
- Issue 16 Pages 1251-
- Issue 15 Pages 1165-
- Issue 14 Pages 1033-
- Issue 13 Pages 989-
- Issue 12 Pages 899-
- Issue 11 Pages 795-
- Issue 10 Pages 721-
- Issue 9 Pages 653-
- Issue 8 Pages 569-
- Issue 7 Pages 513-
- Issue 6 Pages 427-
- Issue 5 Pages 395-
- Issue 4 Pages 343-
- Issue 3 Pages 89-
- Issue 2 Pages 35-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
- Issue 16 Pages 2157-
- Issue 15 Pages 1805-
- Issue 14 Pages 1613-
- Issue 13 Pages S1141-
- Issue 12 Pages S1037-
- Issue 11 Pages 1443-
- Issue 10 Pages 1273-
- Issue 9 Pages 1077-
- Issue 8 Pages 917-
- Issue 7 Pages 751-
- Issue 6 Pages 585-
- Issue 5 Pages S389-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 403-
- Issue 2 Pages 233-
- Issue 1 Pages 19-
- Issue 16 Pages 2153-
- Issue 15 Pages 1977-
- Issue 14 Pages 1813-
- Issue 13 Pages S1285-
- Issue 12 Pages S1043-
- Issue 11 Pages 1667-
- Issue 10 Pages 1481-
- Issue 9 Pages 1231-
- Issue 8 Pages 891-
- Issue 7 Pages 711-
- Issue 6 Pages 538-
- Issue 5 Pages S407-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 347-
- Issue 2 Pages 173-
- Issue 1 Pages 14-
- Issue 16 Pages 1837-
- Issue 15 Pages 1711-
- Issue 14 Pages 1569-
- Issue 13 Pages S1205-
- Issue 12 Pages S1034-
- Issue 11 Pages 1423-
- Issue 10 Pages 1269-
- Issue 9 Pages 1059-
- Issue 8 Pages 925-
- Issue 7 Pages 775-
- Issue 6 Pages 627-
- Issue 5 Pages S287-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 301-
- Issue 2 Pages 147-
- Issue 1 Pages 12-
- Issue 16 Pages 2179-
- Issue 15 Pages 1795-
- Issue 14 Pages 1631-
- Issue 13 Pages S1053-
- Issue 12 Pages S1023-
- Issue 11 Pages 1501-
- Issue 10 Pages 1315-
- Issue 9 Pages 987-
- Issue 8 Pages 767-
- Issue 7 Pages 621-
- Issue 6 Pages 473-
- Issue 5 Pages S305-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 299-
- Issue 2 Pages 151-
- Issue 1 Pages 16-
- Issue 16 Pages 1945-
- Issue 15 Pages 1699-
- Issue 14 Pages 1531-
- Issue 13 Pages S1055-
- Issue 12 Pages S1013-
- Issue 11 Pages 1367-
- Issue 10 Pages 1215-
- Issue 9 Pages 1087-
- Issue 8 Pages 887-
- Issue 7 Pages 721-
- Issue 6 Pages 507-
- Issue 5 Pages S317-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 343-
- Issue 2 Pages 187-
- Issue 1 Pages 17-
- Issue 16 Pages 2405-
- Issue 15 Pages 2067-
- Issue 14 Pages 1865-
- Issue 13 Pages 1675-
- Issue 12 Pages S1055-
- Issue 11 Pages S1015-
- Issue 10 Pages 1479-
- Issue 9 Pages 1129-
- Issue 8 Pages 895-
- Issue 7 Pages 711-
- Issue 6 Pages 545-
- Issue 5 Pages S325-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 369-
- Issue 2 Pages 193-
- Issue 1 Pages 16-
- Issue 16 Pages 2573-
- Issue 15 Pages 2261-
- Issue 14 Pages 2073-
- Issue 13 Pages S1111-
- Issue 12 Pages S1001-
- Issue 11 Pages 1867-
- Issue 10 Pages 1657-
- Issue 9 Pages 1409-
- Issue 8 Pages 1043-
- Issue 7 Pages 841-
- Issue 6 Pages 649-
- Issue 5 Pages S415-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 431-
- Issue 2 Pages 225-
- Issue 1 Pages 3-
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2018Volume 104Issue 1 Pages Cover-
Published: January 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: January 17, 2018
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (662K) -
2018Volume 104Issue 1 Pages Contents-
Published: January 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: January 17, 2018
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (169K) -
2018Volume 104Issue 1 Pages Editorial-
Published: January 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: January 17, 2018
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (229K)
-
