
- Issue 16 Pages 1251-
- Issue 15 Pages 1165-
- Issue 14 Pages 1033-
- Issue 13 Pages 989-
- Issue 12 Pages 899-
- Issue 11 Pages 795-
- Issue 10 Pages 721-
- Issue 9 Pages 653-
- Issue 8 Pages 569-
- Issue 7 Pages 513-
- Issue 6 Pages 427-
- Issue 5 Pages 395-
- Issue 4 Pages 343-
- Issue 3 Pages 89-
- Issue 2 Pages 35-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
- Issue 16 Pages 2157-
- Issue 15 Pages 1805-
- Issue 14 Pages 1613-
- Issue 13 Pages S1141-
- Issue 12 Pages S1037-
- Issue 11 Pages 1443-
- Issue 10 Pages 1273-
- Issue 9 Pages 1077-
- Issue 8 Pages 917-
- Issue 7 Pages 751-
- Issue 6 Pages 585-
- Issue 5 Pages S389-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 403-
- Issue 2 Pages 233-
- Issue 1 Pages 19-
- Issue 16 Pages 2153-
- Issue 15 Pages 1977-
- Issue 14 Pages 1813-
- Issue 13 Pages S1285-
- Issue 12 Pages S1043-
- Issue 11 Pages 1667-
- Issue 10 Pages 1481-
- Issue 9 Pages 1231-
- Issue 8 Pages 891-
- Issue 7 Pages 711-
- Issue 6 Pages 538-
- Issue 5 Pages S407-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 347-
- Issue 2 Pages 173-
- Issue 1 Pages 14-
- Issue 16 Pages 1837-
- Issue 15 Pages 1711-
- Issue 14 Pages 1569-
- Issue 13 Pages S1205-
- Issue 12 Pages S1034-
- Issue 11 Pages 1423-
- Issue 10 Pages 1269-
- Issue 9 Pages 1059-
- Issue 8 Pages 925-
- Issue 7 Pages 775-
- Issue 6 Pages 627-
- Issue 5 Pages S287-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 301-
- Issue 2 Pages 147-
- Issue 1 Pages 12-
- Issue 16 Pages 2179-
- Issue 15 Pages 1795-
- Issue 14 Pages 1631-
- Issue 13 Pages S1053-
- Issue 12 Pages S1023-
- Issue 11 Pages 1501-
- Issue 10 Pages 1315-
- Issue 9 Pages 987-
- Issue 8 Pages 767-
- Issue 7 Pages 621-
- Issue 6 Pages 473-
- Issue 5 Pages S305-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 299-
- Issue 2 Pages 151-
- Issue 1 Pages 16-
- Issue 16 Pages 1945-
- Issue 15 Pages 1699-
- Issue 14 Pages 1531-
- Issue 13 Pages S1055-
- Issue 12 Pages S1013-
- Issue 11 Pages 1367-
- Issue 10 Pages 1215-
- Issue 9 Pages 1087-
- Issue 8 Pages 887-
- Issue 7 Pages 721-
- Issue 6 Pages 507-
- Issue 5 Pages S317-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 343-
- Issue 2 Pages 187-
- Issue 1 Pages 17-
- Issue 16 Pages 2405-
- Issue 15 Pages 2067-
- Issue 14 Pages 1865-
- Issue 13 Pages 1675-
- Issue 12 Pages S1055-
- Issue 11 Pages S1015-
- Issue 10 Pages 1479-
- Issue 9 Pages 1129-
- Issue 8 Pages 895-
- Issue 7 Pages 711-
- Issue 6 Pages 545-
- Issue 5 Pages S325-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 369-
- Issue 2 Pages 193-
- Issue 1 Pages 16-
- Issue 16 Pages 2573-
- Issue 15 Pages 2261-
- Issue 14 Pages 2073-
- Issue 13 Pages S1111-
- Issue 12 Pages S1001-
- Issue 11 Pages 1867-
- Issue 10 Pages 1657-
- Issue 9 Pages 1409-
- Issue 8 Pages 1043-
- Issue 7 Pages 841-
- Issue 6 Pages 649-
- Issue 5 Pages S415-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 431-
- Issue 2 Pages 225-
- Issue 1 Pages 3-
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2022Volume 108Issue 7 Pages Cover-
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 30, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (369K) -
2022Volume 108Issue 7 Pages Contents-
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 30, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (2145K) -
2022Volume 108Issue 7 Pages Editorial-
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 30, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (204K)
-
Hideo Mizukami, Yoshihisa Shirai, Alec MitchellArticle type: Regular Article
2022Volume 108Issue 7 Pages 383-393
