
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Yu Ding, Wenhua Li, Shi Peng, Genqing Zhou, Songwen Chen, Yong Wei, Ju ...2023Volume 46Issue 4 Pages 524-532
Published: April 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2023
Advance online publication: January 26, 2023JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThis study investigated whether pretreatment with puerarin could alleviate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury in a cardiomyocyte oxygen–glucose deprivation and reoxygenation (OGD/R) model and in a mouse I/R injury model. For in vitro experiments, H9C2 cells were divided into control, erastin, OGD/R, OGD/R + puerarin, and OGD/R + ferrostatin (Fer)-1 groups. Parameters related to ferroptosis included levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE), ATP, reactive oxygen species (ROS), glutathione (GSH), prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase (Ptgs) 2 mRNA, glutathione peroxidase (GPX) 4 protein and iron. In H9C2 cells, puerarin or Fer-1 pretreatment reduced ferroptosis, as indicated by decreased ROS and increased GSH, ATP levels. In vivo, wild-type mice were randomly divided into sham, I/R + vehicle, I/R + puerarin, and IR + Fer-1 groups. The I/R model was established by 30 min of left anterior descending artery occlusion followed by 24 h of reperfusion. Pretreatment with puerarin or Fer-1 significantly reduced infarct size in I/R mice, and decreased the activities of Myeloperoxidase (MPO) and cardiac enzymes such as creatine kinase MB isoenzyme (CK-MB), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) compared to those in the vehicle-treated group. Puerarin also reduced the production of MDA and 4-HNE, reduced the mRNA expression of Ptgs2 mRNA, and increased GPX4 protein expression. These results showed that puerarin exerted protective effects against myocardial I/R injury by inhibiting ferroptosis and inflammation, and therefore may have therapeutic potential for treatment of acute myocardial infarction.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (7260K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (7260K) Full view HTML -
Zhiyu Zhang, Tian Zhang, Yijia Zhang, Yingxia Liang2023Volume 46Issue 4 Pages 533-541
Published: April 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2023
Advance online publication: February 15, 2023JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLC-C motif chemokine ligand 17 (CCL17), an important chemokine, plays a vital role in regulating immune balance in the central nervous system. In this study, we explored the potential roles of CCL17 in a rat postoperative pain model and that of blocking CCL17 in the prevention of postoperative pain in rats. A right plantar incision in rat was used as a model of postoperative pain. A behavioral change was measured preoperatively and postoperatively using mechanical withdrawal thresholds and thermal withdrawal latency. CCL17 and its upstream Jmjd-3 mRNA levels in the spinal cord were detected using real-time PCR, CCL17 levels in the serum were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and the expression of interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4), which interacts with Jmjd-3, was detected by immunohistochemistry staining. After that, rats were intraperitoneally injected with either anti-CCL17 monoclonal antibody (mAb) or GSK-J4 (the Jmjd3 inhibitor) to evaluate the protective effects of blocking CCL17 on postoperative pain. We found that CCL17 and Jmjd-3 were significantly increased in the spinal cords of the postoperative pain rat, consistent with changes in hyperalgesia. In addition, our results showed that the mechanical and thermal allodynia was significantly ameliorated using anti-CCL17mAb or GSK-J4. Moreover, we found that anti-CCL17mAb or GSK-J4 treatment decreased c-fos expression in response to peripheral stimulation. Finally, our preliminary exploration found that anti-CCL17mAb or GSK-J4 had a protective effect on tissue damage. These findings indicated that high expression of CCL17 played a critical role in postoperative pain induced by plantar incision and that CCL17 blockade may serve as an effective approach to managing postoperative pain.
