- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 549-555
Published: March 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2024
Download PDF (2418K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 556-561
Published: March 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2024
Download PDF (2458K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 562-579
Published: March 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2024
Download PDF (730K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 580-590
Published: March 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2024
Download PDF (10329K) Full view HTML
-
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 591-599
Published: March 05, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 05, 2024
Download PDF (4309K) Full view HTML
-
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 600-605
Published: March 05, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 05, 2024
Download PDF (1119K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 606-610
Published: March 08, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 08, 2024
Download PDF (559K) Full view HTML
-
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 611-619
Published: March 13, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 13, 2024
Download PDF (981K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 620-628
Published: March 13, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 13, 2024
Download PDF (15133K) Full view HTML
-
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 629-634
Published: March 15, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 15, 2024
Download PDF (650K) Full view HTML
-
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 635-640
Published: March 15, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 15, 2024
Download PDF (1444K) Full view HTML -
 2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 641-651
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 641-651
Published: March 19, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 19, 2024
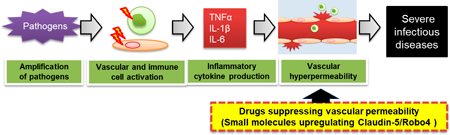
Editor's pickMitochondrial dysfunction is recognized as a key factor in the pathological progression of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and can disrupt the balance of intracellular metabolic pathways (e.g., oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis). The authors focused on oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL), reported to a primary component accumulated in the retina of AMD patients, and elucidated its effect on metabolic alterations with increased mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production in retinal pigment epithelial cells. It was discovered that prolonged exposure to ox-LDL is crucial for the induction of these metabolic alterations. These significantly contribute to understanding the mechanisms underlying AMD metabolic alterations.
Download PDF (6119K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 652-659
Published: March 19, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 19, 2024
Download PDF (740K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 660-668
Published: March 20, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 20, 2024
Download PDF (2068K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 669-679
Published: March 21, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 21, 2024
Download PDF (1026K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 680-691
Published: March 22, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 22, 2024
Download PDF (8436K) Full view HTML -
 2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 692-697
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 692-697
Published: March 25, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
Advance online publication: February 28, 2024Editor's pickManagement of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) after delayed periods presents a significant challenge in cancer chemotherapy. This study represents the first attempt to compare the administration of fosnetupitant (F-NTP), fosaprepitant (F-APR), or aprepitant (APR) from 0 to 168 hours following the initial doses of cisplatin-based regimens. The authors demonstrated that F-NTP was significantly more effective than F-APR and APR in reducing CINV after anticancer drug administration from 0 to 168 hours, without significant side effects. The efficacy of F-NTP was particularly effective in the beyond-delayed periods (120-168 hours), which is the focus of attention of the revised Japanese antiemetic guidelines.
Download PDF (368K) Full view HTML -
 2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 698-707
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 698-707
Published: March 26, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 26, 2024
Editor's pick[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
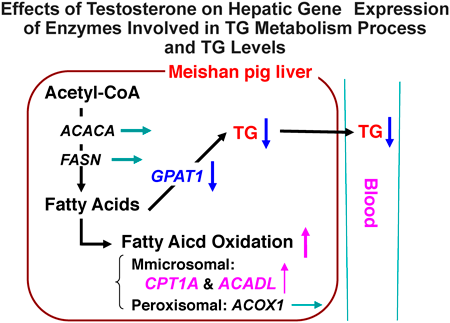
The study examined which cells are responsible for responding to the LNPs used in the approved COVID-19 mRNA vaccine. In this study, the authors incubated immortalized mouse lymphatic endothelial cells (mLECs) or professional antigen presenting cells (APCs) such as RAW 264.7 monocyte/macrophage cells with SM-102 LNPs that contained no mRNA. As a result, chemokines involved in the recruitment of monocytes/neutrophils were produced only by the mLECs following the empty LNP treatment. These findings indicate that LECs appear to serve as the cells that send out initial signals to response LNPs.Download PDF (1578K) Full view HTML
-
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 708-712
Published: March 26, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 26, 2024
Download PDF (328K) Full view HTML
-
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 713-722
Published: March 27, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 27, 2024
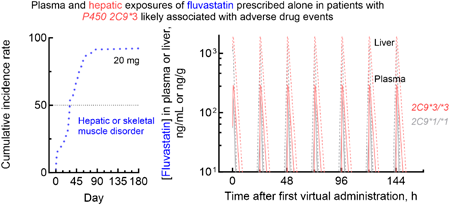
Advance online publication: March 01, 2024Download PDF (4536K) Full view HTML -
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 723-731
Published: March 28, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 28, 2024
Download PDF (2177K) Full view HTML -
 2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 732-738
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 732-738
Published: March 29, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 29, 2024
Editor's pickThe authors mainly investigated the risk factors and preventive strategies of cetuximab-induced hypomagnesemia in head and neck cancer (HNC) patients. Their results indicated that a low pre-treatment serum magnesium level emerges as the only risk factor, and this risk can be effectively mitigated through intravenous prophylactic magnesium sulfate administration from initiating cetuximab treatment. This preventive intervention exhibits minimal adverse events and is thus recommended for managing cetuximab-induced hypomagnesemia. Given that cetuximab interruption due to adverse events directly impacts prognosis, the insights gleaned from their study hold significant relevance for the optimal care of HNC patients undergoing cetuximab treatment.
Download PDF (593K) Full view HTML -
 2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 739-749
2024Volume 47Issue 3 Pages 739-749
Published: March 30, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 30, 2024
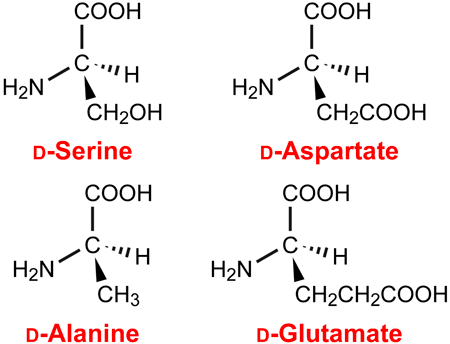
Editor's pickDiabetes patients are well-known to exhibit alteration of taste sensitivity, but the alteration profiles have not been clarified in detail yet. In brief-access tests with a mixture of sucrose and quinine hydrochloride, the lick ratios of control, but not non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM)-model, rats for the mixture and quinine hydrochloride solutions decreased aging-dependently. Metagenomic analysis of gut microbiota revealed strain- and aging-dependent alteration of mucus layer-regulatory microbiota. These findings suggested that control, but not NIDDM-model, rats exhibited an aging-dependent increase of bitter taste sensitivity with alteration of gut microbiota.
Download PDF (5689K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|