
- Issue 16 Pages 2157-
- Issue 15 Pages 1805-
- Issue 14 Pages 1613-
- Issue 13 Pages S1141-
- Issue 12 Pages S1037-
- Issue 11 Pages 1443-
- Issue 10 Pages 1273-
- Issue 9 Pages 1077-
- Issue 8 Pages 917-
- Issue 7 Pages 751-
- Issue 6 Pages 585-
- Issue 5 Pages S389-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 403-
- Issue 2 Pages 233-
- Issue 1 Pages 19-
- Issue 16 Pages 2153-
- Issue 15 Pages 1977-
- Issue 14 Pages 1813-
- Issue 13 Pages S1285-
- Issue 12 Pages S1043-
- Issue 11 Pages 1667-
- Issue 10 Pages 1481-
- Issue 9 Pages 1231-
- Issue 8 Pages 891-
- Issue 7 Pages 711-
- Issue 6 Pages 538-
- Issue 5 Pages S407-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 347-
- Issue 2 Pages 173-
- Issue 1 Pages 14-
- Issue 16 Pages 1837-
- Issue 15 Pages 1711-
- Issue 14 Pages 1569-
- Issue 13 Pages S1205-
- Issue 12 Pages S1034-
- Issue 11 Pages 1423-
- Issue 10 Pages 1269-
- Issue 9 Pages 1059-
- Issue 8 Pages 925-
- Issue 7 Pages 775-
- Issue 6 Pages 627-
- Issue 5 Pages S287-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 301-
- Issue 2 Pages 147-
- Issue 1 Pages 12-
- Issue 16 Pages 2179-
- Issue 15 Pages 1795-
- Issue 14 Pages 1631-
- Issue 13 Pages S1053-
- Issue 12 Pages S1023-
- Issue 11 Pages 1501-
- Issue 10 Pages 1315-
- Issue 9 Pages 987-
- Issue 8 Pages 767-
- Issue 7 Pages 621-
- Issue 6 Pages 473-
- Issue 5 Pages S305-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 299-
- Issue 2 Pages 151-
- Issue 1 Pages 16-
- Issue 16 Pages 1945-
- Issue 15 Pages 1699-
- Issue 14 Pages 1531-
- Issue 13 Pages S1055-
- Issue 12 Pages S1013-
- Issue 11 Pages 1367-
- Issue 10 Pages 1215-
- Issue 9 Pages 1087-
- Issue 8 Pages 887-
- Issue 7 Pages 721-
- Issue 6 Pages 507-
- Issue 5 Pages S317-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 343-
- Issue 2 Pages 187-
- Issue 1 Pages 17-
- Issue 16 Pages 2405-
- Issue 15 Pages 2067-
- Issue 14 Pages 1865-
- Issue 13 Pages 1675-
- Issue 12 Pages S1055-
- Issue 11 Pages S1015-
- Issue 10 Pages 1479-
- Issue 9 Pages 1129-
- Issue 8 Pages 895-
- Issue 7 Pages 711-
- Issue 6 Pages 545-
- Issue 5 Pages S325-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 369-
- Issue 2 Pages 193-
- Issue 1 Pages 16-
- Issue 16 Pages 2573-
- Issue 15 Pages 2261-
- Issue 14 Pages 2073-
- Issue 13 Pages S1111-
- Issue 12 Pages S1001-
- Issue 11 Pages 1867-
- Issue 10 Pages 1657-
- Issue 9 Pages 1409-
- Issue 8 Pages 1043-
- Issue 7 Pages 841-
- Issue 6 Pages 649-
- Issue 5 Pages S415-
- Issue 4 Pages S1-
- Issue 3 Pages 431-
- Issue 2 Pages 225-
- Issue 1 Pages 3-
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2019 Volume 105 Issue 5 Pages Cover-
Published: May 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 30, 2019
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (660K) -
2019 Volume 105 Issue 5 Pages Contents-
Published: May 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 30, 2019
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (955K) -
2019 Volume 105 Issue 5 Pages Editorial-
Published: May 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 30, 2019
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (229K)
-
Reiko Murao, Takayuki Harano, Masao Kimura, In-Ho Jung2019 Volume 105 Issue 5 Pages 493-501
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 30, 2019
Advance online publication: January 29, 2019JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe thermodynamic model of a silico-ferrites of calcium and aluminum solution, SFCA phase (Ca2(Fe, Ca)6Oct(Fe, Al, Si)6TetO20) was newly developed in the framework of the Compound Energy Formalism (CEF). Preferred substitution of Al atoms to tetrahedral sites in the SFCA solution was verified by X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) analysis. On considering crystallographic information in particular the short-range-ordering nature in the SFCA solution – the Ca8(Fe3+)20Oct(CaSi6+, FeFe6+, FeAl6+)3Paired(CaSi6+)1Paired(Fe3+, Al3+)20TetO80 structure was considered for modeling the SFCA solution. The optimized Gibbs energies of all end-members can successfully reproduce the experimental single phase region of the SFCA solution.