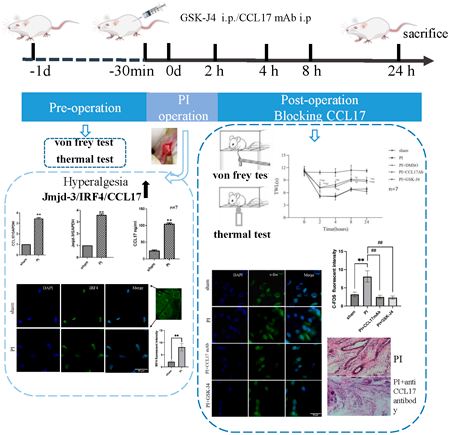 View full abstractDownload PDF (8858K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (8858K) Full view HTML -
Hyun Seung Lee, Heung-Woo Park, Suh-Young Lee2023Volume 46Issue 4 Pages 542-551
Published: April 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialObjective: We aimed to investigate the differences in interleukin (IL)-10, IL-1β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α expression in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated CD14++CD16+ monocytes obtained from asthmatics after dexamethasone or dexamethasone plus rapamycin treatments between clinical steroid responders (R) and non-responders (NR). Methods: Cytokine expressions in LPS-stimulated CD14++CD16+ p-mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) monocytes from R and NR were determined using flow cytometry. Results: IL-10high CD14++CD16+ p-mTOR population following LPS stimulation increased in the R group although decreased in the NR group with dexamethasone treatment. IL-1βhigh population decreased in the R group although increased in the NR group. Rapamycin treatment after LPS and dexamethasone resulted in a significant increase in the IL-10high population and a significant decrease in the IL-1βhigh population in the NR group. Conclusion: Dexamethasone treatment resulted in different patterns of change in cytokine expressions in LPS-stimulated CD14++CD16+ p-mTOR monocytes between the R and NR. mTOR inhibition can restore steroid responsiveness involving IL-10 and IL-1β in CD14++CD16+ p-mTOR monocytes.
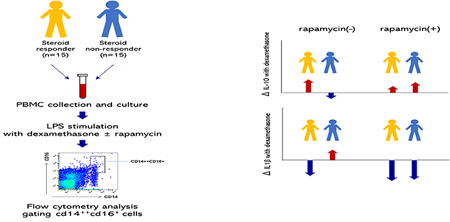 View full abstractDownload PDF (3795K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (3795K) Full view HTML -
Sang Gyun Noh, Hee Jin Jung, Seungwoo Kim, Radha Arulkumar, Ki Wung Ch ...2023Volume 46Issue 4 Pages 552-562
Published: April 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialAging leads to the functional decline of an organism, which is associated with age and sex. To understand the functional change of kidneys depending on age and sex, we carried out a transcriptome analysis using RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) data from rat kidneys. Four differentially expressed gene (DEG) sets were generated according to age and sex, and Gene Ontology analysis and overlapping analysis of Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathways were performed for the DEG sets. Through the analysis, we revealed that inflammation- and extracellular matrix (ECM)-related genes and pathways were upregulated in both males and females during aging, which was more prominent in old males than in old females. Furthermore, quantitative real-time PCR analysis confirmed that the expression of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) signaling-related genes, Birc3, Socs3, and Tnfrsf1b, and ECM-related genes, Cd44, Col3a1, and Col5a2, which showed that the genes were markedly upregulated in males and not females during aging. Also, hematoxylin–eosin (H&E) staining for histological analysis showed that renal damage was highly shown in old males rather than old females. In conclusion, in the rat kidney, the genes involved in TNF signaling and ECM accumulation are upregulated in males more than in females during aging. These results suggest that the upregulation of the genes may have a higher contribution to age-related kidney inflammation and fibrosis in males than in females.