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 30, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThis study examines the evaporation of Al from a molten commercial Ti alloy with different Al concentrations after partial melting in a small electron beam furnace. Electron probe micro analysis confirmed that the Al concentration in the molten region was uniform. The movement of Al in the molten region was not found to be the rate determining step. The Al concentration in the molten region consistently decreased with an increasing melting time but in a non-linear manner. The activity of Al in the molten alloy was calculated using thermodynamic data, which indicated that it increased with an increasing Al concentration in the ingot. However, the activity of Al in the molten alloy did not increase linearly under the influence of the other alloying elements. The overall mass transfer coefficient of Al from molten alloy during evaporation increased with an increasing initial Al concentration with the mass transfer coefficient of Al depending on the activity of Al. An evaporation model was constructed by considering the mutual interaction between Al and the other alloying elements. This evaporation model was able to predict the amount of Al evaporation from the multi-component Ti alloy melt.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2804K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2804K) Full view HTML
-
Kunito Nakajima, Noah Utsumi, Masashi YoshidaArticle type: Regular Article
2022Volume 108Issue 7 Pages 394-404
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 30, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTubes are widely applied as structural members and members for fluid transmission. However, there is a concern that the strength of the tube will decrease because thickness deviation will occur during bending and the thickness on the tension side will decrease. Therefore, the authors devised an eccentric tube that eccentric the inner diameter of the tube and increases or decreases the thickness in the tube. In this study, we conducted an experiment and Finite Element Analysis (FEA) for the purpose of researching the deformation property of the eccentric tube and evaluating the appropriate value of the eccentricity e. As a result, it was found that, as a deformation property of the eccentric tube, even if there is a difference in thickness in the same tube, the thickness deviation becomes large in the case of thin wall. Furthermore, it was found that the flattening was reduced by setting the thick part of the eccentric tube to the tension side. In addition, the target value of the thickness after processing was set, and the eccentricity e at which the thickness after bending was close to the target value was estimated by FEA. As a result of conducting an experiment using the obtained eccentricity e, it was found that the thickness after processing can be made close to the target value by adjusting the eccentricity e.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (3938K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (3938K) Full view HTML
-
Takeshi Yasuda, Raimu Shozui, Koji Nishimoto, Yoshihiro Okumoto, Takah ...Article type: Regular Article
2022Volume 108Issue 7 Pages 405-416
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 30, 2022
Advance online publication: April 08, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe laser-quenching-induced heat-affected zone (HAZ) of carbon steel was nano-mechanically and sub-micro-structurally characterized. Ferrite–pearlite-structured JIS G 4053 SCM440 specimens were laser-irradiated at 275, 260, or 240 W. The specimens were mechanically characterized by nano-indentation, and the micro-structures were observed with scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The HAZ consisted of various phases and micro-structures, including auto-tempered martensite, as-quenched martensite, martensite containing undissolved cementite, and the original ferrite–pearlite. The region and fraction of the HAZ micro-structures depended on the distance from the sample surface and the laser power. The nanohardness of the martensite structures varied widely presumably depending on the thermal history and local carbon content. In particular, the hardness of the martensite containing the undissolved cementite could be interpreted in terms of the solute carbon content estimated based on the area fractions of the undissolved cementite and precipitated carbide, as observed in the binarized SEM images. The thermal history was theoretically simulated to ensure that the micro-structures and associated hardness values were reasonable.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (7221K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (7221K) Full view HTML -
