- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2023Volume 46Issue 5 Pages 640-646
Published: May 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2023
Download PDF (3626K) Full view HTML
-
2023Volume 46Issue 5 Pages 647-654
Published: May 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2023
Download PDF (1888K) Full view HTML -
2023Volume 46Issue 5 Pages 655-660
Published: May 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2023
Download PDF (390K) Full view HTML -
2023Volume 46Issue 5 Pages 661-671
Published: May 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2023
Advance online publication: March 21, 2023Download PDF (1577K) Full view HTML -
2023Volume 46Issue 5 Pages 672-683
Published: May 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2023
Download PDF (11251K) Full view HTML -
2023Volume 46Issue 5 Pages 684-692
Published: May 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2023
Download PDF (8508K) Full view HTML -
2023Volume 46Issue 5 Pages 693-699
Published: May 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2023
Download PDF (8232K) Full view HTML -
 2023Volume 46Issue 5 Pages 700-706
2023Volume 46Issue 5 Pages 700-706
Published: May 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2023
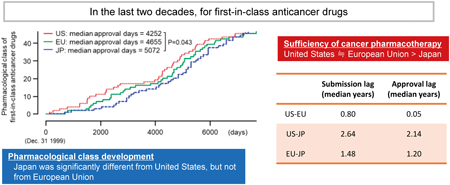
Advance online publication: March 04, 2023Editor's pickRecent improvement of pharmacotherapy on cancer is remarkable, however cancer is still one of the most devastating diseases for patients and their caregivers. The authors compared the development and approval status of first-in-class (FIC) anticancer drugs between the US, EU, and Japan, and found that approval in Japan lagged substantially behind compared to the other regions (more than 1 year vs the EU and more than 2 years vs the US). Considering the high impact of anticancer drugs on society worldwide, we should work together to reduce drug lag among regions using an improved international cooperative framework.
Download PDF (536K) Full view HTML -
 2023Volume 46Issue 5 Pages 707-712
2023Volume 46Issue 5 Pages 707-712
Published: May 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2023
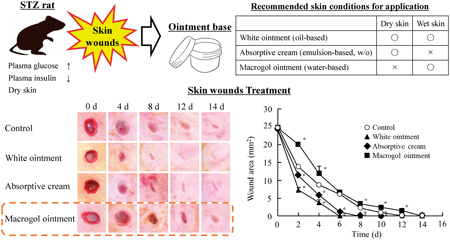
Editor's pickThe authors investigated weather difference ointment bases (absorbent cream, white-, and macrogol-ointment) affect the skin wound healing rate in normal and diabetic models (streptozotocin-induced rat, STZ rat). The wound healing rate was similar in the normal rat treated with three-bases. In contrast of this result, the wound healing in STZ rats treated with macrogol-ointment was delayed in comparison with other two-bases. These results indicate that the wound healing in STZ rats is affected by the properties of ointment base, and the selection of appropriate ointment base according to the skin condition may be important for the wound healing in patients with diabetes.
Download PDF (1379K) Full view HTML -
 2023Volume 46Issue 5 Pages 713-717
2023Volume 46Issue 5 Pages 713-717
Published: May 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2023
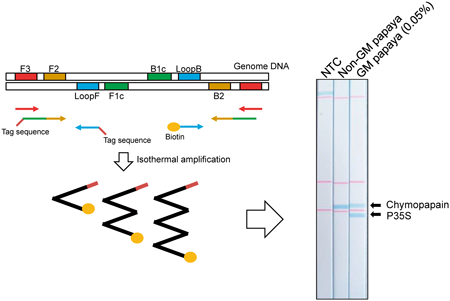
Editor's pickA loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP)-mediated screening detection method for genetically modified (GM) papaya was developed using a Genie II real-time fluorometer. The authors also designed a primer set for the detection of the papaya endogenous reference sequence, chymopapain, and the species-specificity was confirmed. To enhance the simplicity, the authors attempted to develop a lateral flow DNA chromatography to detect LAMP products, and a duplex detection was successfully applied. This simple and quick method for the screening of GM papaya will be useful for the prevention of environmental contamination of unauthorized GM crops.
Download PDF (1580K) Full view HTML -
 2023Volume 46Issue 5 Pages 718-724
2023Volume 46Issue 5 Pages 718-724
Published: May 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2023
Editor's pickThe author found that bio-ventures established in the 1990s and 2000s played a crucial role in creating new drugs approved by the FDA from 2017 to 2022 in regions outside of Japan. In contrast, in Japan, all approved drugs were created by old incumbent pharmaceutical companies, highlighting the urgent need to foster drug discovery start-ups in Japan. A case study of the Japanese company that created the largest number of FDA-approved drugs suggests that focused investment in modality technology development, strengthening collaboration with academia in biology, and the reutilizing small-molecule drug discovery capabilities are essential for improving drug discovery productivity.
Download PDF (553K) Full view HTML
-
2023Volume 46Issue 5 Pages 725-729
Published: May 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2023
Download PDF (1265K) Full view HTML -
2023Volume 46Issue 5 Pages 730-735
Published: May 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2023
Download PDF (4133K) Full view HTML -
2023Volume 46Issue 5 Pages 736-740
Published: May 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2023
Download PDF (1143K) Full view HTML -
2023Volume 46Issue 5 Pages 741-745
Published: May 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2023
Advance online publication: March 14, 2023Download PDF (543K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|