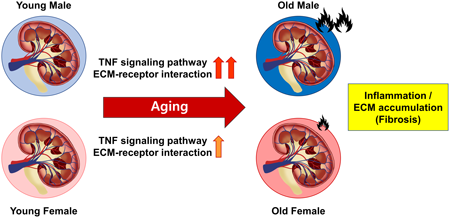 View full abstractDownload PDF (4740K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (4740K) Full view HTML -
Qian Jin, Yi Zhang, Yalan Cui, Meng Shi, Jingjing Shi, Siqing Zhu, Ton ...2023Volume 46Issue 4 Pages 563-573
Published: April 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThis work aimed to assess whether mitochondrial damage in the liver induced by subacute soman exposure is caused by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1 alpha (PGC-1α) and whether PGC-1α regulates mitochondrial respiratory chain damage. Toxicity mechanism research may provide theoretical support for developing anti-toxic drugs in the future. First, a soman animal model was established in male Sprague–Dawley (SD) rats by subcutaneous soman injection. Then, liver damage was biochemically evaluated, and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity was also determined. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was performed to examine liver mitochondrial damage, and high-resolution respirometry was carried out for assessing mitochondrial respiration function. In addition, complex I–IV levels were quantitatively evaluated in isolated liver mitochondria by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). PGC-1α levels were detected with a Jess capillary-based immunoassay device. Finally, oxidative stress was analyzed by quantifying superoxide dismutase (SOD), malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione (GSH), oxidized glutathione (GSSG), and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels. Repeated low-level soman exposure did not alter AChE activity, while increasing morphological damage of liver mitochondria and liver enzyme levels in rat homogenates. Complex I, II and I + II activities were 2.33, 4.95, and 5.22 times lower after treatment compared with the control group, respectively. Among complexes I–IV, I–III decreased significantly (p < 0.05), and PGC-1α levels were 1.82 times lower after soman exposure than in the control group. Subacute soman exposure significantly increased mitochondrial ROS production, which may cause oxidate stress. These findings indicated dysregulated mitochondrial energy metabolism involves PGC-1α protein expression imbalance, revealing non-cholinergic mechanisms for soman toxicity.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (5153K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (5153K) Full view HTML -
 Jie Chen, Puyan Qin, Zhanxia Tao, Weijian Ding, Yunlong Yao, Weifang X ...2023Volume 46Issue 4 Pages 574-585
Jie Chen, Puyan Qin, Zhanxia Tao, Weijian Ding, Yunlong Yao, Weifang X ...2023Volume 46Issue 4 Pages 574-585
Published: April 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialMethyl protodioscin (MPD), a furostanol saponin found in the rhizomes of Dioscoreaceae, has lipid-lowering and broad anticancer properties. However, the efficacy of MPD in treating prostate cancer remains unexplored. Therefore, the present study aimed to evaluate the anticancer activity and action mechanism of MPD in prostate cancer. 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT), wound healing, transwell, and flow cytometer assays revealed that MPD suppressed proliferation, migration, cell cycle, and invasion and induced apoptosis of DU145 cells. Mechanistically, MPD decreased cholesterol concentration in the cholesterol oxidase, peroxidase and 4-aminoantipyrine phenol (COD-PAP) assay, disrupting the lipid rafts as detected using immunofluorescence and immunoblot analyses after sucrose density gradient centrifugation. Further, it reduced the associated mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway protein P-extracellular regulated protein kinase (ERK), detected using immunoblot analysis. Forkhead box O (FOXO)1, a tumor suppressor and critical factor controlling cholesterol metabolism, was predicted to be a direct target of MPD and induced by MPD. Notably, in vivo studies demonstrated that MPD significantly reduced tumor size, suppressed cholesterol concentration and the MAPK signaling pathway, and induced FOXO1 expression and apoptosis in tumor tissue in a subcutaneous mouse model. These results suggest that MPD displays anti-prostate cancer activity by inducing FOXO1 protein, reducing cholesterol concentration, and disrupting lipid rafts. Consequently, the reduced MAPK signaling pathway suppresses proliferation, migration, invasion, and cell cycle and induces apoptosis of prostate cancer cells.
