
- Issue 16 Pages 1251-
- Issue 15 Pages 1165-
- Issue 14 Pages 1033-
- Issue 13 Pages 989-
- Issue 12 Pages 899-
- Issue 11 Pages 795-
- Issue 10 Pages 721-
- Issue 9 Pages 653-
- Issue 8 Pages 569-
- Issue 7 Pages 513-
- Issue 6 Pages 427-
- Issue 5 Pages 395-
- Issue 4 Pages 343-
- Issue 3 Pages 89-
- Issue 2 Pages 35-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
- Issue 16 Pages 2157-
- Issue 15 Pages 1805-
- Issue 14 Pages 1613-
- Issue 13 Pages S1141-
- Issue 12 Pages S1037-
- Issue 11 Pages 1443-
- Issue 10 Pages 1273-
- Issue 9 Pages 1077-
- Issue 8 Pages 917-
- Issue 7 Pages 751-
- Issue 6 Pages 585-
- Issue 5 Pages S389-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 403-
- Issue 2 Pages 233-
- Issue 1 Pages 19-
- Issue 16 Pages 2153-
- Issue 15 Pages 1977-
- Issue 14 Pages 1813-
- Issue 13 Pages S1285-
- Issue 12 Pages S1043-
- Issue 11 Pages 1667-
- Issue 10 Pages 1481-
- Issue 9 Pages 1231-
- Issue 8 Pages 891-
- Issue 7 Pages 711-
- Issue 6 Pages 538-
- Issue 5 Pages S407-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 347-
- Issue 2 Pages 173-
- Issue 1 Pages 14-
- Issue 16 Pages 1837-
- Issue 15 Pages 1711-
- Issue 14 Pages 1569-
- Issue 13 Pages S1205-
- Issue 12 Pages S1034-
- Issue 11 Pages 1423-
- Issue 10 Pages 1269-
- Issue 9 Pages 1059-
- Issue 8 Pages 925-
- Issue 7 Pages 775-
- Issue 6 Pages 627-
- Issue 5 Pages S287-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 301-
- Issue 2 Pages 147-
- Issue 1 Pages 12-
- Issue 16 Pages 2179-
- Issue 15 Pages 1795-
- Issue 14 Pages 1631-
- Issue 13 Pages S1053-
- Issue 12 Pages S1023-
- Issue 11 Pages 1501-
- Issue 10 Pages 1315-
- Issue 9 Pages 987-
- Issue 8 Pages 767-
- Issue 7 Pages 621-
- Issue 6 Pages 473-
- Issue 5 Pages S305-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 299-
- Issue 2 Pages 151-
- Issue 1 Pages 16-
- Issue 16 Pages 1945-
- Issue 15 Pages 1699-
- Issue 14 Pages 1531-
- Issue 13 Pages S1055-
- Issue 12 Pages S1013-
- Issue 11 Pages 1367-
- Issue 10 Pages 1215-
- Issue 9 Pages 1087-
- Issue 8 Pages 887-
- Issue 7 Pages 721-
- Issue 6 Pages 507-
- Issue 5 Pages S317-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 343-
- Issue 2 Pages 187-
- Issue 1 Pages 17-
- Issue 16 Pages 2405-
- Issue 15 Pages 2067-
- Issue 14 Pages 1865-
- Issue 13 Pages 1675-
- Issue 12 Pages S1055-
- Issue 11 Pages S1015-
- Issue 10 Pages 1479-
- Issue 9 Pages 1129-
- Issue 8 Pages 895-
- Issue 7 Pages 711-
- Issue 6 Pages 545-
- Issue 5 Pages S325-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 369-
- Issue 2 Pages 193-
- Issue 1 Pages 16-
- Issue 16 Pages 2573-
- Issue 15 Pages 2261-
- Issue 14 Pages 2073-
- Issue 13 Pages S1111-
- Issue 12 Pages S1001-
- Issue 11 Pages 1867-
- Issue 10 Pages 1657-
- Issue 9 Pages 1409-
- Issue 8 Pages 1043-
- Issue 7 Pages 841-
- Issue 6 Pages 649-
- Issue 5 Pages S415-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 431-
- Issue 2 Pages 225-
- Issue 1 Pages 3-
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2019 Volume 105 Issue 6 Pages Cover-
Published: June 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 31, 2019
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (660K) -
2019 Volume 105 Issue 6 Pages Contents-
Published: June 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 31, 2019
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (797K) -
