current also increases the interface temperature. The increase in the interface temperature has a positive effect in terms of expelling Zn-Fe coated layer. The positive effect of increasing current is more significant than that of decreasing the pressing speed. The increase in temperature near the interface by increasing current promotes the removal of the Zn-Fe coating layer, resulting in plastic deformation near the joining interface. Appropriate pressure and current settings can facilitate the sound spot joints with enough tensile strength. Both tensile-shear and cross-tension tests have confirmed a plug failure in the base material region.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (12903K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (12903K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|