- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 599-604
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2021
Download PDF (1188K) Full view HTML
-
2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 605-610
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2021
Advance online publication: February 20, 2021Download PDF (413K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 611-619
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2021
Download PDF (559K) Full view HTML -
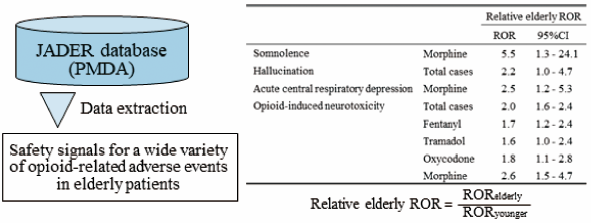
2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 620-626
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2021
Download PDF (406K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 627-634
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2021
Download PDF (605K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 635-641
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2021
Download PDF (1006K) Full view HTML -
 2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 642-652
2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 642-652
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2021
Advance online publication: March 04, 2021Editor's pickThe article by Nomura et al. suggested a novel mechanism of radiation-induced DNA damage repair contributing to radioresistance in melanoma. Authors have shown that the transient receptor potential melastatin 8 (TRPM8) channel is involved in radiation-induced DNA damage response, cell death, and cell cycle regulation. Furthermore, TRPM8 channel inhibitor enhanced tumor growth-inhibitory effect by gamma-ray in vivo. These findings proposed that the TRPM8 channel contributes to the resistance of the growth-inhibitory effect of radiation in melanoma and could be a novel molecular target to improve the efficiency of radiation therapy for melanoma.
Download PDF (4857K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 653-658
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2021
Download PDF (540K) Full view HTML -
 2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 659-668
2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 659-668
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2021
Editor's pickPeroxisome proliferator-activated receptor ɤ (PPARɤ) agonists, such as pioglitazone, are anti-diabetic drugs, but they cause PPARɤ-related adverse effects such as body weight gain, cardiac hypertrophy, and bone loss. The authors found that a novel PPARɤ modulator, KY-903, has similar anti-diabetic effects without PPARɤ-related adverse effects in diabetic mice, possibly due to increases in adiponectin without adipogenesis. KY-903 also has anti-obesity effects with slight bone loss in obese rats, possibly by PPARɤ antagonism against endogenous or diet-derived PPARɤ ligands. These findings are useful for research on PPARɤ, and KY-903 is a potential candidate of anti-diabetic and/or anti-obesity drugs.
Download PDF (5116K) Full view HTML -
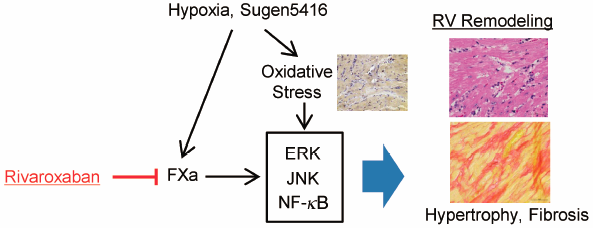
 2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 669-677
2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 669-677
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2021
Advance online publication: February 20, 2021Editor's pickThe authors investigated the effects of rivaroxaban on right ventricular (RV) remodeling in a rat model of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), created with Sugen5416 and chronic hypoxia (SuHx). The Fulton index, RV systolic pressure, and RV Tei index increased by SuHx were significantly decreased when treated with rivaroxaban. Rivaroxaban has the potential of improving RV remodeling in PAH model rats through the suppression of multiple signaling pathways, including ERK, JNK, and NF-kB, associated with protease-activated receptor-2. These findings suggest the additive effects that rivaroxaban may have on the RV remodeling in PAH.
Download PDF (8355K) Full view HTML -
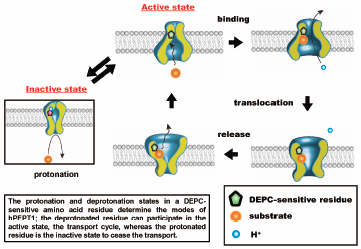
 2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 678-685
2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 678-685
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2021
Editor's pickThe authors indicated that the protonation of the histidine residue at the extracellular site in human oligopeptide transporter (hPEPT1) results in a decrease in the efflux activity, which is distinct from the sites of proton coupling for transport operation and substrate binding. Furthermore, they found that the decrease in extracellular pH reduced the turnover rate of transporters; in other words, the number of available transporters in the cycle was reduced. The protonation/deprotonation state of histidine determines the transport activity; the deprotonated histidine residue can participate in the transport cycle, whereas the protonated histidine residue can cease the transport.
Download PDF (2149K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 686-690
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2021
Download PDF (927K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 691-700
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2021
Download PDF (2779K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 701-706
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2021
Download PDF (755K) Full view HTML -
 2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 707-713
2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 707-713
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2021
Advance online publication: February 27, 2021Editor's pickAtrial fibrillation (AF) is one of the most frequent arrhythmias in patients with hypertension. The authors found that an L/N-type calcium channel blocker cilnidipine exerts anti-AF effects in the remodeled atria of Dahl salt-sensitive rats more potently than amlodipine. Since plasma catecholamine levels is lower in the cilnidipine-treated animals than those in amlodipine-treated ones, blockade of N-type calcium channels presumably contributes to the superior cardioprotective effect of cilnidipine. These findings provide important information for considering treatment of hypertension complicating AF.
Download PDF (2176K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 714-723
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2021
Download PDF (13131K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 724-731
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2021
Download PDF (1170K) Full view HTML
-
2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 732-736
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2021
Download PDF (563K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 737-741
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2021
Download PDF (375K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 5 Pages 742-746
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2021
Download PDF (2986K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|