
- Issue 16 Pages 995-
- Issue 15 Pages 907-
- Issue 14 Pages 879-
- Issue 13 Pages 803-
- Issue 12 Pages 647-
- Issue 11 Pages 593-
- Issue 10 Pages 551-
- Issue 9 Pages 425-
- Issue 8 Pages 379-
- Issue 7 Pages 355-
- Issue 6 Pages 273-
- Issue 5 Pages 231-
- Issue 4 Pages 187-
- Issue 3 Pages 63-
- Issue 2 Pages 21-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
- Issue 16 Pages 1251-
- Issue 15 Pages 1165-
- Issue 14 Pages 1033-
- Issue 13 Pages 989-
- Issue 12 Pages 899-
- Issue 11 Pages 795-
- Issue 10 Pages 721-
- Issue 9 Pages 653-
- Issue 8 Pages 569-
- Issue 7 Pages 513-
- Issue 6 Pages 427-
- Issue 5 Pages 395-
- Issue 4 Pages 343-
- Issue 3 Pages 89-
- Issue 2 Pages 35-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
- Issue 16 Pages 2157-
- Issue 15 Pages 1805-
- Issue 14 Pages 1613-
- Issue 13 Pages S1141-
- Issue 12 Pages S1037-
- Issue 11 Pages 1443-
- Issue 10 Pages 1273-
- Issue 9 Pages 1077-
- Issue 8 Pages 917-
- Issue 7 Pages 751-
- Issue 6 Pages 585-
- Issue 5 Pages S389-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 403-
- Issue 2 Pages 233-
- Issue 1 Pages 19-
- Issue 16 Pages 2153-
- Issue 15 Pages 1977-
- Issue 14 Pages 1813-
- Issue 13 Pages S1285-
- Issue 12 Pages S1043-
- Issue 11 Pages 1667-
- Issue 10 Pages 1481-
- Issue 9 Pages 1231-
- Issue 8 Pages 891-
- Issue 7 Pages 711-
- Issue 6 Pages 538-
- Issue 5 Pages S407-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 347-
- Issue 2 Pages 173-
- Issue 1 Pages 14-
- Issue 16 Pages 1837-
- Issue 15 Pages 1711-
- Issue 14 Pages 1569-
- Issue 13 Pages S1205-
- Issue 12 Pages S1034-
- Issue 11 Pages 1423-
- Issue 10 Pages 1269-
- Issue 9 Pages 1059-
- Issue 8 Pages 925-
- Issue 7 Pages 775-
- Issue 6 Pages 627-
- Issue 5 Pages S287-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 301-
- Issue 2 Pages 147-
- Issue 1 Pages 12-
- Issue 16 Pages 2179-
- Issue 15 Pages 1795-
- Issue 14 Pages 1631-
- Issue 13 Pages S1053-
- Issue 12 Pages S1023-
- Issue 11 Pages 1501-
- Issue 10 Pages 1315-
- Issue 9 Pages 987-
- Issue 8 Pages 767-
- Issue 7 Pages 621-
- Issue 6 Pages 473-
- Issue 5 Pages S305-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 299-
- Issue 2 Pages 151-
- Issue 1 Pages 16-
- Issue 16 Pages 1945-
- Issue 15 Pages 1699-
- Issue 14 Pages 1531-
- Issue 13 Pages S1055-
- Issue 12 Pages S1013-
- Issue 11 Pages 1367-
- Issue 10 Pages 1215-
- Issue 9 Pages 1087-
- Issue 8 Pages 887-
- Issue 7 Pages 721-
- Issue 6 Pages 507-
- Issue 5 Pages S317-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 343-
- Issue 2 Pages 187-
- Issue 1 Pages 17-
- Issue 16 Pages 2405-
- Issue 15 Pages 2067-
- Issue 14 Pages 1865-
- Issue 13 Pages 1675-
- Issue 12 Pages S1055-
- Issue 11 Pages S1015-
- Issue 10 Pages 1479-
- Issue 9 Pages 1129-
- Issue 8 Pages 895-
- Issue 7 Pages 711-
- Issue 6 Pages 545-
- Issue 5 Pages S325-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 369-
- Issue 2 Pages 193-
- Issue 1 Pages 16-
- Issue 16 Pages 2573-
- Issue 15 Pages 2261-
- Issue 14 Pages 2073-
- Issue 13 Pages S1111-
- Issue 12 Pages S1001-
- Issue 11 Pages 1867-
- Issue 10 Pages 1657-
- Issue 9 Pages 1409-
- Issue 8 Pages 1043-
- Issue 7 Pages 841-
- Issue 6 Pages 649-
- Issue 5 Pages S415-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 431-
- Issue 2 Pages 225-
- Issue 1 Pages 3-
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2024Volume 110Issue 7 Pages Contents-
Published: May 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (2073K) -
2024Volume 110Issue 7 Pages Editorial-
Published: May 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (206K)
-
Koga Hori, Kengo Kato, Hideki OnoArticle type: Regular Article
2024Volume 110Issue 7 Pages 513-521
Published: May 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
Advance online publication: February 23, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIncreasing the utilization of steel scrap is strongly required for reducing CO2 emission in iron- and steel-making processes. In steel scrap recycling, the content of tramp elements in steel (such as copper and tin) inevitably increases. Accordingly, it is important to understand the thermodynamic characteristics of relevance to the accumulation of tramp elements in molten steel. The values of the interaction coefficients of Mo, B, Ni, Ti, and Nb with Sn in molten iron were reported previously. However, little is known about the interaction coefficients of alloying elements with tramp elements in molten high-chromium steel. In this work, the interaction coefficients of Mo, B, Ni, Ti, and Nb with Sn in the molten Fe–18mass%Cr alloy were measured at 1873 K by a chemical equilibration technique that uses the liquid immiscibility of the Fe–18mass%Cr alloy and Ag, yielding the following results:
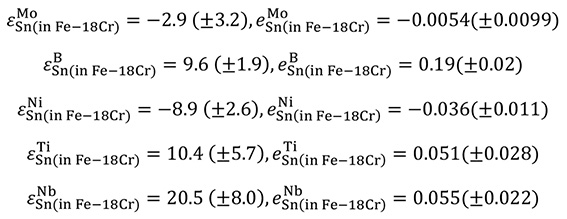
The results show that the values of the interaction coefficients of M with Sn in the Fe–18mass%Cr alloy are smaller than those for molten iron, which were measured in the previous work, except for titanium. The interaction coefficients of M with Sn in Fe and Fe–18mass%Cr alloy were estimated based on a regular solution model. The estimated interaction coefficients of B, Ni, and Ti with Sn in molten iron and Ni and Ti with Sn in the molten Fe–18mass%Cr alloy reasonably agree with the measured values.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (3431K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (3431K) Full view HTML
-
Yuki Tanaka, Ryohei Nishino, Kazunori Kamimiyada, Kohei Morishita, Hir ...Article type: Regular Article
2024Volume 110Issue 7 Pages 522-531
Published: May 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
