
- Issue 16 Pages 1251-
- Issue 15 Pages 1165-
- Issue 14 Pages 1033-
- Issue 13 Pages 989-
- Issue 12 Pages 899-
- Issue 11 Pages 795-
- Issue 10 Pages 721-
- Issue 9 Pages 653-
- Issue 8 Pages 569-
- Issue 7 Pages 513-
- Issue 6 Pages 427-
- Issue 5 Pages 395-
- Issue 4 Pages 343-
- Issue 3 Pages 89-
- Issue 2 Pages 35-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
- Issue 16 Pages 2157-
- Issue 15 Pages 1805-
- Issue 14 Pages 1613-
- Issue 13 Pages S1141-
- Issue 12 Pages S1037-
- Issue 11 Pages 1443-
- Issue 10 Pages 1273-
- Issue 9 Pages 1077-
- Issue 8 Pages 917-
- Issue 7 Pages 751-
- Issue 6 Pages 585-
- Issue 5 Pages S389-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 403-
- Issue 2 Pages 233-
- Issue 1 Pages 19-
- Issue 16 Pages 2153-
- Issue 15 Pages 1977-
- Issue 14 Pages 1813-
- Issue 13 Pages S1285-
- Issue 12 Pages S1043-
- Issue 11 Pages 1667-
- Issue 10 Pages 1481-
- Issue 9 Pages 1231-
- Issue 8 Pages 891-
- Issue 7 Pages 711-
- Issue 6 Pages 538-
- Issue 5 Pages S407-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 347-
- Issue 2 Pages 173-
- Issue 1 Pages 14-
- Issue 16 Pages 1837-
- Issue 15 Pages 1711-
- Issue 14 Pages 1569-
- Issue 13 Pages S1205-
- Issue 12 Pages S1034-
- Issue 11 Pages 1423-
- Issue 10 Pages 1269-
- Issue 9 Pages 1059-
- Issue 8 Pages 925-
- Issue 7 Pages 775-
- Issue 6 Pages 627-
- Issue 5 Pages S287-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 301-
- Issue 2 Pages 147-
- Issue 1 Pages 12-
- Issue 16 Pages 2179-
- Issue 15 Pages 1795-
- Issue 14 Pages 1631-
- Issue 13 Pages S1053-
- Issue 12 Pages S1023-
- Issue 11 Pages 1501-
- Issue 10 Pages 1315-
- Issue 9 Pages 987-
- Issue 8 Pages 767-
- Issue 7 Pages 621-
- Issue 6 Pages 473-
- Issue 5 Pages S305-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 299-
- Issue 2 Pages 151-
- Issue 1 Pages 16-
- Issue 16 Pages 1945-
- Issue 15 Pages 1699-
- Issue 14 Pages 1531-
- Issue 13 Pages S1055-
- Issue 12 Pages S1013-
- Issue 11 Pages 1367-
- Issue 10 Pages 1215-
- Issue 9 Pages 1087-
- Issue 8 Pages 887-
- Issue 7 Pages 721-
- Issue 6 Pages 507-
- Issue 5 Pages S317-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 343-
- Issue 2 Pages 187-
- Issue 1 Pages 17-
- Issue 16 Pages 2405-
- Issue 15 Pages 2067-
- Issue 14 Pages 1865-
- Issue 13 Pages 1675-
- Issue 12 Pages S1055-
- Issue 11 Pages S1015-
- Issue 10 Pages 1479-
- Issue 9 Pages 1129-
- Issue 8 Pages 895-
- Issue 7 Pages 711-
- Issue 6 Pages 545-
- Issue 5 Pages S325-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 369-
- Issue 2 Pages 193-
- Issue 1 Pages 16-
- Issue 16 Pages 2573-
- Issue 15 Pages 2261-
- Issue 14 Pages 2073-
- Issue 13 Pages S1111-
- Issue 12 Pages S1001-
- Issue 11 Pages 1867-
- Issue 10 Pages 1657-
- Issue 9 Pages 1409-
- Issue 8 Pages 1043-
- Issue 7 Pages 841-
- Issue 6 Pages 649-
- Issue 5 Pages S415-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 431-
- Issue 2 Pages 225-
- Issue 1 Pages 3-
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2023Volume 109Issue 9 Pages Cover-
Published: September 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 31, 2023
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (675K) -
2023Volume 109Issue 9 Pages Contents-
Published: September 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 31, 2023
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (2000K) -
2023Volume 109Issue 9 Pages Editorial-
Published: September 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 31, 2023
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (206K)
-
Norifumi Asahara, Katsuhiro Fuchigami, Masafumi ZezeArticle type: Regular Article
2023Volume 109Issue 9 Pages 721-727
Published: September 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 31, 2023
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLMolten oxides are widely used as refining slag and mold flux in the steelmaking process. In the stationary state, the molten oxide and the molten iron form a layer due to their density difference. However, in the actual operation, they are partially mixed and dispersed as droplets, which can increase the slag-metal reaction area or cause the formation of nonmetallic inclusions. In this study, the dispersion behavior in density stratified flow was investigated by water model experiments. It was suggested that the dispersion behavior of silicone oil was affected by viscosity. As the kinematic viscosity was higher than 100 mm2/s, droplet generation tended to be less likely to occur.
