
- Issue 16 Pages 2157-
- Issue 15 Pages 1805-
- Issue 14 Pages 1613-
- Issue 13 Pages S1141-
- Issue 12 Pages S1037-
- Issue 11 Pages 1443-
- Issue 10 Pages 1273-
- Issue 9 Pages 1077-
- Issue 8 Pages 917-
- Issue 7 Pages 751-
- Issue 6 Pages 585-
- Issue 5 Pages S389-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 403-
- Issue 2 Pages 233-
- Issue 1 Pages 19-
- Issue 16 Pages 2153-
- Issue 15 Pages 1977-
- Issue 14 Pages 1813-
- Issue 13 Pages S1285-
- Issue 12 Pages S1043-
- Issue 11 Pages 1667-
- Issue 10 Pages 1481-
- Issue 9 Pages 1231-
- Issue 8 Pages 891-
- Issue 7 Pages 711-
- Issue 6 Pages 538-
- Issue 5 Pages S407-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 347-
- Issue 2 Pages 173-
- Issue 1 Pages 14-
- Issue 16 Pages 1837-
- Issue 15 Pages 1711-
- Issue 14 Pages 1569-
- Issue 13 Pages S1205-
- Issue 12 Pages S1034-
- Issue 11 Pages 1423-
- Issue 10 Pages 1269-
- Issue 9 Pages 1059-
- Issue 8 Pages 925-
- Issue 7 Pages 775-
- Issue 6 Pages 627-
- Issue 5 Pages S287-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 301-
- Issue 2 Pages 147-
- Issue 1 Pages 12-
- Issue 16 Pages 2179-
- Issue 15 Pages 1795-
- Issue 14 Pages 1631-
- Issue 13 Pages S1053-
- Issue 12 Pages S1023-
- Issue 11 Pages 1501-
- Issue 10 Pages 1315-
- Issue 9 Pages 987-
- Issue 8 Pages 767-
- Issue 7 Pages 621-
- Issue 6 Pages 473-
- Issue 5 Pages S305-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 299-
- Issue 2 Pages 151-
- Issue 1 Pages 16-
- Issue 16 Pages 1945-
- Issue 15 Pages 1699-
- Issue 14 Pages 1531-
- Issue 13 Pages S1055-
- Issue 12 Pages S1013-
- Issue 11 Pages 1367-
- Issue 10 Pages 1215-
- Issue 9 Pages 1087-
- Issue 8 Pages 887-
- Issue 7 Pages 721-
- Issue 6 Pages 507-
- Issue 5 Pages S317-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 343-
- Issue 2 Pages 187-
- Issue 1 Pages 17-
- Issue 16 Pages 2405-
- Issue 15 Pages 2067-
- Issue 14 Pages 1865-
- Issue 13 Pages 1675-
- Issue 12 Pages S1055-
- Issue 11 Pages S1015-
- Issue 10 Pages 1479-
- Issue 9 Pages 1129-
- Issue 8 Pages 895-
- Issue 7 Pages 711-
- Issue 6 Pages 545-
- Issue 5 Pages S325-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 369-
- Issue 2 Pages 193-
- Issue 1 Pages 16-
- Issue 16 Pages 2573-
- Issue 15 Pages 2261-
- Issue 14 Pages 2073-
- Issue 13 Pages S1111-
- Issue 12 Pages S1001-
- Issue 11 Pages 1867-
- Issue 10 Pages 1657-
- Issue 9 Pages 1409-
- Issue 8 Pages 1043-
- Issue 7 Pages 841-
- Issue 6 Pages 649-
- Issue 5 Pages S415-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 431-
- Issue 2 Pages 225-
- Issue 1 Pages 3-
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2021 Volume 107 Issue 8 Pages Cover-
Published: August 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 31, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (663K) -
2021 Volume 107 Issue 8 Pages Contents-
Published: August 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 31, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (1715K) -
2021 Volume 107 Issue 8 Pages Editorial-
Published: August 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 31, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (254K)
-
Hiroshi Otsuka, Yusuke Dohi, Takashi Matsui, Kazutoshi Hanada2021 Volume 107 Issue 8 Pages 617-623
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 31, 2021
Advance online publication: May 14, 2021JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLCoal fluidity is an important parameter in coal blending techniques for coke making because it strongly influences coke qualities. On the other hand, recently, the amount of high fluidity coal has been limited. To cope with this problem, caking additive method which improves fluidity of coal has been developed and commercialized. However, since tight supply of high fluidity coal is anticipated in the future, it is of great importance to develop more effective caking additive. Therefore, in this study, we investigated effect of 11 kinds of polyaromatic hydrocarbons which include oxygen, sulfur and nitrogen containing compounds on coal fluidity in order to search for more effective chemical substances. The additives were added to low fluidity coal, and fluidity analyses were carried out according to the Gieseler plastometer method. Addition of sulfur and oxygen containing compounds lowered fluidity of coal, whereas addition of aromatic amines enhanced fluidity of coal. Coal fluidity ameliorated with increasing the molecular weight of aromatic amine, and N, N'-di-2-naphthyl-1, 4-phenylenediamine (DNPD) was the most effective aromatic amine in this study. Carbonization tests in an electric furnace were conducted to investigate an effect of DNPD on coke strength. As a result of adding only 1 wt% DNPD, fluidity of blended coal and coke strength (Drum Index) were highly improved.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (929K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (929K) Full view HTML
-
Atsushi Kushimoto, Shuhei Kasahara2021 Volume 107 Issue 8 Pages 624-632
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 31, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLRH water model experiments were carried out in order to evaluate penetrating phenomena of fine particles into liquid. Effects of particle velocity, particle mass flow rate and liquid velocity on deposition of fine particles on liquid surface, and amount of penetrated particle into liquid were investigated. The following results were obtained:
(1) Particle layer was formed on liquid surface and prevented penetration of particles when fine particles were blown.