Advance online publication: March 20, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLEffect of copper on solidification microstructure and solidification process were investigated for high carbon high speed steel type alloys (Fe-2.0%C-5%Cr-5%Mo-5%V-0~7.5%Cu in mass%). The microstructure of all as-cast specimens with different copper content is dendrite consisting mainly of primary γ, MC-γ eutectic and M2C-γ eutectic. In the copper-free specimen, the shape of dendrite is granular (or equiaxed), while in the copper added specimens, it is columnar, and the columnarization trend become more pronounced with increasing the amount of copper content. Furthermore, the secondary dendrite arm spacing decreased with increasing amount of copper content. The volume fraction of primary γ dendrite gradually decrease and MC-γ eutectic gradually increase with increasing of the amount of copper content. While the volume fraction of M2C-γ eutectic is approximately constant regardless of the amount of copper content. The concentrations of chromium, molybdenum and vanadium within microstructure were approximately constant regardless of the amount of copper content in any microstructures. While the concentration of copper within microstructure was higher in order of dendrite, MC-γ eutectic and M2C-γ eutectic compared with any copper content, and its order corresponds to the solidification prosses. These results suggest that copper tends to remain in the solid phase (that is dendrite) rather than redistribute to the liquid phase during solidification.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (5306K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (5306K) Full view HTML
-
Takeru Hashiguchi, Kenji MatsudaArticle type: Regular Article
2024Volume 110Issue 7 Pages 532-540
Published: May 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
Advance online publication: March 19, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLFor manufacturers, rapid and accurate quality control of materials and products in the field is essential for improving competitiveness. Rebound hardness testing is one of the fundamental material tests expected to meet this requirement. However, it has been known that many factors affect rebound hardness which may cause the fluctuation in the measured value. In order to elucidate the effect of the fixing method of the specimen, the coefficient of restitution of a hammer using a Vickers indenter was compared with and without bolting the specimen to the base. The motions of the hammer and the specimen were measured simultaneously using two laser Doppler vibrometers and were also numerically analyzed using an elastoplastic finite element method. It has been clarified that, in the case of without bolting, the restitution coefficient is decreased compared to with bolting. The decreasing tendency becomes larger as the impact point moves away from the specimen center. The rebounding behaviors of the hammer and the specimen without bolting can be reproduced with a numerical model in which an appropriate elastic film is inserted between the specimen and the base. The numerical results show that the hammer impact causes rigid body motion in the specimen, which consumes hammer energy, resulting in a decrease in the coefficient of restitution. The range in which the coefficient of restitution can change is also evaluated by assuming a simple two-body collision model.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2339K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2339K) Full view HTML
-
Takahiro Kamimoto, Yoshihiro DeguchiArticle type: Regular Article
2024Volume 110Issue 7 Pages 541-547
Published: May 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
Advance online publication: March 12, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn the measurement of iron and steel processes, the measurement of temperature concentration distribution is very important for the analysis and control of in-furnace phenomena in order to obtain in-furnace information. However, thermocouples and gas sampling methods are used, but since they are contact and point measurements, they disturb the measurement field, require modification of equipment and piping, have low time response (10 Hz), and are affected in accuracy (20% or more) by environmental fluctuations. This report describes the development of a technology for simultaneous measurement of multiple components such as O2, CO, and CO2 concentrations in a furnace, acquisition of a spectral database necessary for measurement using various calibrators, adjustment of the optical axis when installing a sensor with a large laser beam path length (several tens of meters), and development of a technology for adjusting the optical axis by feeding back the laser beam position in real time to prevent optical axis fluctuations during equipment operation. We have developed a technology to adjust the optical axis by feeding back the position of the laser beam in real time when the optical axis fluctuates during the operation of the equipment.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2764K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2764K) Full view HTML
-
Chihiro Hayama, Mariko Kadowaki, Yoshiharu Murase, Hideki Katayama, To ...Article type: Regular Article
2024Volume 110Issue 7 Pages 548-557
Published: May 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
Advance online publication: March 12, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThis paper presents the effect of P addition on the corrosion resistance of steels before and after rust formation. Electrochemical measurements and surface analysis of P-containing steels (Fe-0.5 mass% P, Fe-1.0 mass% P, and Fe-1.5 mass% P) were conducted to analyze the contribution of P to their initial corrosion resistance before rust formation. The results showed that the initial corrosion resistance of the steel was worse with higher P content. According to the surface analysis conducted by SEM/EDS, more P-segregations at grain boundaries existed with higher P content. Based on the results of polarization measurements, it was considered that these P-segregation became the initiation sites of localized corrosion, resulting in the decrease in the initial corrosion resistance.
