Volume 41, Issue 3
Displaying 1-23 of 23 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Current Topics - Cutting-Edge Studies Using Artificial Membranes
-
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 287
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Download PDF (176K) Full view HTML
Current Topics: Reviews
-
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 288-293
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Download PDF (1269K) Full view HTML -
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 294-302
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Download PDF (3474K) Full view HTML -
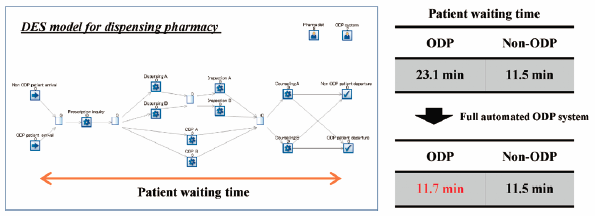
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 303-311
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Download PDF (4145K) Full view HTML
Regular Articles
-
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 312-318
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Download PDF (572K) Full view HTML -
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 319-325
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Download PDF (1275K) Full view HTML -
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 326-337
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Download PDF (1013K) Full view HTML -
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 338-341
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Download PDF (611K) Full view HTML -
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 342-349
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Download PDF (2017K) Full view HTML -
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 350-359
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Advance online publication: December 16, 2017Download PDF (4806K) Full view HTML -
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 360-367
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Download PDF (1550K) Full view HTML -
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 368-373
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Download PDF (947K) Full view HTML -
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 374-382
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Download PDF (1479K) Full view HTML -
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 383-393
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Download PDF (1229K) Full view HTML -
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 394-398
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Download PDF (734K) Full view HTML -
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 399-408
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Download PDF (1211K) Full view HTML -
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 409-418
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Download PDF (646K) Full view HTML -
 2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 419-426
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 419-426
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Advance online publication: December 22, 2017Editor's pickNADPH oxidase (Nox) isozymes are implicated in the diseases associated with oxidative stress, and search of their selective inhibitors has been a focus of attention. By screening microbial metabolites, Nakano and colleagues identified a novel Nox1 inhibitor (NOS31) produced from actinomyces. NOS31 inhibited Nox1-mediated hydrogen peroxide production with high Nox1 selectivity and suppressed proliferation of colon and gastric cancer cells that up-regulate Nox1. Thus, NOS31 may have the therapeutic potential for treating cancer involving the over-activation of Nox1.
Download PDF (791K) Full view HTML -
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 427-434
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Download PDF (1637K) Full view HTML -
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 435-439
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Download PDF (459K) Full view HTML
Notes
-
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 440-444
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Download PDF (1772K) Full view HTML -
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 445-449
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Download PDF (1046K) Full view HTML
Errata
-
2018 Volume 41 Issue 3 Pages 450
Published: March 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2018
Download PDF (144K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|