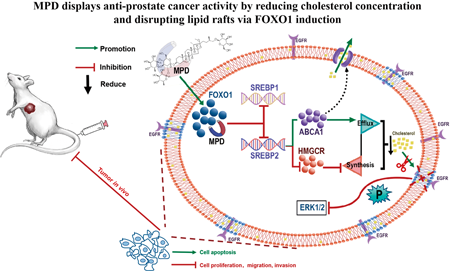 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickHigh cholesterol concentration can promote the growth of prostate cancer. Methyl protodioscin (MPD), a furostanol saponin found in the rhizomes of Dioscoreaceae, has lipid-lowering and broad anticancer properties. In this research, MPD decreased expression of SREBP1 and SREBP2 by inducing FOXO1, lead to the induction of the expression of cholesterol export pump ABCA1 and reduction of the expression of the rate-limiting enzyme of cholesterol synthesis HMGCR. Reduced cholesterol caused to disrupted lipid rafts and MAPK pathway on it, contributing to MPD anti-prostate cancer activity. Consequently, MPD may be used as an active drug for treatment in prostate cancer.
Download PDF (14910K) Full view HTML -
Potha Amulya Reddy, Kunchithapatham Saravanan, Akkala Madhukar2023Volume 46Issue 4 Pages 586-591
Published: April 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialDiabetes is a combination of heterogeneous disorders presenting with episodes of hyperglycemia and glucose intolerance, as a result of lack of insulin, defective insulin action, or both. There are more than 387 million people with Diabetes Mellitus (DM) and the number is likely to reach 592 million by 2035. The prevalence of DM is 9.1% in India. With increasing incidence of diabetes worldwide, evaluation of diabetes knowledge, attitude and practice (KAP) has become crucial for guiding behavioral changes for persons with diabetes and individuals at risk. KAP-related studies are important in tailoring a health programme to help curb the threats caused by the disease. Adequate information helps the public understand the risks of diabetes and its complications, seeks treatment of existing disease, takes preventive measures and develops proactive attitude towards health. This was an interventional study where patients of either gender with ≥1-year history of DM were enrolled into the study after obtaining the consent. A total of 200 patients were included in this study. The p-value (<0.0001) showed that there was significant improvement in the KAP score of intervention group patients from baseline to follow up compared to that of control group. This study shows that improvement in knowledge of the disease has positive impact on Attitude and Practice of the subjects, thus improving their glycemic control.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (320K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (320K) Full view HTML -
 Ryo Iketani, Shinobu Imai2023Volume 46Issue 4 Pages 592-598
Ryo Iketani, Shinobu Imai2023Volume 46Issue 4 Pages 592-598
Published: April 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialIn April 2014, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor (SGLT-2i) was introduced in Japan. In May 2015, the prescription limitation for SGLT-2i was lifted. Subsequently, SGLT-2i was shown to reduce cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). SGLT-2i prescription is expected to increase and consequently affect the prescription trends for other antidiabetic agents. Therefore, we evaluated the trends for antidiabetic agent prescriptions in Japan from April 2012 to March 2020. In this study, a dynamic cohort consisting of patients with T2DM derived from the Japan Medical Data Center health insurance database and with at least one antidiabetic agent prescription was investigated. The prescription rates were calculated monthly (/1000 person-months) for each class of antidiabetic agent. The eligible cohort comprised 34333 patients. The prescription rate for dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor increased from 424.0 in April 2012 to 656.3 in May 2015, and slightly decreased to 635.4 in March 2020. The prescription rate for biguanide consistently increased from 347.2 in April 2012 to 500.1 in March 2020. The prescription rate for sulfonylurea consistently decreased from 393.8 in April 2012 to 172.5 in March 2020. The prescription rate for SGLT-2i consistently increased from 4.1 in April 2014 to 363.1 in March 2020. SGLT-2i prescription increased and may affect the prescription trends for dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor and sulfonylurea after May 2015, when the prescription limitation for SGLT-2i was lifted. Biguanide prescriptions increased regardless of the introduction of SGLT-2i. The treatment of T2DM in Japan is clearly changing, with a focus on SGLT-2i and biguanide.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickThe authors described prescription trends of the antidiabetic agents used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in Japan from 2012 to 2020 using administrative claims data. Noteworthy, this study examined the prescription trends in every line for T2DM treatment, including the combinations of antidiabetic agents, and showed that sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors were rapidly introduced into T2DM treatment from several perspectives. Such a descriptive study revealed how T2DM treatment changed in accordance with cumulated evidence and can provide interesting information on public health.
