- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1815-1822
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1815-1822
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
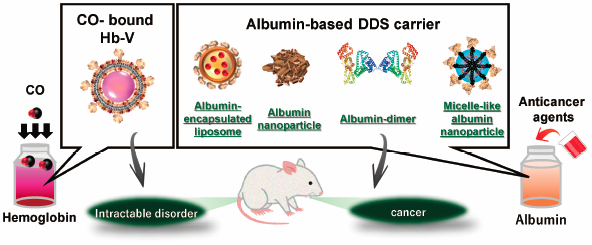
Editor's pickHemoglobin and albumin are biogenic molecules with unique and interesting inherent characteristics. The utilization of their inherent characteristics makes it possible to develop innovative pharmaceutical and biomedical preparations for the treatment and diagnosis of intractable disorders that can be a groundbreaking strategy to resolve and improve several clinical problems. In this review, author introduces the pharmaceutical technology, strategies, and therapeutic application of drug delivery system carriers that have been designed on the basis of the structure and function of hemoglobin and albumin.
Download PDF (2549K) Full view HTML
-
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1823-1830
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Advance online publication: September 19, 2020Download PDF (2817K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1831-1838
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Download PDF (1087K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1839-1846
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Download PDF (1487K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1847-1858
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Download PDF (4191K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1859-1866
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Download PDF (1785K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1867-1875
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Download PDF (883K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1876-1883
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Download PDF (858K) Full view HTML -
 2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1884-1892
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1884-1892
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Editor's pickBone damage in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) occurs in an early stage after disease onset, and osteoclasts play a pivotal role in its progression and subsequent irreversible structural destruction of joints. Colony stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) is a receptor protein tyrosine kinase specifically expressed in monocytic-lineage cells such as macrophages and osteoclasts. Authors investigated the effect of JTE-952, a novel CSF1R tyrosine kinase inhibitor, on osteoclast formation in vitro and on bone destruction in an animal model of RA. In this article, Uesato et al. suggested that JTE-952 effectively prevents the progression of the structural destruction of joints, a major unmet clinical need for RA.
Download PDF (3924K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1893-1898
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Advance online publication: October 01, 2020Download PDF (2366K) Full view HTML -
 2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1899-1905
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1899-1905
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
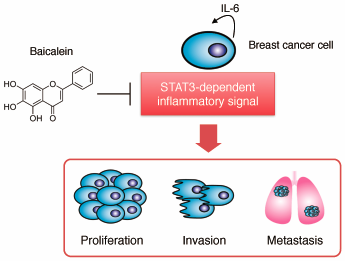
Editor's pickSignal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) plays an essential role in a pro-carcinogenic inflammatory microenvironment, both at the initiation of malignant transformation and during cancer progression. In this study, Hayakawa and colleagues found that baicalein, a flavone isolated from the roots of Scutelleria baicalensis, inhibited STAT3 transcriptional activity and its phosphorylation, and further exhibited anti-proliferative effects in breast cancer cells. Moreover, baicalein suppressed the production of IL-6 and the metastatic potential of breast cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. This study suggests baicalein as an attractive phytochemical compound for reducing metastatic potential of breast cancer cells by regulating STAT3 activity.
Download PDF (2828K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1906-1910
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Download PDF (577K) Full view HTML -
 2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1911-1916
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1911-1916
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Editor's pickRoyal jelly (RJ) is a well-known functional foodstuff derived from honey bees and contains various functional substances. In this report, the authors focused on major royal jelly protein 3 (MRJP3), which is one of the major protein components in RJ, and found that MRJP3 possessed cell proliferation activities in cultured cell lines. The activities were identified in the tandem penta-peptide repeats (TPRs) consisting of Q-N-x-N-[K/R] at its C-terminus of MRJP3. As the cell proliferation activities remained even after treatment of TRPs with trypsin, it is plausible that the penta-peptide is the minimal functional unit.
Download PDF (985K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1917-1923
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Advance online publication: October 02, 2020Download PDF (545K) Full view HTML -
 2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1924-1930
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1924-1930
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Editor's pickIn this study, Maki et al., evaluated changes in DNA methylation induced by silver nanoparticles and attempted to elucidate the induction mechanism. The results showed that silver nanoparticles with diameter of 10 nm (nAg10) induces DNA hypomethylation accompanied with a decrease in the level of Dnmt1 in A549 alveolar epithelial cells. We The authors also revealed that nAg10 promotes the degradation of Dnmt1 by the proteasome system. Collectively, these results suggest that nAg10 induced DNA hypomethylation through a proteasome-mediated degradation of Dnmt1. This paper provides basic evidence for the effect of silver nanoparticles on DNA methylation.
Download PDF (4270K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1931-1939
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Download PDF (2497K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1940-1944
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Download PDF (2051K) Full view HTML
-
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1945-1949
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Download PDF (723K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1950-1953
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Download PDF (575K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1954-1959
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Download PDF (562K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1960-1965
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Download PDF (434K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1966-1968
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Download PDF (423K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1969-1974
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Download PDF (565K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1975-1978
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Download PDF (1310K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1979-1982
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Advance online publication: September 30, 2020Download PDF (497K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1983-1986
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Download PDF (2231K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1987-1992
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Download PDF (963K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 12 Pages 1993-1996
Published: December 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Advance online publication: October 06, 2020Download PDF (569K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|