2019 Volume 105 Issue 6 Pages Editorial-
Published: June 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 31, 2019
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (229K)
-
Tatsuro Ariyama2019 Volume 105 Issue 6 Pages 567-586
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 31, 2019
Advance online publication: April 05, 2019JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLGlobal warming has been regarded as a crucial issue in every industry. Since long term global goal was set on the basis of Paris Agreement, a considerable evolution toward CO2 mitigation in 2050 is desired even in steel industry. Until now, many various technology developments were carried out in the ironmaking area; however, the innovative progress beyond the past progressive developments is required to attain the long-term goal in 2050. This review focuses on the current technology development on CO2 mitigation to date and the design of an ambitious ironmaking process for the future. In particular, the directions for low carbon and decarbonization are discussed from the viewpoints of technological aspects and the comprehensive consistency with sustainability in steel industry. Moreover, the perspectives on CCU (CO2 Capture and Utilization) and hydrogen ironmaking process based on the renewable energy aiming for carbon direct avoidance are described.
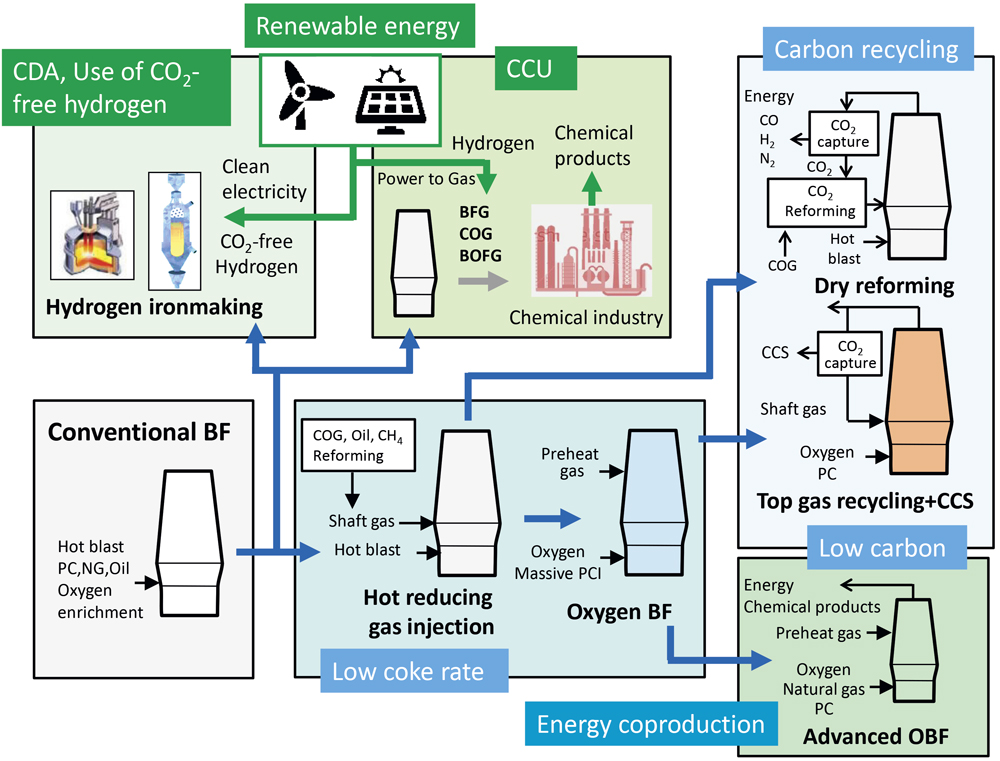 Diversification of ironmaking processes toward CO2 mitigation. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (16581K) Full view HTML
Diversification of ironmaking processes toward CO2 mitigation. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (16581K) Full view HTML
-
Kohei Miwa, Ryota Matsugi, Masakatsu Hasegawa2019 Volume 105 Issue 6 Pages 587-594
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 31, 2019
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn steelmaking processes, there are incentives to reduce slag volume and CaO consumption. The key to meet these requirements is the better understanding of CaO dissolution mechanism into molten slag, which relies on the knowledge of the thermochemical properties of slags and fluxes used for dephosphorization. In this study, the liquidus compositions coexisted with solid CaO and Ca2SiO4-Ca3P2O8 solid solution simultaneously were determined in the quaternary system CaO-SiO2-P2O5-FexO at 1573 K. Measurements were also conducted on the FexO activities at temperatures between 1542 K and 1604 K by virtue of an electrochemical technique. By using the present experimental results, phosphorus distribution ratios were estimated.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1741K) Full view HTML -
Masahito Hanao2019 Volume 105 Issue 6 Pages 595-600
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 31, 2019
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLInterfacial free energy of solid iron was experimentally evaluated for solid/liquid interface and grain boundary of austenite phase in solid Fe/liquid FeO-SiO2 system. Multi-phase equilibrium method was adopted and two kinds of angles such as dihedral angle between solid/liquid interface and grain boundary, and contact angle of sessile drop of molten oxide on solid iron were measured. On the basis of experimental results and literature data of activity of FeO, surface tension of liquid FeO-SiO2 oxide and solid Fe, interfacial tension (interfacial free energy) of solid/liquid interface and grain boundary of γ-Fe were evaluated. Oxygen partial pressure in the experimental atmosphere was evaluated as 1×10–12~10–11 atm. Under this condition, solid/liquid interfacial free energy was evaluated as 1440-1500 mJ/m2 and grain boundary free energy of γ-Fe as 860-940 mJ/m2 at 1350ºC. The evaluated value for the grain boundary was agreed well with the data of previous works.