Download PDF (3406K) Full view HTML -
 Mitsushi J. Ikemoto, Yukine Aihara, Noriyuki Ishii, Hideyuki Shigemori2023Volume 46Issue 4 Pages 599-607
Mitsushi J. Ikemoto, Yukine Aihara, Noriyuki Ishii, Hideyuki Shigemori2023Volume 46Issue 4 Pages 599-607
Published: April 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe polyphenol derivative 3,4-dihydroxybenzalacetone (DBL) is the primary antioxidative component of the medicinal folk mushroom Chaga (Inonotus obliquus (persoon) Pilat). In this study, we investigated whether the antioxidative effect of DBL could propagate to recipient cells via secreted components, including extracellular vesicles (EVs), after pre-exposing SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells to DBL. First, we prepared EV-enriched fractions via sucrose density gradient ultracentrifugation using conditioned medium from SH-SY5Y cells exposed to 100 µM hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) for 24 h, with and without 1 h of 5 µM DBL pre-treatment. CD63 immuno-dot blot analysis demonstrated that fractions with density of 1.06–1.09 g/cm3 had CD63-like immuno-reactivities. Furthermore, the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl assay revealed that the radical scavenging activity of fraction 11 (density of 1.06 g/cm3), prepared after 24-h H2O2 treatment, was significantly increased compared to that in the control group (no H2O2 treatment). Notably, 1 h of 5 µM DBL pre-treatment or 5 min of heat treatment (100 °C) diminished this effect, although concentrating the fraction by 100 kDa ultrafiltration enhanced it. Overall, the effect was not specific to the recipient cell types. In addition, the uptake of fluorescent Paul Karl Horan-labeled EVs in concentrated fraction 11 was detected in all treatment groups, particularly in the H2O2-treated group. The results suggest that cell-to-cell communication via bioactive substances, such as EVs, in conditioned SH-SY5Y cell medium, propagates the H2O2-induced radical scavenging effect, whereas pre-conditioning with DBL inhibits it.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickThe polyphenol derivative 3,4-dihydroxybenzalacetone (DBL) is the primary antioxidative component of the medicinal folk mushroom Chaga. The authors investigated whether the antioxidative effect of DBL could propagate to recipient cells using extracellular vesicles (EVs)-enriched fractions prepared by sucrose density gradient ultracentrifugation from conditioned medium of SH-SY5Y cells exposed to hydrogen peroxide after pre-exposing DBL. The results obtained from cell-based tests including the radical scavenging and the fluorescent Paul Karl Horan-labeled EVs uptake assays suggest that cell-to-cell communication via bioactive substances, such as EVs propagate the hydrogen peroxide-induced radical scavenging effect, whereas pre-conditioning with DBL inhibits it.
