- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 1-10
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 1-10
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
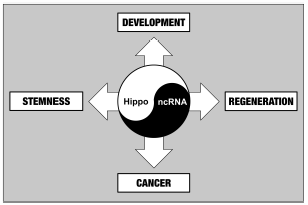
Editor's pickExtensive studies in recent years have revealed important functions of the Hippo intracellular signaling pathway in the control of organ development, stem cell biology, regeneration, and cancer. While a number of novel drugs are currently under development to modulate the Hippo pathway for cancer treatment and regenerative medicine, the molecular networks involving in the regulation of the Hippo pathway are just beginning to be elucidated. The review article by Shimoda and Moroishi summarizes the emerging understanding of the interplay between the Hippo pathway and non-coding RNAs, discussing a new approach to target this pathway for future drug discovery.
Download PDF (776K) Full view HTML
-
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 11
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Download PDF (158K) Full view HTML
-
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 12-19
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Download PDF (1067K) Full view HTML -
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 20-30
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Download PDF (1863K) Full view HTML -
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 31-35
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Download PDF (432K) Full view HTML -
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 36-40
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Download PDF (1313K) Full view HTML -
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 41-48
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Download PDF (1760K) Full view HTML
-
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 49-52
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Download PDF (522K) Full view HTML -
 2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 53-58
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 53-58
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
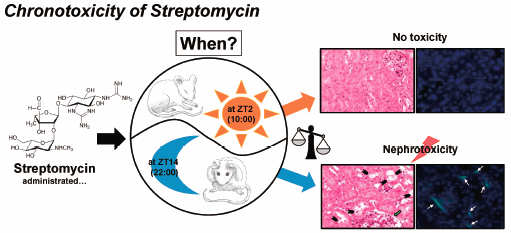
Editor's pickYoshioka and Miura et al. have focused on the relationship between the injection timings and the severity of toxicity, which they advocated as “chronotoxicology”. The aim of this study was to investigate the “chronotoxicity” of streptomycin (SM) in relation to its circadian periodicity. Both the mortality and the nephrotoxicity levels were severe by the SM injection during the “dark phase” than during the “light phase”, representing that SM showed evident chronotoxicity. The results indicated that chronotoxicology may provide valuable information on the importance of injection timings for evaluations of toxicity, and considering when determining any undesirable side effects.
Download PDF (2546K) Full view HTML -
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 59-67
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Download PDF (947K) Full view HTML -
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 68-76
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Download PDF (1128K) Full view HTML -
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 77-86
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Download PDF (373K) Full view HTML -
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 87-92
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Download PDF (2439K) Full view HTML -
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 93-101
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Download PDF (4855K) Full view HTML -
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 102-109
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Download PDF (599K) Full view HTML -
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 110-115
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Download PDF (3754K) Full view HTML -
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 116-123
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Download PDF (773K) Full view HTML -
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 124-128
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Advance online publication: October 24, 2019Download PDF (426K) Full view HTML -
 2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 129-137
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 129-137
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Editor's pickAllergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is one of the most common skin diseases caused by hapten-modified proteins. The article demonstrated that metformin inhibited inflammatory responses in macrophages. Furthermore, metformin also enhanced autophagic flux, inhibited the phosphorylation of AKT/mTOR, MAPKs related protein levels and the level of miR-221 in macrophages. Besides, metformin attenuated 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene (DNFB) -induced ACD partly through the inhibition of macrophage activation and the induction of autophagic flux. Taken together, the results indicated that metformin ameliorates ACD through enhanced autophagic flux to inhibit macrophage activation and provides a potential contribution to ACD treatment.
Download PDF (4387K) Full view HTML -
 2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 138-144
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 138-144
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Editor's pickThrombin is a serine protease as a blood coagulation factor, but also has been implicated in the pathology of brain ischemia, stroke or neurogenerative diseases. In this study, Akaishi et al. have demonstrated that the synthetic curcumin derivative CNB-001 suppresses thrombin-induced NO production through the inhibition of ERK and p38 MAPK pathways in microglia. In contrast, the authors have previously reported that CNB-001 suppressed LPS-induced NO production through the inhibition of p38 MAPK, but not ERK. Therefore, additional studies on differences in signaling cascades by which thrombin and LPS promote ERK phosphorylation will help to identify the direct molecular target of CNB-001.
Download PDF (1165K) Full view HTML -
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 145-152
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Advance online publication: October 30, 2019Download PDF (2472K) Full view HTML -
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 153-157
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Download PDF (2463K) Full view HTML -
 2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 158-168
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 158-168
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Editor's pickHypersensitive reaction to pathogenic attacks in plants triggers the expression of numerous plant genes encoding defense proteins. Pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins play an important role in inducing strong self-defense systems by getting accumulated in intercellular parts and vacuoles. Joo et al. cloned a PR protein gene from Oenanthe javanica (OJPR), which included PR-10 allergen without putative IgE binding residues, comprising 154-amino acids with a molecular mass of 16 kDa. The results of this study suggested that the newly identified and expressed OJPR may possess the biological activity and play a role in modulating host defense responses via Toll-like receptor signal cascades together with anti-viral activities in immune cells.
Download PDF (2546K) Full view HTML
-
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 169-174
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Advance online publication: October 22, 2019Download PDF (554K) Full view HTML -
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 175-178
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Download PDF (391K) Full view HTML -
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 179-183
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Download PDF (476K) Full view HTML -
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 184-187
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Download PDF (972K) Full view HTML -
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 188-193
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Download PDF (715K) Full view HTML
-
2020 Volume 43 Issue 1 Pages 194
Published: January 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
Download PDF (83K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|