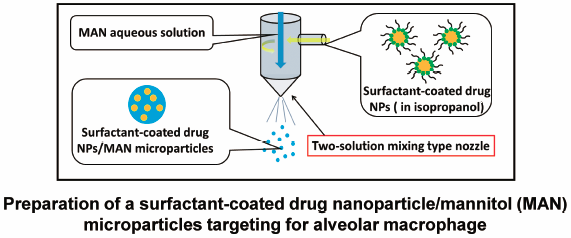
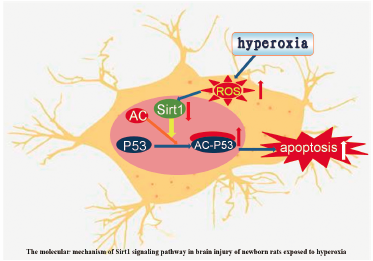
Volume 42, Issue 11
Displaying 1-26 of 26 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Review
-
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1773-1782
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Download PDF (5099K) Full view HTML
Regular Articles
-
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1783-1788
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Advance online publication: August 07, 2019Download PDF (1320K) Full view HTML -
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1789-1798
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Download PDF (5753K) Full view HTML -
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1799-1804
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Download PDF (523K) Full view HTML -
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1805-1813
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Advance online publication: August 20, 2019Download PDF (741K) Full view HTML -
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1814-1822
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Download PDF (2384K) Full view HTML -
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1823-1829
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Download PDF (17112K) Full view HTML -
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1830-1838
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Advance online publication: August 21, 2019Download PDF (6473K) Full view HTML -
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1839-1845
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Download PDF (762K) Full view HTML -
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1846-1853
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Download PDF (2924K) Full view HTML -
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1854-1860
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Advance online publication: September 13, 2019Download PDF (5771K) Full view HTML -
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1861-1866
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Advance online publication: September 03, 2019Download PDF (512K) Full view HTML -
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1867-1876
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Advance online publication: September 03, 2019Download PDF (4228K) Full view HTML -
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1877-1882
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Download PDF (539K) Full view HTML -
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1883-1890
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Download PDF (8918K) Full view HTML -
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1891-1897
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Download PDF (411K) Full view HTML -
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1898-1905
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Download PDF (5091K) Full view HTML -
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1906-1912
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Download PDF (698K) Full view HTML -
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1913-1920
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Download PDF (1857K) Full view HTML -
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1921-1925
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Download PDF (882K) Full view HTML -
 2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1926-1935
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1926-1935
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Editor's pickElevated intraocular pressure (IOP) is the major cause of glaucoma, which is the second leading cause of blindness. To develop new IOP-lowering treatments, the article by Nagano et al. generated a novel ATX inhibitor as an ophthalmic drug by high-throughput screening, followed by inhibitor optimization. Administration of the optimized ATX inhibitor (Aiprenon) reduced IOP in laser-treated mice exhibiting elevated IOP and higher level of ATX activity in AH and normal mice in vivo. The stimulation of ATX induced outflow resistance in the trabecular pathway; however, administration of Aiprenon recovered the outflow resistance in vitro.
Download PDF (3780K) Full view HTML -
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1936-1941
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Advance online publication: August 27, 2019Download PDF (1292K) Full view HTML -
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1942-1946
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Advance online publication: August 29, 2019Download PDF (801K) Full view HTML
Notes
-
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1947-1952
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Download PDF (584K) Full view HTML -
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1953-1956
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Download PDF (271K) Full view HTML
Notice of Withdrawal
-
2019Volume 42Issue 11 Pages 1957
Published: November 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2019
Download PDF (119K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|