Download PDF (6068K) Full view HTML -
Ryo Onodera, Yoko Jimma, Anna Suzuki, Wataru Habano, Shogo Ozawa, Jun ...2023Volume 46Issue 4 Pages 608-613
Published: April 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAngiogenesis is involved in the malignant transformation of cancers. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is important in inducing angiogenesis. Cultured cells play an important role in analyzing the regulation of VEGF expression, and it is revealed that VEGF expression is induced under hypoxia. However, it has been shown that there are differences in the pathway for gene expression between two-dimensional (2D) cells and in vivo cells. Three-dimensional (3D) spheroids constructed in 3D culture with a gene expression pattern more similar to that of in vivo cells than 2D cells have been used to solve this problem. This study analyzed the VEGF gene expression pathway in 3D spheroids of human lung cancer cells, A549 and H1703. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT) regulated VEGF gene expression in 3D spheroids. However, VEGF gene expression was not regulated by HIF-1α in 2D cells. To conclude, we found that the regulatory pathway of VEGF gene expression is different between 2D cells and 3D spheroids in human lung cancer cells. These results suggest the possibility of a new VEGF gene expression regulation pathway in vivo. In addition, they show useful knowledge for the analysis of angiogenesis induction mechanisms and also demonstrate the usefulness of 3D spheroids.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2502K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2502K) Full view HTML -
Yuki Asai, Takumi Tashiro, Yoshihiro Kondo, Makoto Hayashi, Hiroki Ari ...2023Volume 46Issue 4 Pages 614-620
Published: April 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDigoxin toxicity (plasma digoxin concentration ≥0.9 ng/mL) is associated with worsening heart failure (HF). Decision tree (DT) analysis, a machine learning method, has a flowchart-like model where users can easily predict the risk of adverse drug reactions. The present study aimed to construct a flowchart using DT analysis that can be used by medical staff to predict digoxin toxicity. We conducted a multicenter retrospective study involving 333 adult patients with HF who received oral digoxin treatment. In this study, we employed a chi-squared automatic interaction detection algorithm to construct DT models. The dependent variable was set as the plasma digoxin concentration (≥ 0.9 ng/mL) in the trough during the steady state, and factors with p < 0.2 in the univariate analysis were set as the explanatory variables. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was conducted to validate the DT model. The accuracy and misclassification rates of the model were evaluated. In the DT analysis, patients with creatinine clearance <32 mL/min, daily digoxin dose ≥1.6 µg/kg, and left ventricular ejection fraction ≥50% showed a high incidence of digoxin toxicity (91.8%; 45/49). Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that creatinine clearance <32 mL/min and daily digoxin dose ≥1.6 µg/kg were independent risk factors. The accuracy and misclassification rates of the DT model were 88.2 and 46.2 ± 2.7%, respectively. Although the flowchart created in this study needs further validation, it is straightforward and potentially useful for medical staff in determining the initial dose of digoxin in patients with HF.
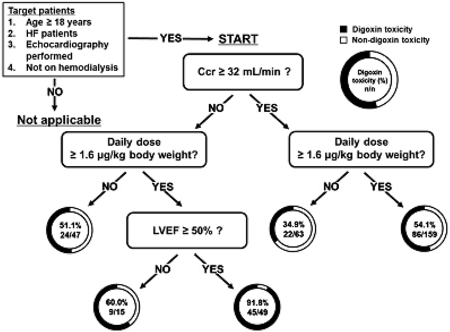 View full abstractDownload PDF (770K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (770K) Full view HTML -
Hiroko Shibata, Kazuko Nishimura, Yoshiro Saito, Akiko Ishii-Watabe2023Volume 46Issue 4 Pages 621-629
Published: April 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLMonitoring serum infliximab (INF) concentrations is crucial for designing appropriate doses for patients with rheumatoid arthritis. It is recommended to maintain the serum trough INF level at least 1.0 µg/mL. In Japan, an in vitro diagnostic kit using immunochromatography has been approved to determine whether the serum INF concentration is over 1.0 µg/mL or not, and to support the determination of the necessity of increasing the dose or switching to another drug. Biosimilars (BS) of INF may have immunochemical properties different from those of its innovator product, which may show different reactivities on the diagnostic kit. In this study, the responses of the innovator and five BS products on the kit were compared. Based on visually comparing the intensity of color development between the test and control samples, differences were found in the judgment results depending on the analyst. In particular, 1.0 µg/mL was not determined as positive in some cases, whereas 2.0 µg/mL was reliably determined as positive. Overall, no significant difference in reactivity was found between the innovator and five BS products. To further compare the differences in immunochemical properties, the reactivity of these products with three enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits was compared. The results confirmed that there were no significant differences among the innovator and BS products in reactivity with the examined kits. When using that diagnostic kit, the users need to be aware that the judgement around 1.0 µg/mL INF may differ depending on the test conditions, including the analyst.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2002K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2002K) Full view HTML -