(2) Weight of particle layer decreased with increase of of particle velocity and liquid velocity, with decrease particle mass flow rate.
(3) Amount of penetrated particle into liquid increased with decrease of weight of particle layer.
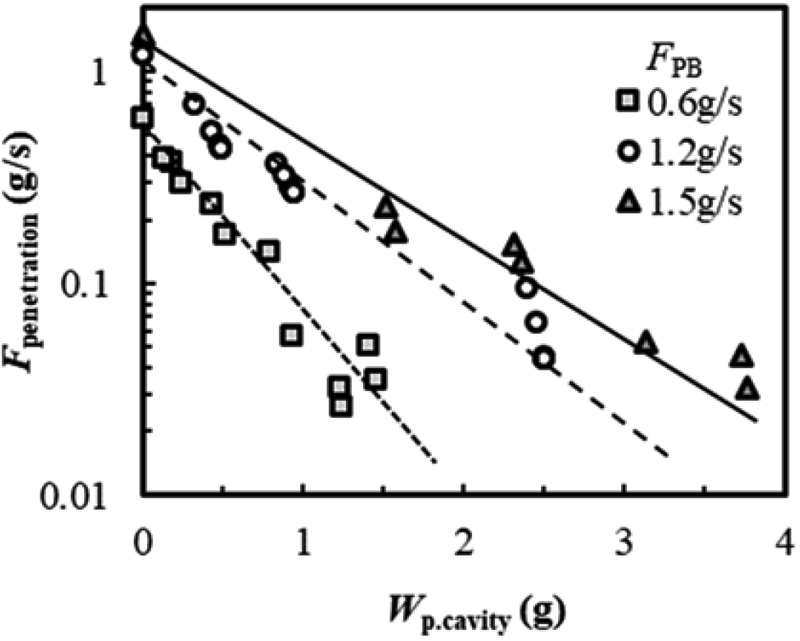 View full abstractDownload PDF (3995K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (3995K) Full view HTML
-
Kohei Shimasaki, Zulhaj Muhammad Aliansyah, Taku Senoo, Idaku Ishii, T ...2021 Volume 107 Issue 8 Pages 633-643
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 31, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn this study, we propose a novel non-contact vision sensing method for wide-area monitoring of operation of conveyors in ironworks by using a panoramic vibration camera in real time. This method can capture magnified images including vibration contribution from single camera with mirror-driven based viewpoint switching. The small vibrations and rotations in multiple pillars and belts were detected using a function of a full-pixel vibration spectrum imaging which can calculate peak frequencies from time frequency responses. Through some experiments of different situation, such as loading and unloading, we evaluate the efficiency of this method which can monitor the operation of multiple rollers and conveyors, when the camera located in 15 m or more away from the conveyors to be monitored.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (11134K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (11134K) Full view HTML
-
Tomoharu Ishida, Katsumi Yamada, Katsuhisa Yamauchi2021 Volume 107 Issue 8 Pages 644-651
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 31, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLFine precipitates in steel have various effects on the properties of steel products. Therefore, it is important to investigate the state of existence of precipitates in steel in order to consider their effect on the material. In this study, the size and shape of Nb and V precipitates were observed by electron microscopy and the amount of precipitation was evaluated by electrolytic extraction analysis in austenitic stainless steels which has excellent heat resistance. For steels with a certain chemical composition, stable nitride (Cr2N) formation was observed when only Nb was added, whereas combined addition of Nb and V suppressed the formation of Cr2N and produced extremely fine precipitates in the steel (in lath martensite). The fine precipitates could be observed in thin film samples by using a high-resolution transmission electron microscope (TEM). In order to evaluate the state of formation of the fine precipitates in the steel quantitatively, the difference in the precipitation behaviors of the two materials was investigated by the size-classified quantitative analysis method. This method is considered to be a useful analytical technique in the development and design of high performance steels using fine nitrides and carbides with sizes of the several nm level.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (4957K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (4957K) Full view HTML
-
Miyuri Kameya, Toshiyuki Manabe, Naoki Matsui, Shingo Yamasaki, Tomohi ...2021 Volume 107 Issue 8 Pages 652-660
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 31, 2021
