- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1435-1442
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Download PDF (2761K) Full view HTML
-
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1443-1447
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Download PDF (460K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1448-1450
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Advance online publication: August 04, 2020Download PDF (648K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1451-1454
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Download PDF (2857K) Full view HTML
-
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1455-1462
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Advance online publication: August 04, 2020Download PDF (891K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1463-1468
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Download PDF (449K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1469-1475
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Advance online publication: August 08, 2020Download PDF (1833K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1476-1480
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Download PDF (331K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1481-1489
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Download PDF (1986K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1490-1500
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Advance online publication: August 13, 2020Download PDF (2999K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1501-1505
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Download PDF (737K) Full view HTML -
 2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1506-1510
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1506-1510
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Editor's pickThe usefulness of the urine protein:creatine ratio (UPCR) in management of molecular targeted therapy has not been studied, although urine protein dipstick testing (uPr) is widely used. The authors investigated the usefulness of UPCR as compared to uPr in patients undergoing molecular targeted therapy for advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC). They found that uPr-based grade tends to be higher than UPCR-based grade, which may lead to overestimate of proteinuria and unnecessary interruption of treatment. UPCR may be a better tool for evaluation of proteinuria in RCC patients receiving molecular targeted therapy.
Download PDF (424K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1511-1518
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Download PDF (3689K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1519-1525
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Download PDF (390K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1526-1533
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Download PDF (3083K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1534-1541
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Download PDF (3736K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1542-1550
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Advance online publication: August 05, 2020Download PDF (4246K) Full view HTML -
 2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1551-1555
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1551-1555
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Advance online publication: August 04, 2020Editor's pickIntroduction: The present study was designed to explore the impacts of sinomenine on cell proliferation and invasion ability of RB cells and the related mechanism. WERI-RB-1 and Y79 cells were cultured and treated by different concentration of sinomenine. The authors found that sinomenine was able to decrease the proliferation and promote the apoptosis of RB cells in a dose-dependent manner; and also significantly suppressed the migration as well as invasion ability of WERI-RB-1 and Y79 cells in vitro via regulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, suggesting that sinomenine has the potential to become an alternative medication for the treatment of RB.
Download PDF (2987K) Full view HTML -
 2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1556-1561
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1556-1561
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
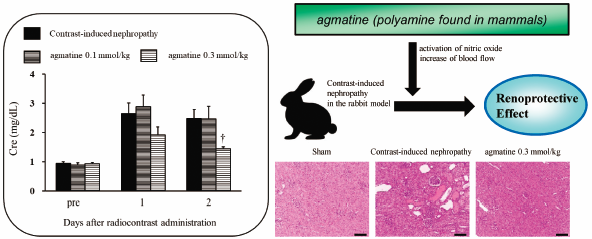
Editor's pickThe rapid degradation in kidney function caused by contrast media usually is temporary, but it can result in chronic kidney disease or even end-stage renal disease. Contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) is a common clinical problem for which there is no effective medical treatment. The aim of this study was to examine the protective effects of agmatine, which is a polyamine found in mammals, in a rat and a rabbit model of CIN. The results indicate that agmatine prevents the development of CIN-induced renal insufficiency in rabbits, and the effect is accompanied by activation of nitric oxide synthase and subsequent increase of blood flow.
Download PDF (4738K) Full view HTML -
 2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1562-1569
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1562-1569
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Editor's pickElaidic acid (EA) is the most abundant food-derived trans-fatty acid (TFA), whose intake is associated with neurodegenerative diseases (NDs) including Alzheimer’s disease. Hirata et al. provide evidence implicating a novel microglial apoptosis signaling pathway in TFA-related NDs. In microglial cell lines such as MG6 and BV2, extracellular ATP, a damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) leaked from injured cells, triggered reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent activation of the apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1)-p38 MAP kinase pathway, and ultimately apoptosis. EA strongly enhanced activation of the microglial apoptosis pathway, which may account for the underlying pathological mechanisms of TFA-related NDs that are closely associated with neuronal cell death and inflammation.
Download PDF (1273K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1570-1576
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Download PDF (530K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1577-1582
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Advance online publication: August 14, 2020Download PDF (387K) Full view HTML -
 2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1583-1590
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1583-1590
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Editor's pickCinacalcet is a calcimimetic that permits impaired endothelial functions to be recovered via inhibiting parathyroid hormone (PTH) production in SHPT patients receiving hemodialysis. However, the underlying mechanism for its action remains unknown. The article by Imafuku et al. reported cinacalcet improves the redox status of human serum albumin (HSA) by inhibiting PTH production and partially by its radical scavenging action and increaed the anti-oxidant defense system in the blood circulation of SHPT patients. Such an anti-oxidative action of cinacalcet may, in part, explain the reduced risk for cardiovascular and all-cause mortality during cinacalcet treatment.
Download PDF (650K) Full view HTML
-
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1591-1594
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Download PDF (3515K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1595-1599
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Advance online publication: July 29, 2020Download PDF (548K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1600-1603
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Download PDF (474K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1604-1608
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Download PDF (1040K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1609-1614
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Download PDF (1675K) Full view HTML
-
2020Volume 43Issue 10 Pages 1615
Published: October 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2020
Download PDF (108K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|