- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 382-393
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 382-393
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Editor's pickOrganic cation transporter 2 (OCT2) and multidrug and toxin extrusion 1 and 2-K (MATE1/2-K) are critically involved in renal secretion, pharmacokinetics (PK), and toxicity of cationic drugs. Drug-drug interactions (DDIs) at OCT2 and/or MATE1/2-K have been shown to result in clinical impacts on PK, therapeutic efficacy and are probably involved in the renal accumulation of drugs. In this work, an overview of OCT2 and MATE1/2-K is presented. The primary structure, membrane location, functional properties, and clinical impact of OCT2 and MATE1/2-K are described. In addition, clinical aspects of DDIs in OCT2 and MATE1/2-K and their involvement in drug nephrotoxicity are compiled.
Download PDF (1124K) Full view HTML
-
 2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 394-396
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 394-396
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Advance online publication: January 22, 2022Editor's pickThe severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Omicron variant has multiple receptor-binding domain (RBD) mutations. Some of these mutations can increase infectivity and reduce antibody affinity. In this study, the authors successfully developed a rapid screening assay to simultaneously identify RBD mutations in the Omicron and Delta variants using high-resolution melting (HRM) analysis. As this HRM-based genotyping assay does not require sequence-specific probes, unlike the TaqMan probe assay, it is easy to perform and cost-effective. This simple method may contribute to the rapid identification and prevention of the potential widespread infection of SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Download PDF (428K) Full view HTML
-
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 397-402
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (668K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 403-408
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (589K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 409-420
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (6112K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 421-428
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (877K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 429-437
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (2024K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 438-445
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Advance online publication: February 03, 2022Download PDF (3334K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 446-451
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (596K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 452-459
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (434K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 460-466
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (574K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 467-476
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (1772K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 477-482
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (540K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 483-490
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (7401K) Full view HTML -
 2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 491-496
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 491-496
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
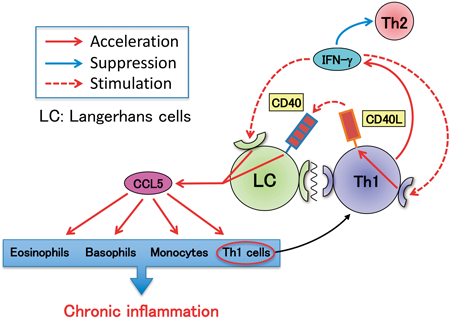
Editor's pickIt has long been known that the chronic skin lesions of atopic dermatitis (AD) patients show increased amounts of Th1 cells in addition to Th2 cells. However, it has remained unclear whether these Th1 cells actually participate in the exacerbation of skin inflammation. In this paper, the authors showed that Langerhans cells (LCs) augmented CCL5 production by responding to Th1 cytokine, IFN-g while presenting antigen to Th cells, and that this augmentation of CCL5 production would contribute to infiltration of eosinophils and other Th1 cells into skin lesions, followed by expansion of chronic inflammation in the skin.
Download PDF (604K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 497-507
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (979K) Full view HTML -
 2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 508-516
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 508-516
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
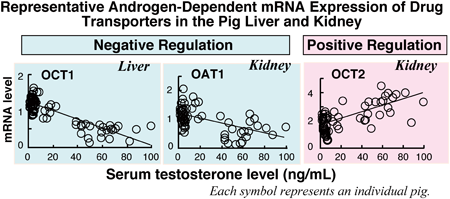
Editor's pickBreed and organ-dependent sex differences in the mRNA amounts of several drug transporters in the liver and kidney were found in pigs. In Meishan pigs, the sex differences in the amounts of hepatic MDR1, OATP1B3, and OCT1 mRNAs and in those of renal MRP2, OAT1, OAT2, OAT3, and OCT2 mRNAs were found. However, no such sex differences were observed in Landrace pigs. Furthermore, additional experiments using castrated and/or testosterone propionate-treated pigs suggested that breed-dependent sex differences in the gene expression of drug transporters, especially hepatic OCT1 and renal OAT1, were primarily due to the difference in serum testosterone concentration.
Download PDF (740K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 517-521
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (536K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 522-527
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (651K) Full view HTML
-
 2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 528-533
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 528-533
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
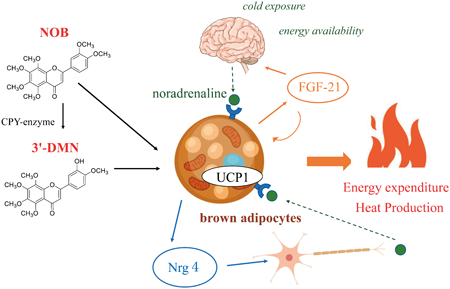
Editor's pickBrown adipose tissue (BAT) specifically regulates energy expenditure via heat production. Hence, BAT may have the potential to combat obesity in humans. The activity of BAT is directly regulated by β-adrenergic stimulation. In this study, the authors report the effects of Nobiletin (NOB), a natural polymethoxylated flavone present in citrus fruits, on BAT activation using β-adrenergic agonists. NOB can enhance the thermogenic functions of brown adipocytes and promote brown adipokine secretion due to enhanced β-adrenergic stimulation. NOB could be a promising candidate for activating BAT under β-adrenergic stimulation and preventing the onset of obesity.
Download PDF (584K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 534-537
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (746K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 538-541
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (672K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 542-546
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (771K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 547-551
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (6037K) Full view HTML
-
2022Volume 45Issue 4 Pages 552
Published: April 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (146K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|