Shiho Fukumoto, Taishiroh FukumaruArticle type: Regular Article
2022Volume 108Issue 7 Pages 417-423
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 30, 2022
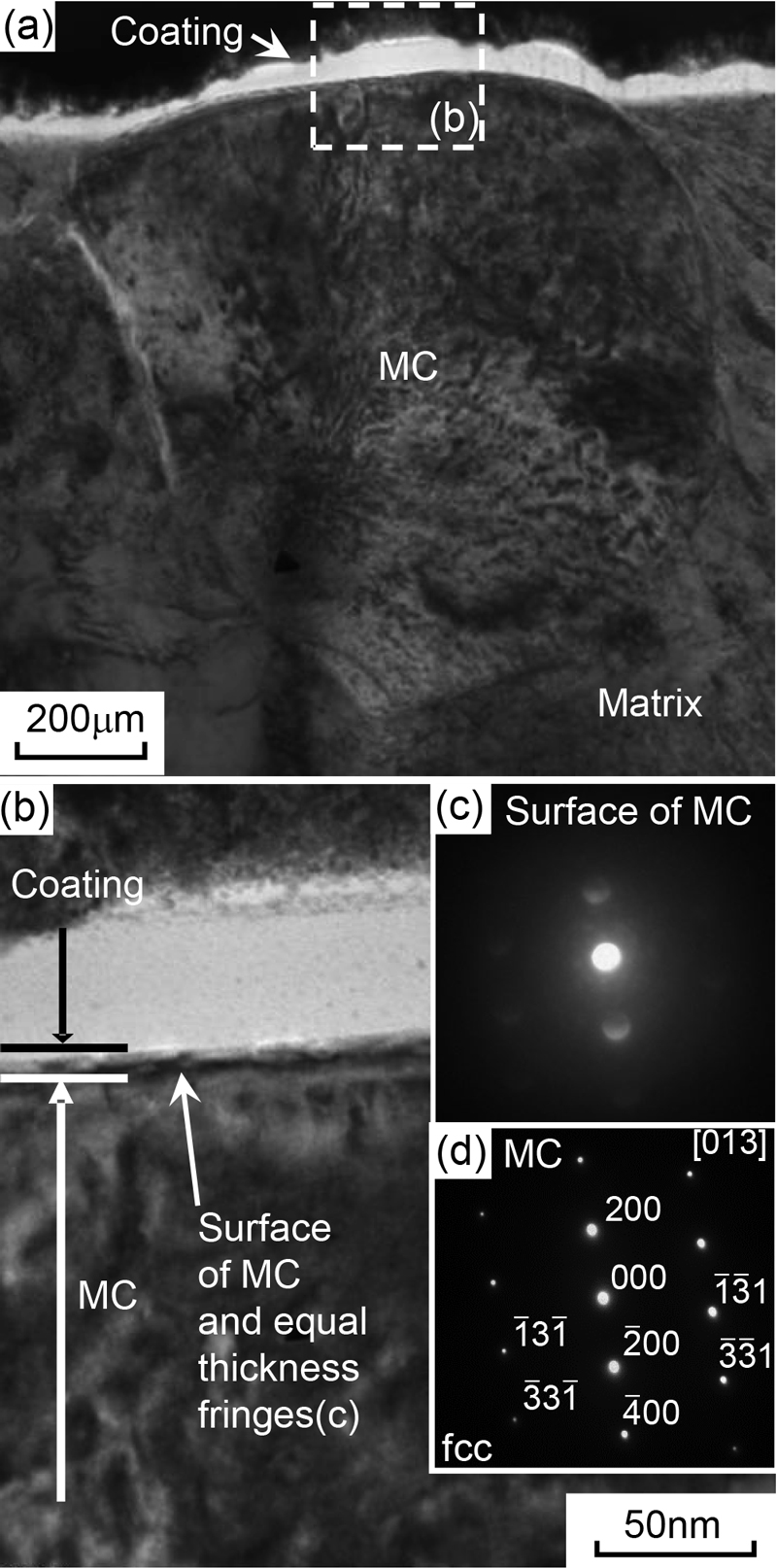
Advance online publication: April 21, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe present study investigated the microstructure of cutting tool in order to clarify their wear mechanism of cutting tool made of high speed tool steel in the metal cutting process. A special protective oxide surface, which mainly consist of iron, vanadium and oxygen is formed on the surface of the tool during dry cutting wear test. Iron could be diffused from cutting tool and cutting material, and vanadium which alloyed to improve tool life as MC carbide in high speed steel is from cutting tool. During cutting wear test, an amorphous oxide surface seems to exist in a liquid state. At the cutting temperature on the contact point of tool, the surface as so-called “Belag” is melted as a result of eutectic reaction of iron oxide and vanadium oxide. The surface has a role of fluid lubrication between work material and tool. Therefore, the surface is effective in protecting against tool wear at this cutting speed.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2220K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2220K) Full view HTML
-
Junya Sakurai, Masahiko Demura, Junya Inoue, Masayoshi YamazakiArticle type: Regular Article
2022Volume 108Issue 7 Pages 424-437
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 30, 2022
Advance online publication: April 14, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLWe have attempted to predict creep rupture time for a wide range of ferritic heat resistant steels with machine learning methods using the NIMS Creep Data Sheet (CDS). The dataset consisted of commercial steel data from 27 sheets in the CDS, covering various grades of carbon steels, low alloy steels, and high Cr steels. The prediction models were constructed using three methods, support vector regression (SVR), random forest, and gradient tree boosting with 5132 training data in order to predict log rupture time from chemical composition (19 elements), test temperature, and stress. Evaluation with 451 test data proved that all three models exhibited high predictivity of creep rupture time; in particular, the performance of the SVR model was the highest with a root mean squared error as low as 0.14 over the log rupture time, which value means that, on average, the prediction error was factor 1.38 (=100.14). The high predictivity achieved with no use of information on microstructure was presumably because the data used was for commercial steels in which there should be a correlation between the composition and the microstructure. We confirmed that the prediction did not work well exceptionally for two heats having the same composition but different microstructures with and without stress relief annealing. The predictivity could be drastically improved by adding the 0.2% proof stress at the creep test temperature as one of the explanatory variables. As a use case of the prediction model, the effect of elements was evaluated for modified 9Cr 1Mo steels.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (6378K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (6378K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|