View full abstractDownload PDF (4255K) Full view HTML
-
Takashi Morohoshi, Masafumi Zeze, Tooru Matsumiya2019 Volume 105 Issue 5 Pages 502-511
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 30, 2019
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe disregistry between β-ZrO2 and γ-Fe is small. In this study, the effect of β-ZrO2 on the nucleation of γ-Fe was investigated by two experiments. First, 20 kg ingots containing 0.75 mass%C with Zr addition or with Al addition were cast and solidification structure was observed. High fraction of equiaxed grain structure was formed in the ingots with Zr addition, but not formed with Al addition. Next, undercooling of 500 g molten steel during cooling was measured. In this experiment a ZrO2 tablet or an Al2O3 tablet was set at the bottom of the crucible. Undercooling with a ZrO2 tablet was smaller than that with an Al2O3 tablet. These two results indicate that β-ZrO2 acts an effective heterogeneous nucleation site for γ-Fe. Interfacial energy differences between liquid Fe and solid γ-Fe both in cases of facing ZrO2 and Al2O3, which are key elements for heterogeneous nucleation capability, were compared and it was found that the difference in the former case is larger than that in the latter case and that chemical contribution is larger in comparison to structural contribution, i.e., lattice misfit energy, in the former case and vice versa in the latter case.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1841K) Full view HTML
-
Tomoyoshi Ogasahara, Takuya Kitamura, Shin-ichiro Aoe, Jun-ichi Tateno ...2019 Volume 105 Issue 5 Pages 512-521
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 30, 2019
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThis paper proposes a dynamic control method of flatness and elongation of the strip in a skin pass mill. In the conventional feedback control, the target values of the flatness and the elongation are fixed. However, the elongation control to the fixed target value is often insufficient to achieve the strip flatness when the work roll deflection is caused by the rolling force manipulation of the elongation control. To improve the flatness control performance, the elongation control in consideration of the flatness is proposed. Periodically, the proposed method solves the optimization problem. The objective function including the control error of the flatness is minimized subject to the constraints such as the range of the elongation, strip thickness and control outputs. In addition, the feedforward control which suppresses the elongation deviations during mill speed change is also proposed. It is difficult to predict accurate rolling force online using a physical model because the computation load is very heavy. The proposed method utilizes the relationship between strain rate and deformation resistance of the strip which is measured offline and the designated rolling force change from the lowest to top rolling speed. This method doesn’t require a physical model and heavy computation load. The proposed method is evaluated by simulation and experiments and the results show that this control method has improved the flatness and the elongation control performance.