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1805K) Full view HTML
-
Yuki Hata, Hideyuki Hayashizaki, Takafumi Takahashi, Koji Kanehashi2019 Volume 105 Issue 6 Pages 601-609
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 31, 2019
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLUnderstanding chemical structure of primary coal tar is substantially important to promote advanced application and utilization of coal where chemical reaction plays a key role. Mass spectrometry allows us to characterize complex mixture like coal tar pitch, coal extractions, and heavy oil. In the present study, two kinds of primary coal tar A and B were prepared from different types of coal A (bituminous coal) and B (subbituminous coal). The main components such as Hexane Soluble (HS) and Hexane Insoluble-Toluene Soluble (HI-TS) fractions obtained by extraction of each tar were measured by Field Desorption Mass Spectrometry (FD-MS) to determine their constituent chemical structures. 1H NMR spectra of HS and HI-TS were measured to confirm the reliability of proportion of hydrogen types that have been determined by FD-MS. As a result, both of the proportions in HS fractions were found to be almost consistent, while those in HI-TS fractions were not consistent because they have more complex chemical components than HS fractions. Based on the combined analysis of FD-MS and NMR, we concluded that the HS in primary coal tar A mainly consists of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and aliphatic structures including aromatic carbons, while the HS in primary coal tar B mainly consists of aliphatic structures. These results suggest that determining chemical structures and their ratios only from FD-MS spectra is useful to concretely clarify difference between some types of primary coal tar.
 Classification of chemical structures contained HS fractions for primary coal tar A and B. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2036K) Full view HTML
Classification of chemical structures contained HS fractions for primary coal tar A and B. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2036K) Full view HTML
-
Naoki Kikuchi, Akitoshi Matsui, Yu-ichi Uchida2019 Volume 105 Issue 6 Pages 610-618
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 31, 2019
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn order to clarify the effect of the lime dissolution rate in slag on hot metal dephosphorization, a 150 kg scale hot metal dephosphorization experiment was carried out. The rate of decrease of free CaO and the dephosphorization rate were measured while varying the ratio of the CaO and SiO2 which was denoted as basicity.
The dephosphorization rate showed its maximum value at basicity of around 1.0. At basicity higher than 1.0, the dephosphorization rate decreased due to poor dissolution of CaO in the flux.
