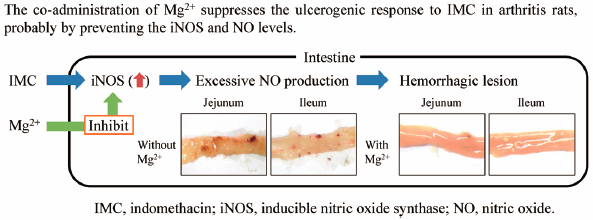
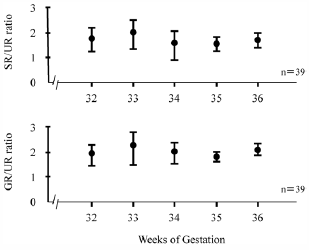
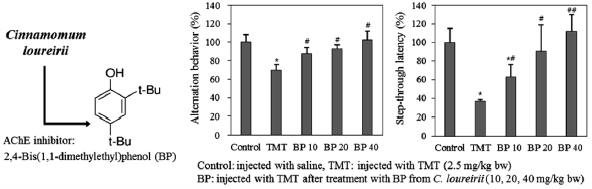
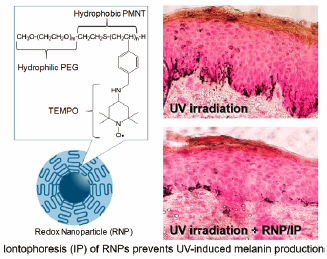
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 739-750
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Download PDF (1517K) Full view HTML
-
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 751-757
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Download PDF (1446K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 758-764
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Download PDF (775K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 765-773
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Download PDF (2841K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 774-781
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Advance online publication: March 04, 2017Download PDF (1542K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 782-788
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Download PDF (936K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 789-796
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Advance online publication: March 04, 2017Download PDF (724K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 797-806
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Download PDF (2197K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 807-814
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Download PDF (902K) Full view HTML -
 2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 815-823
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 815-823
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Editor's pickIn their report, Ibrahim et al. described that generating platinum chloroquine diphosphate dichloride (PtCQ)-loaded polyethylene glycol (PEG)-modified (PEGylated) cationic liposomes exhibiting high drug encapsulation and high drug retention. PtCQ was encapsulated in PEGylated cationic liposomes comprising various amounts of cationic lipids using the remote-loading method. PEGylated neutral liposomes and cationic liposomes exhibited minimum leakage of PtCQ after two months’ storage at 4˚C, and further exhibited little release under in vitro culture conditions at 37˚C for 72 hours. These results provide a useful framework for the design of future liposome-based in vivo drug delivery systems targeting the drug-resistant malaria parasite.
Download PDF (1089K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 824-829
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Download PDF (319K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 830-836
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Advance online publication: January 17, 2017Download PDF (2710K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 837-843
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Download PDF (619K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 844-851
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Download PDF (2075K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 852-859
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Download PDF (1981K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 860-866
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Advance online publication: April 01, 2017Download PDF (424K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 867-877
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Advance online publication: April 01, 2017Download PDF (1974K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 878-887
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Advance online publication: March 24, 2017Download PDF (4166K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 888-893
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Download PDF (921K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 894-901
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Download PDF (1430K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 902-909
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Download PDF (664K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 910-915
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Download PDF (720K) Full view HTML
-
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 916-921
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Download PDF (1035K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 922-925
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Download PDF (293K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 926-931
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Download PDF (553K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 932-935
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Download PDF (356K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 936-940
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Advance online publication: March 17, 2017Download PDF (4149K) Full view HTML -
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 941-944
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Download PDF (2031K) Full view HTML
-
2017 Volume 40 Issue 6 Pages 945
Published: June 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2017
Download PDF (86K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|