View full abstractDownload PDF (3200K) Full view HTML
-
Hiroki Tsuneda, Susumu Imashuku, Kazuaki Wagatsuma2019 Volume 105 Issue 5 Pages 522-529
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 30, 2019
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn steelmaking industry of Japan, one-third steelmaking slag is reused for road constructions. Steelmaking slag contains a few weight percent of calcium oxide, which is termed as free-lime. Free-lime expands its volume by the reactions with water and carbon dioxide, leading to collapse of road substrates. To prevent the road collapse, free-lime in steelmaking slag is now treated to be transformed to Ca(OH)2 and CaCO3 by an aging process; however, the residual free-lime still causes the road collapse. Therefore, it is necessary to detect free-lime in steelmaking slag to safely reutilize it for road constructions. In the present study, we carried out a cathodoluminescence (CL) analysis for identification of free-lime in steelmaking slag. For this purpose, we prepared a synthesized slag sample including free-lime by heating mixtures of reagents. A part of the sample was soaked in water at 70°C for 3 h (aging process). Crystallized free-lime in the sample illuminated orange due to an emission peak of Mn2+ at 600 nm regardless of the precipitation forms of free-lime. Undissolved free-lime illuminated blue due to an emission peak of oxygen vacancy at 460 nm. The sample after the aging process illuminated orange because of CaCO3 having with an emission peak of Mn2+ at 620 nm. We could identify free-lime and CaCO3 by camera detecting light over 680 nm selectively because the luminescence of CaCO3 also appeared on longer wavelength side over 690 nm. Thus, we could detect free-lime in steelmaking slag by capturing CL images within 30 s.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (6130K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (6130K) Full view HTML
-
Kaneharu Okuda, Xiao Xu, Ryosuke Kainuma2019 Volume 105 Issue 5 Pages 530-539
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 30, 2019
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe phase transformation behavior during heating process after various cold-rolling reductions was investigated for Fe - 20% Mn alloy and the phase stabilities of γ and ε phases were discussed. The initial hot-rolled material was composed of ε martensite matrix and a small amount of γ austenite phase at room temperature. The deformation of the martensite alloy in cold rolling was not homogeneous and the microstructure in some regions was clearly inherited from that in the hot rolled sample. Moreover, the residual γ phase was still detected even after 35% cold rolling reduction. In the heating stage, the reverse transformation to the γ phase remarkably started at 200ºC or higher and the reverse transformation finishing temperature obviously rose with rolling reduction ratio. However, it was confirmed by in-situ XRD and EBSD observation that the reverse transformation had already started from the residual γ phase particles even at temperatures below 200 ºC. In addition, from the EBSD-IQ map, distribution of dislocations was considered to remain even in the γ phase after the reverse transformation.
View full abstractDownload PDF (4742K) Full view HTML -
Yoshihiro Suwa, Miho Tomita, Yasuaki Tanaka, Kohsaku Ushioda2019 Volume 105 Issue 5 Pages 540-549
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 30, 2019
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA unified theory for continuous and discontinuous annealing phenomena based on the subgrain growth mechanism was proposed by Humphreys about twenty years ago. With the developments in the unified subgrain growth theory, a number of Monte Carlo, vertex and phase-field (PF) simulations have been performed to investigate the nucleation and growth mechanisms of recrystallization by considering the local alignment of the subgrain structure.
In this study, the effects of the microstructural inhomogeneities created in the deformed state on recrystallization kinetics and texture developments were investigated. Numerical simulations of static recrystallization were performed in 3D polycrystalline structures by coupling the unified subgrain growth theory with PF methodology. In order to prepare the initial microstructures, 2D electron back scattering diffraction (EBSD) measurements were performed on 90% and 99.8% cold-rolled pure iron. Our previous experimental study has shown that the texture formation processes in the recrystallization of those samples have large difference.
In cold-rolled iron with 90% reduction, simulated texture exhibited nucleation and growth of γ-fiber (ND//<111>) grains by consuming α-fiber (RD//<011>) components, where ND and RD denote normal direction and rolling direction respectively. On the other hand, in cold-rolled iron with 99.8% reduction, simulation results reproduced the high stability of the rolling texture during recrystallization. As a consequence, the simulation results were in good agreements with experimentally observed textures in the both samples.