Akihiro Matsuzawa, Katsuhiro Sasai, Hiroshi Harada, Mitsuhiro Numata2018Volume 104Issue 1 Pages 1-10
Published: 2018
Released on J-STAGE: December 31, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLFor improvement of property of steel, lower sulfur concentration is required. Therefore, improvement of desulfurization efficiency is important at desulfurization treatment in the secondary refining process. Powder blasting is often operated for desulfurization in RH process. In this study, effects of velocity of a particle on penetration and flotation behavior were examined by water model experiment under the reduced pressure. A poly-propylene particle was blasted onto water surface with Ar gas through a single-hole nozzle, and particle behavior during penetration into water and flotation to water surface was recorded by a high-speed camera. According to penetration of a particle, an air column was generated and a residual bubble was remained on the particle after rupture of the air column. In case that particle velocity before penetration was low, detention time of a particle increases with increasing of maximum penetration depth. Besides, in case that particle velocity before penetration was high, detention time did not increase so much with increasing of maximum penetration depth because diameter of residual bubble was larger than 2 mm and buoyancy became large. Therefore, increasing particle velocity before penetration does not archive increasing detention time of the particle. To avoid generating residual bubble, a particle should be penetrated with the velocity that an air column is not generated. In addition, flotation behavior of a particle was analyzed by kinetic equation. As a result, in case that diameter of residual bubble is larger than 2 mm, apparent resistance coefficient increases with diameter of a residual bubble.
View full abstractDownload PDF (4691K) Full view HTML
-
Hiroaki Ono, Akihiro Ogawa, Takahiro Yamasaki, Takahiro Koshihara, Tos ...2018Volume 104Issue 1 Pages 11-17
Published: 2018
Released on J-STAGE: December 31, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn optical surface inspection of steel products under hot conditions, overdetection caused by signals from harmless features such as scale and surface texture is usually a problem. Therefore, the authors proposed a new inspection technique called the “twin-illumination and subtraction technique,” which is able to remove only harmless signals, based on the finding that most harmful defects on these products have concave shapes, whereas most harmless features that might be overdetected have flat or convex shapes. As an application of this technique, after laboratory tests to confirm its effectiveness, we set up a prototype system for hot pipes which have poor surface properties. Although harmless signals from flat surfaces could be removed as expected, harmless signals from convex surfaces such as peeling scale and micro-surfaces which cause specular reflection conditions remained in addition to harmful signals from concave defects. To improve detectability, we introduced a discrimination method based on the characteristic bright/dark patterns of concave defects, a detection and decision tree judgment function using features from images and so on. At present, the installed prototype system presents information concerning detected defects to operators. As a result, we have confirmed that the system has sufficient performance for prevention of large outbreaks of nonconforming products and is an effective technique for detection of poor surface condition.
