- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 668
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
Download PDF (188K) Full view HTML
-
2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 669-674
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
Download PDF (949K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 675-683
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
Download PDF (969K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 684-690
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
Download PDF (1559K) Full view HTML
-
2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 691-697
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
Download PDF (648K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 698-702
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
Download PDF (1460K) Full view HTML
-
 2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 703-708
2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 703-708
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
Advance online publication: April 02, 2022Editor's pickChanges in drug-metabolizing activity via pregnane X receptor (PXR) is one of the mechanisms involved in drug-drug interactions. The authors reported cases in which the anticoagulant effects of warfarin were reversibly attenuated by the concomitant administration of rifampicin or bosentan, which are potent PXR ligands. However, no recovery of the response to warfarin was observed in the patients switched from bosentan to macitentan, which is considered not to activate PXR in clinical settings. The authors describe the importance of long-term monitoring and additional examinations to clarify the sustained mechanism for the drug interaction with warfarin, when switching from bosentan to macitentan.
Download PDF (531K) Full view HTML -
 2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 709-719
2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 709-719
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
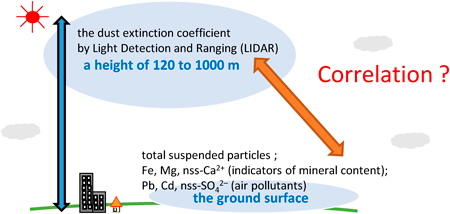
Editor's pickThe dust extinction coefficient measured by light detection and ranging (LIDAR) has been used as an indicator of exposure to Asian dust in many epidemiological studies; however, few reports exist which explore the relationship between the dust extinction coefficient and the distribution of airborne particles near the ground surface. In this study, authors repot that the dust extinction coefficient is a useful indicator of Asian dust near the ground surface; however, as harmful air pollutants occasionally move with Asian dust, it is necessary to monitor these pollutants near the ground surface when conducting an epidemiological study on the health effect of airborne particles.
Download PDF (1842K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 720-723
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
Download PDF (411K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 724-729
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
Download PDF (983K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 730-737
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
Advance online publication: April 16, 2022Download PDF (5448K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 738-742
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
Advance online publication: March 19, 2022Download PDF (445K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 743-750
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
Advance online publication: April 15, 2022Download PDF (7887K) Full view HTML -
 2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 751-756
2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 751-756
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
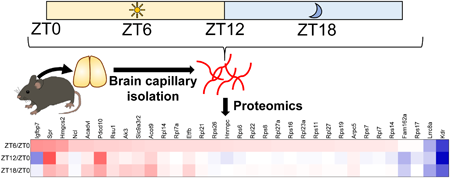
Editor's pickCircadian rhythms influence various physiological functions, including drug distribution and efficacy. However, the influence of circadian rhythms on the blood-brain barrier (BBB) remains unclear. Ogata et al. comprehensively investigated diurnal protein changes in mouse BBB by quantitative proteomics analysis. Expression of proteins associated with transport and physical barrier at the BBB remained constant throughout the day, whereas expression of proteins involved in protein synthesis, angiogenesis, and energy metabolism varied diurnally. These findings may help predict the biological responses to circadian changes in the BBB and brain drug distribution.
Download PDF (2294K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 757-762
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
Download PDF (412K) Full view HTML -
 2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 763-769
2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 763-769
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
Advance online publication: April 02, 2022Editor's pickAn administration plan for vancomycin in bedridden elderly patients has not been established. This study evaluated the prediction accuracy of the Bayesian-derived area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) of vancomycin using creatinine-based equations for estimating kidney function in such patients. In this paper, the authors showed that the Bayesian approach using the estimated creatinine clearance calculated by substituting the serum creatinine level + 0.2 into the Cockcroft-Gault equation has the highest prediction accuracy for the AUC in bedridden elderly patients. These results may contribute to improving the efficacy and safety of vancomycin in such patients.
Download PDF (701K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 770-779
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
Download PDF (4161K) Full view HTML -
 2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 780-792
2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 780-792
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
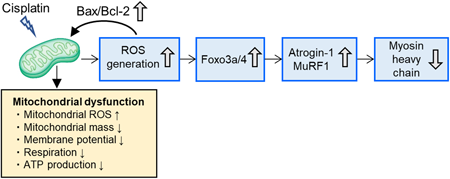
Advance online publication: April 08, 2022Editor's pickRecently, chemotherapy-induced secondary sarcopenia has emerged as an important clinical issue; however, the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood. In this study, the authors focused on the possible involvement of mitochondrial disturbances in cisplatin-induced muscle atrophy using a cellular model. They concluded that mitochondrial dysfunction and the resultant generation of excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS), but not energy disruption, play a central role in cisplatin-induced C2C12 myotube atrophy. These results suggest that mitochondrial protection and/or ROS scavenging may be promising strategies for preventing muscle atrophy associated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy.
Download PDF (3038K) Full view HTML
-
2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 793-797
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
Download PDF (703K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 798-802
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
Download PDF (1278K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 6 Pages 803-805
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
Download PDF (476K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|