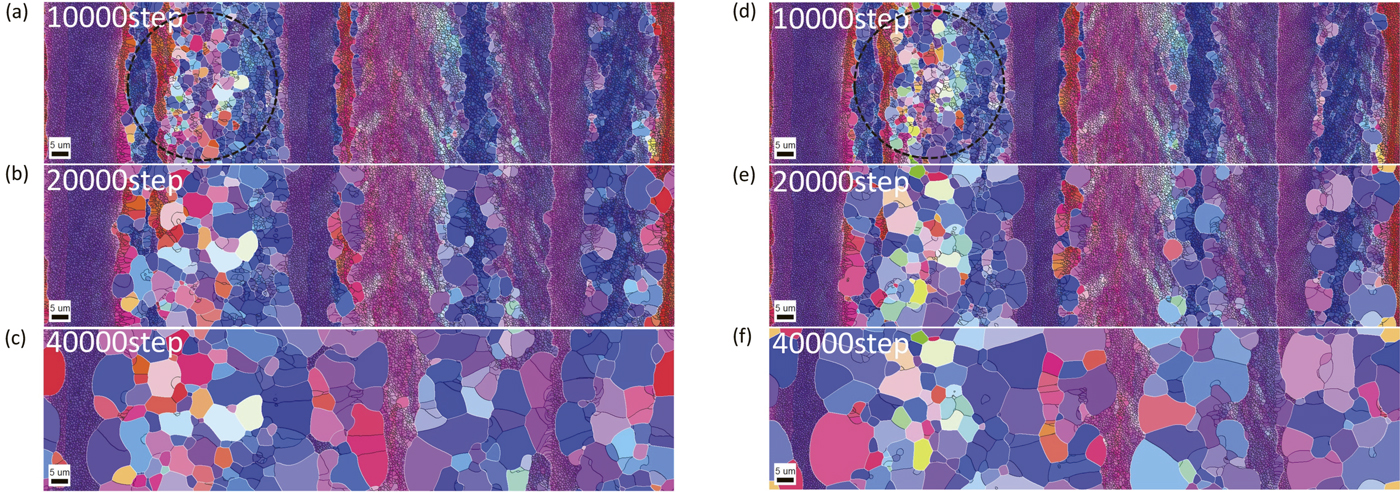 View full abstractDownload PDF (7930K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (7930K) Full view HTML
-
Kohei Kanetani, Tsuyoshi Mikami, Kohsaku Ushioda2019 Volume 105 Issue 5 Pages 550-559
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 30, 2019
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe effect of retained austenite (γR) on rolling contact fatigue (RCF) properties was carefully investigated using carburized SAE4320 steel. We intentionally prepared specimens with four different volume fractions of γR from 6% to 39% controlling subzero heat treatment. The effect of γR on RCF was examined by means of hardness measurement, X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) and Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM). RCF test revealed that sub-surface initiated spalling life is prolonged as volume fraction of γR increases. At the region of the depth z0 where the orthogonal shear stress becomes maximum, γR mostly transformed to martensite, resulting in the significant increase in Vickers hardness. SEM observation showed that the region of initially γR exhibited high resistance to RCF. Moreover, TEM analysis revealed that the initially γR region changed into mixed structure of very fine hard martensite with still remaining γR. This suggests that the transformation of γR to fine hard martensite during RCF contributed to the improvement in RCF life.
View full abstractDownload PDF (4240K) Full view HTML
-
Yoshiyuki Kataoka, Atsushi Morikawa, Yasuko Furunushi, Masahiro Makita ...2019 Volume 105 Issue 5 Pages 560-565
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 30, 2019
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAn accurate quantitative analysis method including total iron had been proposed for the iron ore analysis by wavelength dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometry using fusion method and was accepted at ISO TC 102 meeting in 2010. The project has been proceeded in ISO TC 102/SC 2/WG54 as ISO/WD 9516-2 project. Number of covered elements is 19, and 14 elements among them including total iron are for referee analysis. The calibration discs are prepared only from reagents and the calibration equation includes coexisting component correction, overlap correction, flux/sample and oxidizer/sample mixing ratio corrections. The coexisting component correction method is based on the absorption/enhancement correction coefficients obtained by a FP (fundamental parameter) method so that LOI (loss on ignition) and GOI (gain on ignition) during fusion do not affect to analyzed results. In the verification experiments with 20 certified reference materials, the accuracy obtained by root mean square of the difference between certified values and analyzed values using proposed method was 0.14 mass%, which indicated analytical accuracy could be greatly improved compared with the existing method. For the other components, the values of accuracy obtained were almost same as the existing method. We are conducting final round-robin test in foreign laboratories and have a plan to set the method as an ISO standard.
View full abstractDownload PDF (997K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|