View full abstractDownload PDF (2184K) Full view HTML -
Kazuhiro Nakatsuji2018Volume 104Issue 1 Pages 18-26
Published: 2018
Released on J-STAGE: December 31, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe reduction of molten steel temperature from the tapping to the casting is crucial for energy conservation in the steel making process. The one of the reasons that the steel temperature reduction is the heat transfer from molten steel to ladle. After the end of casting, the ladle is empty and its temperature continues to drop until next assignment to the appropriate tapping which is scheduled in advance. Therefore, it is important to schedule the ladle assignment plan with taking account into shorten the ladle empty time. The goal of this study is development of the algorithm which can calculate the optimal plan satisfied the several complex operational constraints. We developed the algorithm based on the breadth-first search algorithm. It has features to search the wide range of solution space while limiting search space in order to search optimal solution efficiently. This algorithm is simplified to treat the change and addition of operational constraint flexibly. As the result of test using actual data, this algorithm could calculate the plans satisfied all the constraints while the representative optimization methods, which are using genetic algorithm and mixed integer liner programming, couldn’t. Furthermore, the result shows 20% reduction of the ladle empty time compared with the conventional result scheduled by operator.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1609K) Full view HTML
-
Hiroshi Okano, Shusaku Takagi2018Volume 104Issue 1 Pages 27-35
Published: 2018
Released on J-STAGE: December 31, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThere are risks of hydrogen embrittlement in ultra-high strength steels. We need to clarify the mechanism of hydrogen embrittlement and to develop steels which have superior hydrogen embrittlement resistance. Hydrogen is trapped at various trapping sites in steels. The influence of hydrogen on hydrogen embrittlement depends on the hydrogen trapping sites. Therefore, it is important to identify the kinds of hydrogen trapping sites in steels. The purpose of this study is to identify the hydrogen trapping sites in ultra-high strength steel sheets. 1180 MPa grade dual-phase steel was used. Various strain were applied to the samples by rolling, which was followed by cathodic electrolytic hydrogen charging. Hydrogen desorption rate was measured from –50 ºC using a Thermal Desorption Analysis device (TDA), which enables evaluation of each hydrogen trapping site. The TDA results were analyzed with using Gaussian function to identify each hydrogen trapping site. Four types of hydrogen trapping sites were identified in the DP steel. Hydrogen desorption peak appeared at 35°C was assigned to dislocations, peak appeared at 54°C was assigned to carbide in the martensite structure of the DP steel, Peak at 75°C was assigned to various boundaries in martensite and ferrite-martensite interface in the DP steel, and Peak at 110°C was assigned to a vacancy cluster.
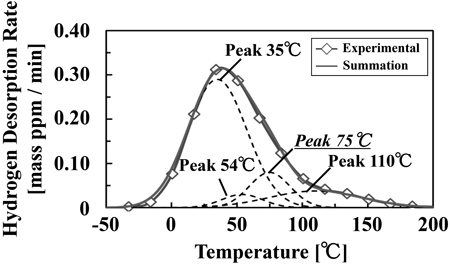 Comparison of hydrogen desorption curves between an experimental result and a calculated result using Gaussian function in the DP steel with strain of 0.26. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1906K) Full view HTML
Comparison of hydrogen desorption curves between an experimental result and a calculated result using Gaussian function in the DP steel with strain of 0.26. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1906K) Full view HTML
-
Ryosuke Konno, Toshiyuki Manabe, Daisuke Hirakami, Kenichi Takai2018Volume 104Issue 1 Pages 36-45
Published: 2018
Released on J-STAGE: December 31, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLFactors causing hydrogen embrittlement of cold-drawn pearlitic steel fractured in plastic/elastic region have been investigated from the viewpoint of lattice defects. Tensile tests were conducted for hydrogen-charged specimens containing 1.5 and 4.0 ppm hydrogen under various crosshead speeds. The amount of tracer hydrogen which corresponds to the amount of lattice defects in the specimens subjected to plastic strain or elastic stress was measured using a thermal desorption analysis. As a result, specimens containing 1.5 ppm hydrogen fractured in the plastic region under all experimental conditions in the present study. In contrast, specimens containing 4.0 ppm hydrogen fractured in the elastic region at crosshead speed of 0.01 mm·min–1 or less and fractured in the plastic region at 0.1 mm·min–1 or more. Subjecting plastic strain in the presence of hydrogen increased the amount of lattice defects corresponding to vacancies. In contrast, the presence of hydrogen had no effects on the formation of lattice defects under subjecting elastic stress. The amount of lattice defects in the specimens fractured in plastic region with hydrogen was equivalent to that of lattice defects in the specimens fractured under same conditions without hydrogen. The amount of lattice defects in the specimens fractured in elastic region with hydrogen was less than that of lattice defects in the specimens fractured under same conditions without hydrogen. These results indicated that lattice defects enhanced by hydrogen affected the fracture in plastic region with hydrogen. However, the effects of lattice defects on the fracture in elastic region with hydrogen were small.