 Stella Amarachi Ihim, Yukiko K. Kaneko, Moe Yamamoto, Momoka Yamaguchi ...2023Volume 46Issue 4 Pages 630-635
Stella Amarachi Ihim, Yukiko K. Kaneko, Moe Yamamoto, Momoka Yamaguchi ...2023Volume 46Issue 4 Pages 630-635
Published: April 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe improvement of type 2 diabetes mellitus induced by naturally occurring polyphenols, known as flavonoids, has received considerable attention. However, there is a dearth of information regarding the effect of the trihydroxyflavone apigenin on pancreatic β-cell function. In the present study, the anti-diabetic effect of apigenin on pancreatic β-cell insulin secretion, apoptosis, and the mechanism underlying its anti-diabetic effects, were investigated in the INS-ID β-cell line. The results showed that apigenin concentration-dependently facilitated 11.1-mM glucose-induced insulin secretion, which peaked at 30 µM. Apigenin also concentration-dependently inhibited the expression of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress signaling proteins, CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP) homologous protein (CHOP) and cleaved caspase-3, which was elevated by thapsigargin in INS-1D cells, with peak suppression at 30 µM. This was strongly correlated with the results of flow cytometric analysis of annexin V/propidium iodide (PI) staining and DNA fragmentation analysis. Moreover, the increased expression of thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) induced by thapsigargin was remarkably reduced by apigenin in a concentration-dependent manner. These results suggest that apigenin is an attractive candidate with remarkable and potent anti-diabetic effects on β-cells, which are mediated by facilitating glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and preventing ER stress-mediated β-cell apoptosis, the latter of which may be possibly mediated by reduced expression of CHOP and TXNIP, thereby promoting β-cell survival and function.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickProtection against impaired insulin secretion and β-cell apoptosis is an important strategy to prevent the progression of type 2 diabetes. The authors have reported the effects of apigenin, a dietary trihydroxyflavone, on pancreatic β-cell functions, underlying its anti-diabetic effects. The study demonstrated that apigenin exerts insulinotropic and anti-apoptotic effects in the β-cell line INS-1D. The anti-apoptotic effect of apigenin was further supported by reduced expression of apoptotic signaling proteins and pro-apoptotic protein. The results suggest and provide a basis for the development of apigenin as a potential therapeutic for type 2 diabetes through promoting β-cell survival and function.
Download PDF (4261K) Full view HTML
-
Daisuke Ihara, Tomoaki Miyata, Mamoru Fukuchi, Masaaki Tsuda, Akiko Ta ...2023Volume 46Issue 4 Pages 636-639
Published: April 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2023
Advance online publication: February 18, 2023JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialSerum response factor (SRF) is a transcription factor that plays essential roles in multiple brain functions in concert with SRF cofactors such as ternary complex factor (TCF) and megakaryoblastic leukemia (MKL)/myocardin-related transcription factor (MRTF), which comprises MKL1/MRTFA and MKL2/MRTFB. Here, we stimulated primary cultured rat cortical neurons with brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and investigated the levels of SRF and SRF cofactor mRNA expression. We found that SRF mRNA was transiently induced by BDNF, whereas the levels of SRF cofactors were differentially regulated: mRNA expression of Elk1, a TCF family member, and MKL1/MRTFA were unchanged, while in contrast, mRNA expression of MKL2/MRTFB was transiently decreased. Inhibitor experiments revealed that BDNF-mediated alteration in mRNA levels detected in this study was mainly due to the extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK)/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. Collectively, BDNF mediates the reciprocal regulation of SRF and MKL2/MRTFB at the mRNA expression level through ERK/MAPK, which may fine-tune the transcription of SRF target genes in cortical neurons. Accumulating evidence regarding the alteration of SRF and SRF cofactor levels detected in several neurological disorders suggests that the findings of this study might also provide novel insights into valuable therapeutic strategies for the treatment of brain diseases.
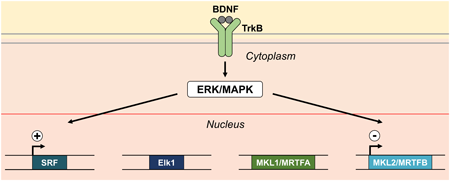 View full abstractDownload PDF (612K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (612K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|