- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1353-1364
Published: October 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2023
Download PDF (594K) Full view HTML
-
 2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1365-1370
2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1365-1370
Published: October 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2023
Editor's pickLinezolid (LZD) has been reported to cause severe hyponatremia, but infection per se is also a potential cause of hyponatremia by increasing vasopressin secretion. The author compared the incidence and risk of developing hyponatremia between LZD and vancomycin (VCM) using propensity score analysis to demonstrate that hyponatremia is associated with LZD rather than infection. The analysis indicated a significantly higher incidence and 3.7-fold higher risk of developing hyponatremia associated with LZD than with VCM, regardless of patient background characteristics. Regularly monitoring serum sodium and infusing sodium promptly when the level decreases would be required when administering LZD.
Download PDF (348K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1371-1384
Published: October 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2023
Advance online publication: August 03, 2023Download PDF (13387K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1385-1393
Published: October 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2023
Download PDF (23732K) Full view HTML -
Acute Inhibition of the Human Kv1.5 Channel by H1 Receptor Antagonist Dimenhydrinate: Mode of Action2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1394-1402
Published: October 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2023
Download PDF (2527K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1403-1411
Published: October 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2023
Download PDF (3076K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1412-1420
Published: October 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2023
Download PDF (3571K) Full view HTML -
 2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1421-1426
2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1421-1426
Published: October 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2023
Editor's pickDespite the fact that liver fibrosis is an intractable disease with a poor prognosis, effective therapeutic agents are not available. The authors focused on bone morphogenetic factor 7 (BMP7) that inhibits TGF-β signaling. They prepared a long-acting albumin-fused BMP7 (HSA-BMP7) and evaluated its inhibitory effect on liver fibrosis. In the mice with bile duct ligation, HSA-BMP7 administration suppressed the infiltration of inflammatory cells and fibrosis area around the bile duct. In the carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis mice, HSA-BMP7 administration also decreased the hepatic fibrosis. HSA-BMP7 has the potential for serving as a therapeutic agent for the treatment of liver fibrosis.
Download PDF (3084K) Full view HTML -
 2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1427-1434
2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1427-1434
Published: October 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2023
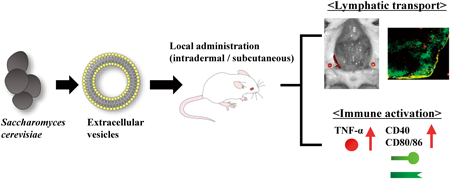
Editor's pickThe yeast strain Saccharomyces cerevisiae is an eukaryotic organism that secrete extracellular vesicles (EVs). The authors characterized the biodistribution of locally (intradermally and subcutaneously) administered Saccharomyces cerevisiae-derived EVs (S-EVs) and the EV-mediated immune responses to evaluate their potential use as biocompatible vaccine adjuvants. Locally administered S-EVs were delivered to the lymph nodes, mainly reaching the B-cell zone. Furthermore, S-EVs increased the expression of cytokine and costimulatory molecules. Especially, subcutaneously injected S-EVs showed potent adjuvanticity, indicating that subcutaneous administration of S-EVs is the desirable approach for achieving effective immune stimulation. These findings will facilitate the development of novel EV-based immunotherapies.
Download PDF (2872K) Full view HTML -
 2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1435-1443
2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1435-1443
Published: October 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2023
Editor's pickOsteoporosis is caused by an imbalance between osteoblast bone formation and osteoclast bone resorption, thus is treated with oral and parenteral bone-resorption inhibitors and parenteral bone-formation promoting drugs. The authors demonstrated that KY-054, a novel coumarin derivative, has osteoblast differentiation-promoting activities in mouse and rat mesenchymal stem cells, increasing metaphyseal and diaphyseal cortical bone volume and bone strength parameters without reducing medullary volume by micro-computed tomography in ovariectomized rats. KY-054 is a potential orally active osteogenic anti-osteoporosis drug candidate with a unique mode of action by acceleration of osteoblast differentiation.
Download PDF (1153K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1444-1450
Published: October 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2023
Download PDF (498K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1451-1460
Published: October 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2023
Download PDF (3675K) Full view HTML -
 2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1461-1467
2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1461-1467
Published: October 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2023
Editor's pickAuthors fabricated 3D-printed contact lenses composed of polyethylene glycol diacrylate and an antibiotic, azithromycin. The drug-loaded contact lenses were prepared using vat photopolymerization 3D printer, and the effect of second curing on 3D printed object was investigated. The mechanical strength and drug release of contact lens formulation were evaluated in the present study. The 3D printed contact lenses exhibited antimicrobial effect in vitro. The current results suggested that the preparation of antibiotic-loaded contact lenses by 3D printing provides useful information for manufacture of ophthalmic device and personalized therapy.
Download PDF (2433K) Full view HTML
-
2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1468-1478
Published: October 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2023
Download PDF (4403K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1479-1483
Published: October 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2023
Download PDF (513K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1484-1489
Published: October 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2023
Advance online publication: August 18, 2023Download PDF (1300K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1490-1493
Published: October 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2023
Download PDF (380K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 10 Pages 1494-1497
Published: October 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2023
Download PDF (552K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|