Advance online publication: May 15, 2021JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLHydrogen absorption behavior and microstructural change of carburized JIS SCr420 steels containing different amounts of retained austenite in rolling contact fatigue were investigated. The thermal desorption analysis confirmed hydrogen desorption at the second-peak between 423 and 623 K after rolling contact fatigue. The hydrogen concentration at the second-peak increased with number of cycles in the rolling contact. This increment was larger when using the steel with a higher amount of retained austenite before the fatigue test. The increment of hydrogen concentration at the second-peak was large even when the introduction of new dislocations due to the martensitic transformation of retained austenite was considered to be small. The activation energies of desorption for the second-peak hydrogen were calculated to be 50.6 kJ·mol−1 for the steel with 10.4% retained austenite and 55.8 kJ·mol−1 for the steel with 4.9% retained austenite. The activation energies of cathodically charged 0.8%C steels with 10.9% and 6.0% retained austenite, simulating carburized layer before the test, were 36.2 and 42.2 kJ·mol−1, respectively. This means that the activation energy of hydrogen desorption increased during rolling contact. The absorbed hydrogen during the rolling contact fatigue was likely trapped in more stable trapping sites related to the retained austenite which were formed under cyclic stress.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2512K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2512K) Full view HTML
-
Shin-ichi Teraoka, Akira Seki2021 Volume 107 Issue 8 Pages 661-671
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 31, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLGrain boundary segregation of Sn in 16.5 mass%Cr-0.15 mass%Ti steel and 16.5 mass%Cr-0.40 mass%Nb steel was investigated along with its toughness effects. Comparing ductile-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) after aging at 973 K for 3.6 ks, the increase in DBTT per 0.1 mass% Sn addition was twice as large for 0.15 mass%Ti steel as for 0.4 mass%Nb steel, and their brittle fracture surfaces were mainly intergranular in 0.15 mass%Ti steel and intragranular in 0.4 mass%Nb steel, respectively. The grain boundary segregation of Sn was also recognized in the 0.4 mass%Nb steel, suggesting that the intergranular embrittlement was suppressed by the intergranular reinforcement of Nb. In 16.5 mass%Cr-0.15 mass%Ti-0.3 mass%Sn-P steels after various aging time and temperature, it was found that the amount of the grain boundary segregation of Sn changed by the precipitation amount of the phosphorous compound and P content, indicating that there is a site competition effect (SC effect) in the grain boundary segregation of Sn and P. The grain boundary segregation energy of Sn estimated from this study was ‐46 kJ/mol, which was similar to the reported value of the carbon steel. As P content increased from 0 to 0.03 mass%, the grain boundary segregation amount of Sn after aging at 773 K for 604.8 ks was decreased from 4.3 at% to the bulk concentration, which is lower than the segregation amount of Sn estimated from the grain boundary segregation energy of P in the carbon steel, suggesting that due to the effect of the Cr content, the grain boundary segregation energy of P decreased by about 1.4-fold compared to the carbon steel.