The conventional equations for interface instability and energy balance underestimated the critical velocity of droplet generation when the kinematic viscosity of oil was higher than 100 mm2/s. On the other hand, we were able to reproduce the influence of viscosity in this experiment by applying the empirical formula using the Ohnesorge number. Furthermore, an energy balance formula including the influence of viscosity was newly constructed. We confirmed that the new formula agreed with the experimental results.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2454K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2454K) Full view HTML -
Koichi Momono, Jun Ishii, Seiji Hosohara, Hideo KijimaArticle type: Regular Article
2023Volume 109Issue 9 Pages 728-737
Published: September 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 31, 2023
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLUsed plastic waste flowing into ocean has become a worldwide problem. In recent years international trade in used waste plastics has been regulated. Therefore, a large amount of used plastic should be disposed domestically. On the other hand, used waste plastics with high calorific value could be used as an energy source. Then a gasification process of used plastics using fluidized bed has been newly developed. In this process, used plastics were decomposed in a fluidized bed reactor at around 600°C which was lower temperature than that used in current commercial processes. Higher calorific value gas could be attained by a gasification reaction control at the lower temperature. Hydrogen enriched gas generated from the water gas shift reaction of the basic oxygen furnace gas was used as fluidizing, or gasifying agent since hydrogen was considered to have an effect for promoting the decomposition reaction of hydrocarbon in used plastics. As fluid medium in the reactor, catalysts were used to improve gasification efficiency. In this study, the effect of gasification temperature and the type of the catalyst on a calorific value of produced gas and a gasification efficiency were investigated. High calorific value gas (LHV: 5000 kcal/Nm3) could be successfully produced from pyrolysis of used plastics by appropriate gasification temperature and catalyst.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (3149K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (3149K) Full view HTML
-
Takayuki Harano, Yuki Yoshimoto, Yasuo Takeichi, Tomohito Tanaka, Eiji ...Article type: Regular Article
2023Volume 109Issue 9 Pages 738-746
Published: September 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 31, 2023
Advance online publication: May 18, 2023JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn this study, we performed scanning transmission X-ray microscopy with a spatial resolution of approximately 50 nm to investigate the two-dimensional mapping of the chemical states of carbon in Fe–C alloy. The lamellar texture (pearlite) consisting of ferrite (α-Fe) and θ-Fe3C with an interval of approximately 100 nm was identified by absorption from the carbon 1s→2p excitation in the X-ray absorption image. It was clearly observed that there exist more than two types of chemical states of carbon in θ-Fe3C depending on the microtextures. The differences in chemical states were found between grained θ-Fe3C and lamellar θ-Fe3C in pearlite, which might have originated from the texture and morphology of the θ-Fe3C. To consider the origins of the differences, we performed first-principles calculations by assuming the distortion and crystal anisotropy of the unit cell of the θ-Fe3C structure. The results suggest that the anisotropy of the crystal structure of θ-Fe3C and the lattice strain within lamellar θ-Fe3C fail to explain the differences, and therefore, other factors should be considered.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2796K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2796K) Full view HTML
-
Koharu Nishio, Ryo Matsumoto, Hiroshi Utsunomiya, Kosuke Hayashi, Yasu ...Article type: Regular Article
2023Volume 109Issue 9 Pages 747-752
Published: September 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 31, 2023
Advance online publication: May 31, 2023JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn hot rolling process of low carbon steel sheets, oxide scale formed on the sheets may result in surface defects on the rolled products. The major phase of the scale is wustite FeO, which shows sufficient plasticity to follow the sheet deformation only at elevated temperature. However, thick scale is cracked, fragmented and indented to the sheets by the rolling even at elevated temperature because scale surface is instantly cooled by cold rolls to brittle temperature. Therefore, thick scale should be removed by descalers just before the rolling. It is reported that manganese decreases the eutectoid temperature between ductile wustite and brittle magnetite. Therefore, manganese may have a positive effect to widen wustite window to lower temperature and to suppress surface defects. In this study, 0 mass% and 2 mass% manganese bearing steel sheets with controlled scale on surface were hot rolled in a laboratory. The sheets were reduced 30% in thickness by unlubricated rolling at temperature between 1173 K and 1373 K. Scanning electron microscopy on longitudinal section showed that manganese decreases crack depth and increases spacing between scales indented to the steel. It is concluded manganese makes the scale on steel more ductile and suppresses surface defects.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1412K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1412K) Full view HTML
-
Hirokazu Kobayashi, Gentaro Takeda, Kenji Katoh, Tatsuro WakimotoArticle type: Regular Article
2023Volume 109Issue 9 Pages 753-760
Published: September 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 31, 2023
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn the gas wiping process for hot-dip galvanizing, the coating thickness has two thinning limits. The first is the limit due to splashing of the molten zinc liquid film, and the second is the thinning limit of the wiping capacity of the equipment.
