- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 1978-1991
Published: December 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2024
Download PDF (1545K) Full view HTML
-
 2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 1992-2002
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 1992-2002
Published: December 07, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 07, 2024
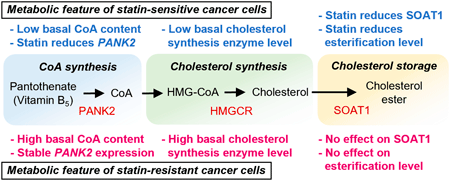
Editor's pickStatins exert anti-cancer effects by inhibiting the cholesterol synthesis pathway. However, the efficacy of statins varies among cancer cell types. In this study, the authors explored novel parameters associated with statin sensitivity in lung cancer cells, focusing on cholesterol-related metabolism. Statin-sensitive cancer cells showed lower CoA content and lower expression of cholesterol synthesis enzymes compared to statin-resistant cancer cells. The authors also suggested that the processes of CoA synthesis and cholesterol storage may be more susceptible to statin treatment in statin-sensitive cancer cells. These findings may contribute to a more detailed understanding of statin sensitivity in cancer cells.
Download PDF (3582K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2003-2010
Published: December 07, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 07, 2024
Download PDF (3996K) Full view HTML -
 2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2011-2020
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2011-2020
Published: December 07, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 07, 2024
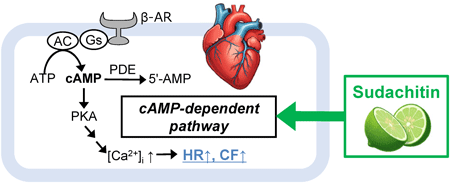
Editor's pickCitrus sudachi, a popular fruit in Tokushima Prefecture, Japan, and its peel contains high amounts of polymethoxyflavones with the most abundant being sudachitin. The effects of sudachitin on the cardiovascular system have not been fully investigated. The authors investigated the effects of sudachitin on beating rate and contractile force, and its mechanism of action, using rat atrial preparations. The results demonstrated that sudachitin-induced positive chronotropic and inotropic effects similar to those of other polymethoxyflavones, though its maximum efficacy was lower than that of isoproterenol, and that the mechanism of action of SDC is associated with the enhancement of cAMP-dependent pathways.
Download PDF (1866K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2021-2027
Published: December 07, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 07, 2024
Download PDF (591K) Full view HTML
-
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2028-2031
Published: December 07, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 07, 2024
Download PDF (1348K) Full view HTML
-
 2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2032-2040
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2032-2040
Published: December 07, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 07, 2024
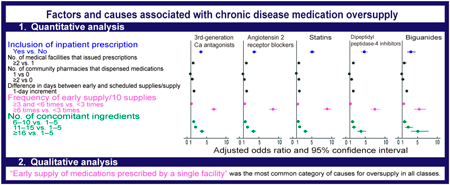
Editor's pickEliminating medication waste and controlling the rising healthcare costs are urgent issues facing Japan’s healthcare system. This study, which analyzed the factors and causes of oversupply of chronic disease medications, provides insights into addressing them. The authors found that ‘early supply’ and ‘duplicate between outpatient and inpatient prescriptions’ were notably associated with oversupply, by estimating the degree of oversupply for each individual using insurance claims data and analyzing these associations both quantitatively and qualitatively. It is essential to implement measures based on this study’s implications, which suggest the unique structure and customs within Japan’s healthcare system contribute to the oversupply.
Download PDF (1822K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2041-2049
Published: December 13, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 13, 2024
Download PDF (5233K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2050-2057
Published: December 13, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 13, 2024
Download PDF (1495K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2058-2064
Published: December 13, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 13, 2024
Download PDF (979K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2065-2075
Published: December 14, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 14, 2024
Download PDF (13930K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2076-2082
Published: December 14, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 14, 2024
Download PDF (4227K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2083-2091
Published: December 14, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 14, 2024
Download PDF (3558K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2092-2100
Published: December 21, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2024
Download PDF (728K) Full view HTML -
 2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2101-2118
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2101-2118
Published: December 21, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2024
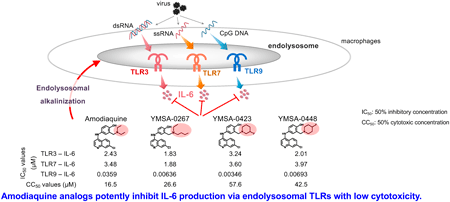
Editor's pickThe article presented novel potent inhibitors of IL-6 production via TLRs recognizing pathogen nucleic acids in murine macrophages. Authors have shown that an antimalarial drug, amodiaquine can inhibit IL-6 production induced by agonists of TLR3, TLR7 and TLR9. Amodiaquine can more potently inhibit IL-6 production via TLR9 than that via other TLRs. Also, authors succeeded in creating amodiaquine analogs with higher activity against IL-6 production via TLRs and lower cytotoxicity. These findings suggest that some amodiaquine analogs may have potential for the treatment of sepsis.
Download PDF (4430K) Full view HTML -
 2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2119-2126
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2119-2126
Published: December 21, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2024
Editor's pick[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
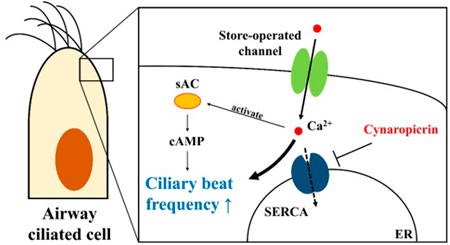
Cynaropicrin is known to exhibit numerous biological activities and associated pharmacological effects. The authors clarified the impact of cynaropicrin as an activator of airway epithelial ciliated cells (AECCs). Cynaropicrin induces store-operated calcium entry through SOCs (transient receptor potential channel and ORAI calcium release-activated calcium modulator channel) by inhibiting sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase and increases intracellular Ca2+ concentration, which activates soluble adenylyl cyclase and increases intracellular cAMP concentration. Consequently, cynaropicrin increases the ciliary beat frequencies of AECCs. These observations present the potential for developing a strategy to prevent respiratory infection.Download PDF (4815K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2127-2137
Published: December 21, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2024
Download PDF (5395K) Full view HTML
-
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2138-2142
Published: December 21, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2024
Download PDF (694K) Full view HTML
-
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2143-2153
Published: December 21, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 21, 2024
Download PDF (8150K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2154-2164
Published: December 28, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 28, 2024
Download PDF (2887K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2165-2172
Published: December 28, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 28, 2024
Download PDF (3899K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2173-2181
Published: December 28, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 28, 2024
Download PDF (1450K) Full view HTML
-
2024Volume 47Issue 12 Pages 2182
Published: December 31, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: December 31, 2024
Download PDF (125K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|