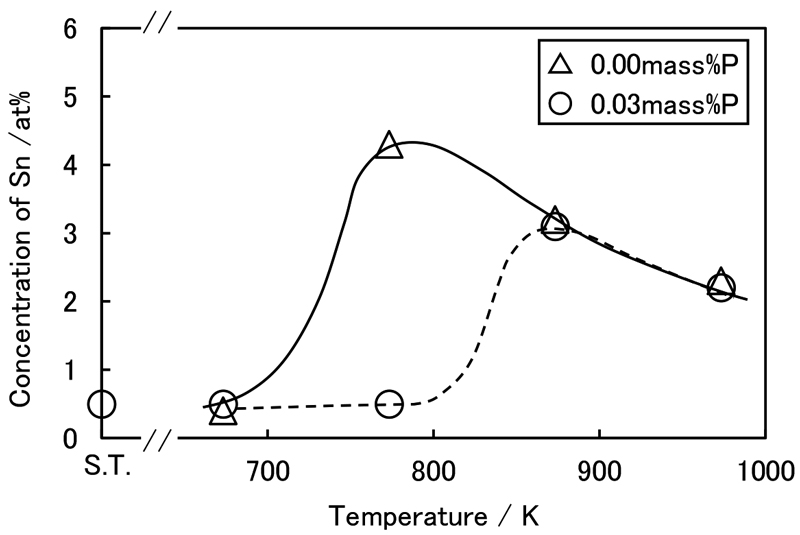 View full abstractDownload PDF (3882K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (3882K) Full view HTML -
Tomohiko Hojo, Junya Kobayashi, Koh-ichi Sugimoto, Yoshito Takemoto, A ...2021 Volume 107 Issue 8 Pages 672-680
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 31, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTo develop ultrahigh-strength steels for automotive impact safety parts, the effects of the microstructure and nitrogen content on the fatigue properties of ultrahigh-strength low alloy transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP)-aided steels with martensite (TM), bainitic ferrite-martensite (TBM), and bainitic ferrite (TBF) matrices were investigated. Compared to TBF steels, both the TM and TBM steels achieved high tensile strength, of more than 980 MPa, and excellent fatigue properties. This results from the suppression of crack propagation due to the effective TRIP of the relatively stable interlath retained austenite and the increase in tensile and yield strengths attributed to the low isothermal transformation treatment. The fatigue strengths of the ultrahigh-strength low alloy TRIP-aided steels were slightly increased by the addition of 100 ppm of nitrogen. The increase in fatigue strength of TM, TBM, and TBF steels with 100 ppm of nitrogen was caused by the fine and uniform martensite and bainitic ferrite matrices and retained austenite, along with the increase in carbon concentration in the retained austenite due to the precipitation of AlN.
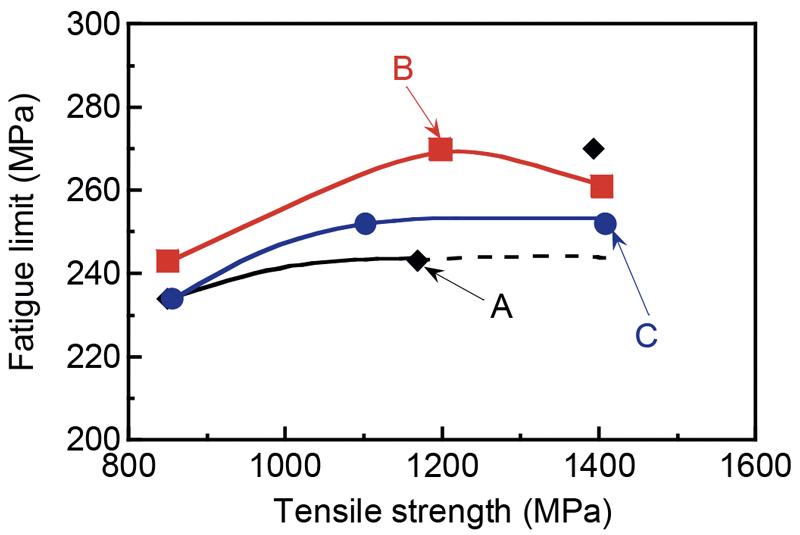 View full abstractDownload PDF (5951K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (5951K) Full view HTML -
Zhipeng Yang, Motomichi Koyama, Hiroshi Fudouzi, Tomohiko Hojo, Eiji A ...2021 Volume 107 Issue 8 Pages 681-686
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 31, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialAn opal photonic crystal film was applied to characterize local strain evolution associated with Lürders band propagation in an annealed low carbon steel. A local change in color of the opal film was observed, which corresponded to the propagation of the Lürders band. In particular, we carried out two tensile experiments for line and area analyses of RGB (Red-Green-Blue) values of the opal films pasted on the specimens. Both of the experiments clearly exhibited a quantitative correspondence between color variation and local strain evolution, namely, the present study demonstrated the potential of the opal films to analyze heterogeneous strain evolution in steels.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2849K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2849K) Full view HTML
-
Setsuo Takaki, Masahiro Tsukahara2021 Volume 107 Issue 8 Pages 687-691
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 31, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn the steels with different particle dispersion, particle dispersion strengthening Δσ was theoretically estimated by Orowan model and Ashby-Orowan model. The comparison of experimental data with theoretical values proved the reasonability of Orowan model rather than Ashby-Orowan model. In Ashby-Orowan model, the line tension coefficient of dislocation is evaluated much smaller and this leads to the under-estimation of Δσ. It was also confirmed that there is no effect of grain size on 0.2% proof stress of the steels used. As a result, it is concluded that the yield stress of steels with finely dispersed particle can be explained by the addition of friction stress and particle dispersion strengthening, in the case the grain size is sufficiently larger than the particle dispersion spacing.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (703K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (703K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|