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1593K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1593K) Full view HTML -
Daisuke Sasaki, Motomichi Koyama, Hiroshi Noguchi2018Volume 104Issue 1 Pages 46-53
Published: 2018
Released on J-STAGE: December 31, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn order to clarify influence of stress re-distribution effect on hydrogen-induced fatigue crack propagation, we investigated fatigue crack propagation rates and brittle-like fracture ratio. The experiments were conducted in nitrogen and hydrogen gas atmosphere with ferrite-pearlite steels having different pearlite ratio, respectively. The crack propagation rates and the brittle-like fracture ratio decreased as pearlite ratio increased. To explain the changes of crack propagation rates and fracture ratio, we proposed that the stress re-distribution effect causing stress and strain relaxation at a crack tip contributes to suppression of the hydrogen-induced fatigue crack propagation. As a verification, finite element methods were operated with models having different width of the hard phase and different distance between a crack tip and a hard phase in plane stress and strain conditions, respectively. The finite element method analysis showed that stress re-distribution effect was smaller in plane strain condition than that in plane stress condition, indicating that a large hardness difference is crucial in plane stress condition to suppress the hydrogen-induced fatigue crack propagation.
View full abstractDownload PDF (4703K) Full view HTML -
Kengo Yoshida, Takuma Tsuchimoto2018Volume 104Issue 1 Pages 54-60
Published: 2018
Released on J-STAGE: December 31, 2017
Advance online publication: October 14, 2017JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLConstitutive equations play an important role for improving the accuracy of finite element analysis used in metal forming simulations. Plastic flow behavior of a steel tube is experimentally investigated in the present study. A thin-walled steel tube is subjected to linear and nonlinear loading paths. For the linear loadings, a ratio of the displacement and rotation of a grip is fixed at constant. Experimentally measured plastic flow is well predicted by the associated flow rule based on an anisotropic yield function at least for the linear loadings. In the nonlinear loadings, the specimen is subjected to the uniaxial tension followed by the simultaneous application of the axial load and torsion. The plastic flow directions in the nonlinear loadings do not agree with those for the linear loadings even though the stress states are identical. These experimental trends cannot be reproduced by the associated flow rule. We have found the linear relationship between the direction of plastic strain rate and the direction of strain rate. Therefore, the experimental data indicates that the direction of plastic flow can be represented by the direction of the strain rate as well as the stress state.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1234K) Full view HTML
-
Tomoyuki Chiba, Kazuaki Wagatsuma, Kunio Takada, Kenji Abiko2018Volume 104Issue 1 Pages 61-63
Published: 2018
Released on J-STAGE: December 31, 2017
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe objective of this paper is to suggest a new technique for evaluating an oxygen content of the bulk in a steel sample separated from the amount of the surface-adsorbed and surface-reacted species in inert gas fusion – infrared absorption method. For this purpose, a correspondence between surface areas of the sample and the analytical values was investigated in detail, indicating that there was a linear relationship between them. Contribution of the surface components could be individually determined from the linear regression analysis, giving a true value of the oxygen content in a steel sample. This method is carried out without any modification of the analytical apparatus; it is thus recommended for quantification of oxygen in steel samples with better accuracy.
View full abstractDownload PDF (434K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|