- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 138
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (187K) Full view HTML
-
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 139-146
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (1614K) Full view HTML
-
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 147-157
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (2104K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 158-162
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (945K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 163-169
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (4123K) Full view HTML
-
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 170-176
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (915K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 177-186
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (1503K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 187-193
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (7181K) Full view HTML -
 2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 194-200
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 194-200
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
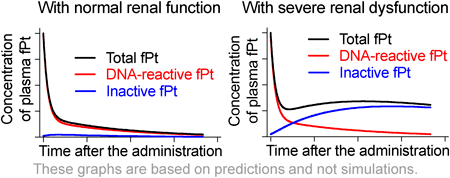
Editor's pickOxaliplatin is a platinum (Pt)-based chemotherapeutic drug that is widely used to treat gastrointestinal and pancreatic cancers. The authors hypothesized that the DNA-binding capacity is one of the properties of reactive Pt species and aimed to evaluate the contribution of the kidney to the plasma levels of DNA-reactive Pt in an animal model and a hemodialysis patient. The results of this study showed that severe renal dysfunction has a limited effect on the plasma levels of DNA-reactive Pt after oxaliplatin administration.
Download PDF (677K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 201-208
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (2714K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 209-218
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (8925K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 219-229
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Advance online publication: December 14, 2022Download PDF (5803K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 230-236
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (644K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 237-244
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Advance online publication: December 07, 2022Download PDF (459K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 245-256
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (16679K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 257-262
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (1864K) Full view HTML -
 2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 263-271
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 263-271
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (4167K) Full view HTML -
 2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 272-278
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 272-278
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
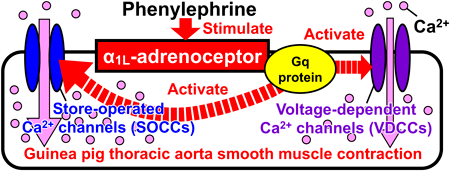
Advance online publication: December 16, 2022Editor's pickVascular damage is often seen in patients with diabetes and is thought to be caused by oxidative stress. Xanthine oxidoreductase exists both intracellularly and extracellularly and causes vascular injury by producing reactive oxygen species. The authors investigated the effects of topiroxostat, a xanthine oxidase inhibitor, and its mechanism of action in a rodent model of diabetes. They found that topiroxostat inhibited anchored xanthine oxidase bound to the surface of vascular endothelial cells in the thoracic aorta and suppressed damage to these cells, suggesting that topiroxostat could potentially have a vasoprotective effect in patients with diabetes-induced macrovascular disease.
Download PDF (1973K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 279-285
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (898K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 286-291
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (421K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 292-300
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (1318K) Full view HTML -
 2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 301-308
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 301-308
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Editor's pickmRNA has many challenges including insufficient delivery owing to the high molecular weight and high negative charge. Authors chemically synthesized a minimal mRNA vaccine encoding human gp10025-33 peptide (KVPRNQDWL), as a potential treatment for melanoma and iontophoresis (IP) was used for its delivery into the skin. After combining IP with the newly synthetized minimal mRNA vaccine, successful intradermal and intracellular delivery of the minimal mRNA was achieved. Results showed stimulation of the immune system which led to tumor inhibition and infiltration of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells in the tumor tissue. This is the first report combining IP and chemically synthesized minimal mRNA vaccine.
Download PDF (6836K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 309-319
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (1036K) Full view HTML -
 2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 320-333
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 320-333
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Editor's pickCholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain are known to degenerate early stage of Alzheimer's disease (AD), and amyloid-β (Aβ) oligomers are suggested to be deeply involved in AD pathogenesis. Authors here established an Aβ oligomer-induced neurodegeneration model using human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cholinergic neurons and demonstrated the neuroprotective effect of plantainoside B identified from herbal extracts as an Aβ-binding small molecule. Radioisotope-labeled plantainoside B showed affinities to Aβ oligomers and brain sections from a mouse model of AD. Results suggest the potential of developing “theranostics” in AD that simultaneously performs diagnoses (Aβ detection) and therapy (neuroprotection).
Download PDF (8840K) Full view HTML
-
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 334-337
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (746K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 338-342
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (1108K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 343-347
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (2883K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 348-353
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (1663K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 354-358
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (611K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 2 Pages 359-363
Published: February 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2023
Download PDF (1919K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|