- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 245-249
Published: March 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2022
Download PDF (1677K) Full view HTML
-
2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 250-259
Published: March 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2022
Download PDF (8467K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 260-267
Published: March 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2022
Advance online publication: January 15, 2022Download PDF (7167K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 268-275
Published: March 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2022
Advance online publication: January 18, 2022Download PDF (2253K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 276-283
Published: March 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2022
Download PDF (1372K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 284-291
Published: March 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2022
Download PDF (3337K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 292-300
Published: March 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2022
Download PDF (3281K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 301-308
Published: March 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2022
Download PDF (1738K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 309-315
Published: March 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2022
Advance online publication: December 22, 2021Download PDF (7193K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 316-322
Published: March 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2022
Download PDF (882K) Full view HTML -
 2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 323-332
2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 323-332
Published: March 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2022
Editor's pickThis report reveals that the persistence rates of infliximab therapy differed across chronic inflammatory diseases in real-world practice. Although infliximab has contributed to the treatment of Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, psoriasis, and rheumatoid arthritis, loss of response to long-term therapy has been a major problem. The authors described the persistence rates of infliximab therapy using the Japanese claims data to estimate its long-term effectiveness. Factors associated with the longer persistence were identified in each disease group. These results could facilitate the proper use of infliximab for persistent successful treatment.
Download PDF (1103K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 333-338
Published: March 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2022
Download PDF (419K) Full view HTML -
 2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 339-353
2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 339-353
Published: March 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2022
Editor's pickThis study reveals that a natural compound, betulin, inhibits the growth of B16 melanoma by enhancing natural killer cell activity through attenuating transforming growth factor (TGF)-b1- and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)-induced immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment. No report has shown such compounds that target TGF-b1- and PGE2-induced immunosuppressive activities so far. Additionally, it is intriguing that the mechanism-of-action of betulin differs from that of TGF-b1 type I receptor kinase inhibitors. Targeting TGF-b1 activity is a promising strategy for cancer therapy. Findings of this study provide new insight to develop drugs for immune checkpoint therapy in an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment.
Download PDF (1906K) Full view HTML -
 2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 354-359
2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 354-359
Published: March 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2022
Editor's pickLive microorganisms with positive effects on the host are known as probiotics. Probiotics secrete extracellular vesicles (EVs) that activate immune response. The authors investigated the involvement of Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) and its downstream signaling of immune cells in cytokines production elicited by EVs from probiotics. TLR2 is a key molecule in EV-mediated immune activation. Furthermore, JNK/MAPK as well as NF-κB signaling pathways play important roles in cytokines production from EV-treated immune cells. These findings offer a promising perspective for the understanding of the host biological function induced by probiotic-derived EVs, which is helpful for developing an EV-based immunotherapeutic system.
Download PDF (1374K) Full view HTML -
 2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 360-363
2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 360-363
Published: March 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2022
Advance online publication: December 21, 2021Editor's pickSpontaneous pain in acute herpes zoster (HZ) is severe, autonomous and inescapable, which makes the patient very uncomfortable. In this study, the authors demonstrated that intravenous injection of fosphenytoin (fPHT), a water-soluble prodrug of phenytoin, suppressed spontaneous pain-related behavior in mice model of acute HZ induced by cutaneous infection with herpes simplex virus type-1. The suppressive effects were more potent than diclofenac or pregabalin. Intravenous fPHT may become a viable option for an acute HZ pain, especially for spontaneous pain.
Download PDF (494K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 364-373
Published: March 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2022
Download PDF (2111K) Full view HTML
-
 2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 374-377
2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 374-377
Published: March 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2022
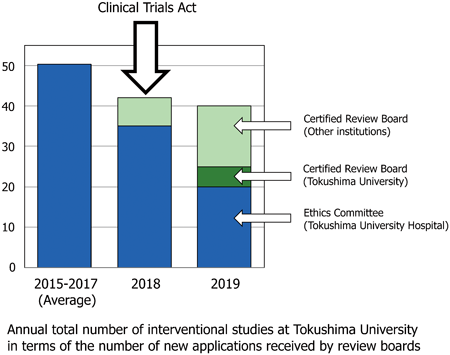
Editor's pickThe Clinical Trials Act was enforced in 2018 with the aim of ensuring public trust in clinical research. The authors examined the activity of interventional research before and after the enforcement of the law, using the number of applications to the ethics committees as an indicator at a university hospital with a certified review board. It was found that the number of applications tended to decrease with the enforcement of the law. Possible way to promote clinical studies in the new Clinical Trials Act era should be further examined.
Download PDF (309K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 3 Pages 378-381
Published: March 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2022
Download PDF (650K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|