- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1569-1575
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (2696K) Full view HTML
-
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1576-1580
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (461K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1581-1587
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (2726K) Full view HTML -
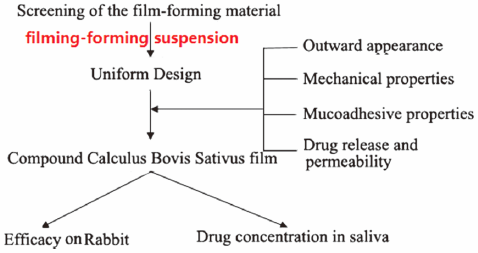
Preparation, in Vitro and in Vivo Evaluations of Compound Calculus Bovis Sativus and Ornidazole Film2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1588-1595
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (2772K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1596-1603
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (814K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1604-1610
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (593K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1611-1622
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (3071K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1623-1630
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Advance online publication: July 14, 2016Download PDF (2158K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1631-1637
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (936K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1638-1645
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (977K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1646-1652
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (481K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1653-1661
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (1927K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1662-1666
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (973K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1667-1674
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (2144K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1675-1682
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (3206K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1683-1686
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (281K) Full view HTML -
 2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1687-1693
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1687-1693
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
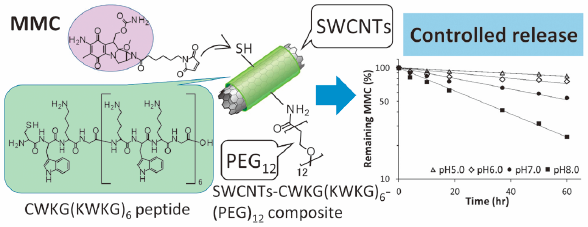
Editor's pickIn their report, Ohta et al. described that single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) with superior dispersion stability in water are expected to serve as a good drug delivery system carrier in various biomedical applications. The SWCNTs composites with designed peptide having polyethylene glycol (PEG) modification were further conjugated with mitomycin C (MMC) for achieving its controlled release. The obtained conjugate of SWCNTs composites and MMC showed good dispersion stability even under physiological conditions. The release of MMC followed the first-order kinetics with half-lives of 32.2-256.2 hours being accelerated by the pH increase. In addition, the MMC conjugate demonstrated the antitumor activity with delayed growth inhibition comparing with free MMC.
Download PDF (783K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1694-1700
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (3729K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1701-1707
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (865K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1708-1717
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (1387K) Full view HTML
-
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1718-1722
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (366K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1723-1727
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (507K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1728-1733
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (597K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1734-1738
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (2823K) Full view HTML -
2016 Volume 39 Issue 10 Pages 1739-1742
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Download PDF (495K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|