Although the initial corrosion resistance was worse with higher P content, the long-term corrosion resistance was better with higher P content. According to the results of atmospheric exposure tests at Miyakojima and the surface analysis of rust layers, P was incorporated into the rust layer, and it promoted the protective ability against corrosion.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (7970K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (7970K) Full view HTML
-
Kenta Matsumoto, Takeru Sunada, Yuki Murata, Tomohiro Yoshida, Yuki Mo ...Article type: Regular Article
2024Volume 110Issue 7 Pages 558-567
Published: May 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
Advance online publication: March 08, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialIonic liquids are salts, and their melting points were less than 100 ºC under atmospheric pressure. In particular, ionic liquids, which melting point of them were less than room temperature under atmospheric pressure, have been researched in recent decades. Ionic liquids are well-known to designer’s solvents since configuration of cation and anion are easily to change then specificity is exhibited. In this work, novel protic ionic liquids (PILs) which are applied for CO2 sorption materials have been synthesized using aromatic amine such as alkylpyridine derivatives and N,N-dimethylaniline and bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl) amide due to co-existing proton conductivity and hydrophobicity. Synthesized PILs exhibited hydrophobicity since 1-octanol–water partition coefficients were more than 0. Also, their ionic conductivities were approximately 10−3 S cm−1 at room temperature, and their mechanism of ionic conduction were different one compared with general electrolyte solution due to high viscosities. In addition, several PILs were high selectivity for CO2 sorption compared with N2. Furthermore, PILs gelatinized with bis[4-(1H,1H,2H,2H-tridecafluorooctyl)phenyl] terephthalates due to improvement of mobility. Some of gel–sol transition temperatures of 5 wt% gels were approximately 100 ºC. The driving force of gelation with ionic liquids might be an entropy driven. Sorption selectivity for CO2 and N2 were similar one before and after gelation.
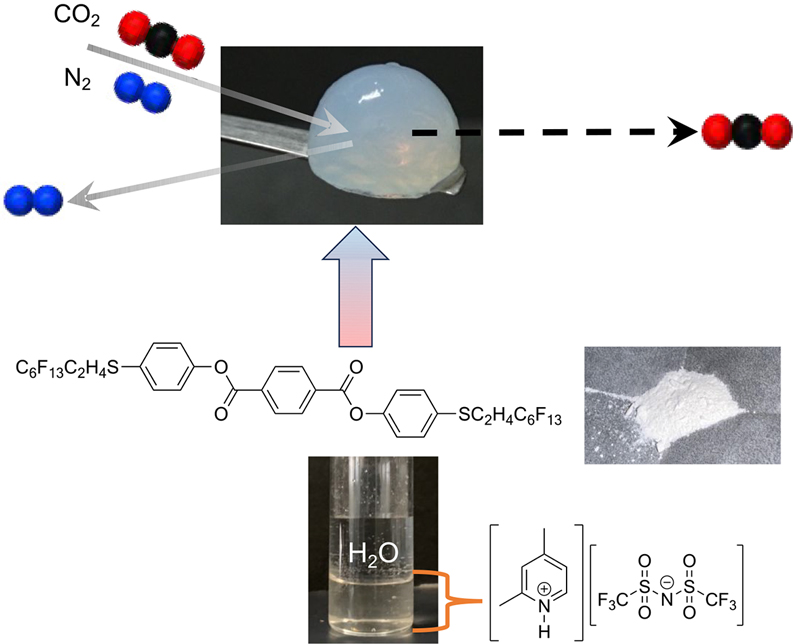 View full abstractDownload PDF (3015K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (3015K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|