A thermodynamic calculation revealed that crystallization of 2CaO·SiO2 (-3CaO·P2O5) in the liquid slag deteriorated lime dissolution when basicity was higher than 1.5.
The mass transfer coefficient of CaO in slag was calculated assuming that the interface between the lime and liquid slag is saturated with CaO. High basicity showed a low mass transfer coefficient.
The apparent slag viscosity was calculated in terms of the solid phase, and correlated with the CaO diffusion rate. The CaO diffusion rate in slag decreased with higher values of not only liquid slag viscosity, but also solid-liquid coexistent slag viscosity. These results suggest the existence of an optimum basicity exists for effective CaO dissolution.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1760K) Full view HTML
-
Tetsuro Hidaka, Nao-Aki Noda, Yoshikazu Sano, Nobuhiro Kai, Hiroyoshi ...2019 Volume 105 Issue 6 Pages 619-628
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 31, 2019
Advance online publication: March 14, 2019JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn this study fatigue experiments are conducted for ductile cast iron (DCI) to compare with the fatigue strength of cruciform welded joints. Here, several DCI specimens are prepared to have nearly the same fatigue strength in smooth specimens before welding and to have similar cruciform shapes in the welded joints. It is found that the fatigue strength of DCI specimen is about three times larger than that of the welded joint specimens. The fatigue strength improvement can be explained in terms of the small stress concentration factor, notch insensitivity and compressive residual stress generated by shot blasting for DCI joints.
View full abstractDownload PDF (5164K) Full view HTML
-
Naoki Sakaguchi, Kotaro Ona, Rui Bao, Nobuo Nakada2019 Volume 105 Issue 6 Pages 629-635
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 31, 2019
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLSuper invar cast steel, 32 mass%Ni-5 mass%Co, with an excellent low thermal expansion coefficient exhibits very low Young’s modulus due to a course solidified columnar structure with <100> austenite texture. For the improvement of the low Young’s modulus, a novel heat treatment consisted of subzero treatment and subsequent annealing was applied to stimulate microstructure evolution accompanied with texture variation. Lenticular martensite preferentially formed along a dendrite structure with lower Ni concentration after subzero treatment at liquid nitrogen temperature and then reversed into austenite again by the subsequent annealing above 873 K via diffusionless shear mechanism, that is, martensitic reversion took place. Since the martensitic reversion realizes a crystallographic reversibility, the course columnar structure at initial state was reconstructed after the completion of reversion. Furthermore, the course structure formed via martensitic reversion recrystallized to equiaxed fine-grained structure when the annealing temperature became higher, because high density dislocations in martensitic reversed austenite caused by the invariant lattice deformation on two directional martensitic transformations drives the austenite recrystallization. The recrystallization leads to the formation of fine-grained austenitic structure with random orientation, and as a result, Young’s modulus of super invar cast steel was improved to be as high as the forged one without any plastic deformation process.
 Macroscopic optical microstructure of austenite in (a) as-cast and (b) 1103 K annealed materials. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (4618K) Full view HTML
Macroscopic optical microstructure of austenite in (a) as-cast and (b) 1103 K annealed materials. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (4618K) Full view HTML
-
Makoto Akama, Mamoru Murahashi2019 Volume 105 Issue 6 Pages 636-647
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 31, 2019
Advance online publication: February 14, 2019JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA numerical model was developed to simulate the competition between crack initiation and growth by rolling contact fatigue (RCF) and wear in a railhead. The simulation model assumes that the materials are polycrystalline ferrite and pearlite and that RCF crack initiation is determined by the total accumulated plastic shear strain. The growth of short cracks is calculated using the Hobson model and the Archard model is used to calculate wear. In order to validate the developed model, twin disc rolling-sliding contact fatigue tests were performed. In the tests, rail material and slip ratio were changed and the crack initiation, crack growth and wear trace on the contact surfaces were investigated by SEM, EPMA and shape measuring instrument. Under these test conditions, simulations were performed using the developed model and compared the results. It was confirmed that the crack occurred at the nonmetallic inclusion/ferrite and ferrite/pearlite boundary at almost the same locations, therefore, the assumption of the model for the initiation was validated. It was also found that cracks of almost the same length and the direction existed in the vicinity of the contact surface at the same rolling cycles. Regarding wear, it was found that accurate analyses can be performed by considering the change of the contact pressure distribution and selecting an appropriate wear coefficient.
