- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 2022Volume 45Issue 2 Pages 155-161
2022Volume 45Issue 2 Pages 155-161
Published: February 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2022
Editor's pickTransforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) from tumor cells has multiple roles, including tumor invasion, tumor proliferation, and tumor immunity. In this paper, the author focused on the role of TGF-β against tumor immunity and summarized the potential of anti-tumor immunity by using anti-TGF-β antibody or chemical components with immune checkpoint inhibitors and chimeric antigen receptor cells. Furthermore, the molecular mechanisms by which TGF-β controlled tumor immunity were described in this review.
Download PDF (1350K) Full view HTML
-
 2022Volume 45Issue 2 Pages 162-168
2022Volume 45Issue 2 Pages 162-168
Published: February 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2022
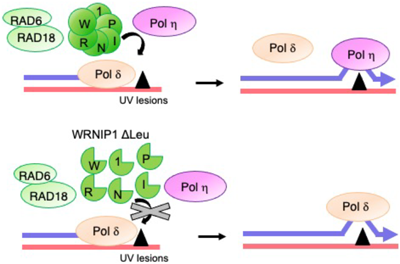
Editor's pickThe authors have previously demonstrated that non-canonical phosphorylation of EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase is catalyzed by ribosomal S6 kinases (RSKs), downstream kinases of the MEK-ERK pathway, and promotes migratory potentials of cancer cells. The article by Yonehara et al. demonstrated that tamoxifen, a selective estrogen receptor (ER) modulator used to treat breast cancers, induces the rapid phosphorylation of EphA2 by RSK in an ER-independent manner. In addition, tamoxifen significantly enhances the migration of ER-negative breast cancer cells possibly via the activation of RSK-EphA2 axis. These results provide novel insights into the tumor-promoting activity of tamoxifen.
Download PDF (2799K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 2 Pages 169-177
Published: February 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2022
Download PDF (1021K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 2 Pages 178-183
Published: February 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2022
Download PDF (1051K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 2 Pages 184-193
Published: February 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2022
Download PDF (3871K) Full view HTML -
 2022Volume 45Issue 2 Pages 194-199
2022Volume 45Issue 2 Pages 194-199
Published: February 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2022
Editor's pickAmeliorating the intratumor delivery of nanoparticles (NPs) is challenging. This study applied weak electric current (WEC) onto the tumor surface to improve the intratumor delivery of I.V. administrated Doxorubicin (DOX) encapsulated NPs. Interestingly, WEC markedly increased NPs accumulation into the tumor. Consequently, WEC/DOX-NPs combination significantly suppressed tumor growth compared to DOX-NPs alone. Mechanistically, WEC-mediated opening of intercellular adhesion in tumor is suggested to employ the increased intratumor accumulation of DOX-NPs utilizing enhanced permeability and retention effect. Therefore, a combined application of WEC and NPs containing chemotherapeutic agents will be useful for effective anticancer therapy.
Download PDF (4402K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 2 Pages 200-206
Published: February 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2022
Download PDF (2602K) Full view HTML -
 2022Volume 45Issue 2 Pages 207-212
2022Volume 45Issue 2 Pages 207-212
Published: February 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2022
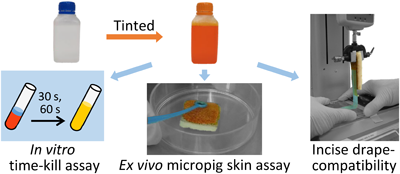
Editor's pickOcta-arginine (R8) has been extensively studied as a cell-penetrating peptide. Meanwhile, R8 is considered a promising cell adhesion molecule owing to its ability to bind to heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) and integrin β1. This study revealed that R8- and octa-lysine (K8)-conjugated agarose matrices mediate cell adhesion via HSPGs and integrin β1, and that the integrin β1 contributes to cell spreading and proliferation on the R8- and K8-matrices. The findings of this study are useful for further understanding of the R8-membrane interactions and demonstrate that R8 and K8 have a potential to be used as a cell adhesion molecule.
Download PDF (2598K) Full view HTML -
 2022Volume 45Issue 2 Pages 213-219
2022Volume 45Issue 2 Pages 213-219
Published: February 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2022
Editor's pickIn the lung alveolar epithelial cells, the innate immune response is induced by bacterial peptides such as Tri-DAP via PEPT2 (a peptide transporter)- and NOD1 (an intracellular pattern recognition receptor)-dependent pathway. In this study, corticosteroids such as budesonide were found to suppress PEPT2 function as well as the increased mRNA expression and secretion of interleukin-8 by Tri-DAP, using NCI-H441 cells having human alveolar type II cell-like phenotype. The results suggest that the innate immune response induced by bacterial peptides in the lung alveolar region may be suppressed during the inhaled corticosteroid therapy.
Download PDF (1503K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 2 Pages 220-225
Published: February 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2022
Advance online publication: November 25, 2021Download PDF (1036K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 2 Pages 226-234
Published: February 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2022
Advance online publication: November 20, 2021Download PDF (800K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 2 Pages 235-239
Published: February 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2022
Download PDF (548K) Full view HTML
-
2022Volume 45Issue 2 Pages 240-244
Published: February 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2022
Download PDF (849K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|