In this study, we investigated the possibility that wiping efficiency is reduced by the effect of zinc solidification due to gas jet cooling by conducting a gas wiping experiment under various temperature conditions.
A galvanized steel strip with a width of 100 mm was immersed in a molten zinc bath in the air atmosphere. The steel strip was heated by induction heating or a gas burner, and the wiping gas was also heated.
The results clarified the fact that high temperature conditions improved gas wiping efficiency. It is suggested that high wiping efficiency is prevented by an increase in viscosity due to an increasing solid volume fraction in the liquid zinc film surface caused by microscopic solidification. In addition, it was also found that the development of the initial alloy layer reduced the liquid phase and prevented wiping.
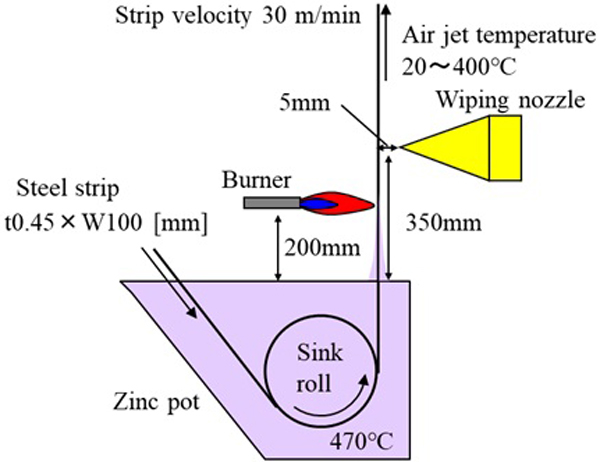 View full abstractDownload PDF (2016K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2016K) Full view HTML -
Ryotaro Miyoshi, Genki TsukamotoArticle type: Regular Article
2023Volume 109Issue 9 Pages 761-769
Published: September 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 31, 2023
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTo investigate the factor that cause the variation in friction coefficient by sliding conditions in commercially pure titanium coated titanium oxide film, in-situ observation of sliding interface during ball on block test and EBSD analysis of a sliding cross-section were performed. At the vertical load of 0.1 N, the friction coefficient stabilized at a low level of approximately 0.12. However, at 0.5 N, the friction coefficient varying widely in the range of 0.20–0.80. At 2.0 and 4.0 N, the friction coefficient stabilized at a high level, approximately 0.30 and 0.40, respectively. At the vertical load of 0.5 N, the friction coefficient was negatively correlated to the Taylor factor for the uniaxial compression of the titanium grains directly beneath the film . Thus, it can be presumed that the ploughing term of friction coefficient increased due to the enhancement of compressive strain of titanium. On the other hands, at vertical loads of 2.0 and 4.0 N, the ball is always in contact with multiple grains due to the larger contact area. As a result, it is considered that the influence of Taylor factor was equalized and the variation of friction coefficient got smaller.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (4905K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (4905K) Full view HTML
-
Yutaro Suzuki, Toshio Ogawa, Fei Sun, Yoshitaka Adachi, Atsushi Yamagu ...Article type: Regular Article
2023Volume 109Issue 9 Pages 770-778
Published: September 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 31, 2023
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLWe analyzed the crystal orientation of pure iron with two-way cold-rolling and subsequent annealing. As-received pure iron sheets were cold-rolled in the vertical direction against the cold-rolling direction of the as-received sheet, and then in the cold-rolling direction of the as-received sheet. The cold-rolled specimens were annealed in two conditions (short-term and long-term annealing). As short-term annealing, cold-rolled specimen was heated to desired temperature, and then water-quenched to room temperature (298 ± 2 K). As long-term annealing, cold-rolled specimen was heated to 1123 K and held for up to 180 min, and then furnace-cooled for up to 150 min and water-quenched to room temperature. The strain distribution of cold-rolled specimen was uniform, and Goss orientation grains were observed at the interface of α-fiber and γ-fiber and within the micro-shear bands in γ-fiber. By short-term annealing, Goss orientation grains within micro-shear bands grew, whereas those at the interface of α-fiber and γ-fiber disappeared. Abnormal grain growth of Goss orientation grains was attributed to the existence of grains having Σ9 grain boundaries against Goss orientation grains. In addition, existence of multiple adjacent Goss orientation grains played crucial role on the abnormal grain growth of Goss orientation grains.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (13484K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (13484K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|