 Simulation results for the competition between short fatigue crack growth and wear in RF disc (sr=1%). Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (8503K) Full view HTML
Simulation results for the competition between short fatigue crack growth and wear in RF disc (sr=1%). Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (8503K) Full view HTML -
Setsuo Takaki, Takuro Masumura, Toshihiro Tsuchiyama2019 Volume 105 Issue 6 Pages 648-654
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 31, 2019
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn the dislocation characterization using radiation diffraction, the modified Williamson-Hall method gives the parameter α, φ and S, in which the information about crystallite size, dislocation density and screw component of dislocation are contained respectively. On the other hand, the direct-fitting method gives the parameter α, micro-strain ε and the correction parameter ωh00. In this study, the correlation in these parameters was investigated in cold rolled ferritic steel (Fe-0.0056%C). Results obtained are as follows: Almost same values were obtained for the parameter α in both methods. The value of parameter ε increases as the S-value becomes small even under the same dislocation density. At the constant S-value, however, linear relationship was found between ε and φ. Between the parameter S and ωh00, there is an identical relationship expressed by the equation; S=1.16+1.46ωh00–3.71ωh002 regardless of dislocation density. In addition, it was confirmed that there is no large effect of texture on the dislocation characterization by the direct-fitting method and the modified Williamson-Hall method.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1229K) Full view HTML
-
Tetsushi Chida, Makoto Kosaka, Manabu Kubota, Toshimi Tarui, Tomohiko ...2019 Volume 105 Issue 6 Pages 655-663
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 31, 2019
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIt is well-known that pearlitic steel wires have a higher resistance to hydrogen embrittlement than tempered martensitic steels. It is significant to clarify the effect of various mechanisms of the hardening on hydrogen embrittlement for the compatibility between high strength and resistance to hydrogen embrittlement. In this study, effects of drawing strain and aging temperature in pearlitic steel wires on hydrogen embrittlement properties were investigated. Absorbed hydrogen content after cyclic corrosion test (HE) was increased with added drawn strain and saturated with large amounts of drawn strain. Furthermore, the higher the aging temperature, the smaller HE is obtained. The critical diffusible hydrogen content (HC) in pearlitic steel wires aged at 450°C is higher than that aged at 250°C and as-drawn pearlitic steel wires. The reasons are considered to be a decrease in the dislocation density and suppression of crack propagation due to the short length of ferrite-cementite interface. Consequently, the pearlitic steel wires aged at 450°C are excellent in resistance to hydrogen embrittlement because HC is much higher than HE, although the tensile strength of pearlitic steel wires is decreased by aging at 450°C and above.
View full abstractDownload PDF (2277K) Full view HTML
-
Shohei Koizumi, Gao Xu, Shigeru Ueda, Shin-ya Kitamura2019 Volume 105 Issue 6 Pages 664-673
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 31, 2019
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTo recover the degraded paddy field, the efficient supply of Fe, Ca, and Si to the soil water is important. Steelmaking slag was confirmed as a useful fertilizer for paddy growth to supply Ca and Si. In addition, to suppress the H2S generation in paddy soil, supplement of Fe from fertilizer made of slag has been expected.
By our previous research, it was found that Fe was supplied mainly from the CaO-SiO2-FeO glassy phase in slag. However, to design the fertilizer made of slag, the optimum composition of the glassy phase has to be clarified.
In this research, the glassy phases with difference iron valence, basicity, and FeO content were synthesized to investigate the dissolution behavior of Fe in paddy water. The experiment was conducted by the addition of grounded power of the synthesized phase into water which kept pH at 5 by adding HNO3 to simulate the initial stage after irrigation of paddy fields. The dissolved amount of each element in water was analyzed by ICP-AES. The result showed that the dissolution ratio of Fe increased by increasing the ratio of Fe2+/T-Fe and the FeO content in the glassy oxides, and showed local maximum by the increase in CaO/SiO2 ratio at 0.67.
View full abstractDownload PDF (3864K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|