- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 806-812
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 806-812
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
Editor's pickDespite the usefulness of nanoparticles, there are now safety concerns about their use. Therefore, the importance of evaluating the safety of vulnerable generations such as pregnant women and infants, who are highly sensitive to chemical substances, has been pointed out worldwide. From this perspective, to analyze the risk from nanoparticles to vulnerable generations, nano-safety science and nano-safety design research has been conducted. The findings of these studies will lead not only to develop a nanotechnology that will enable the sustainable use of nanoparticles; they will also contribute to future developments in the field of health science.
Download PDF (804K) Full view HTML
-
 2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 813
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 813
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
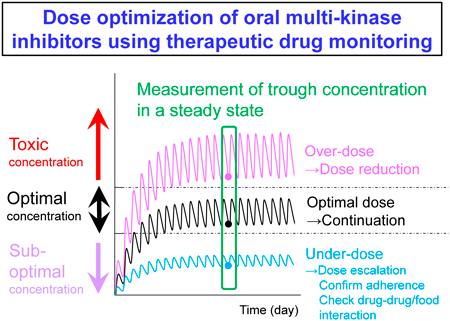
Editor's pickRecently, therapeutic drug monitoring is recommended for many drugs even though the procedure is not covered by health insurance. This Current Topic focuses on four areas: (1) anticancer drugs, (2) anti-infective agents, (3) antipsychotics/antidepressants, and (4) antibody drugs. Among the drugs that are not approved for insurance coverage in Japan, the drugs for which TDM is recommended and drugs that are likely to be approved in the future are summarized in a review, which include their pharmacokinetic characteristics and the usefulness of TDM.
Download PDF (181K) Full view HTML
-
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 814-823
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
Download PDF (597K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 824-833
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
Download PDF (2855K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 834-842
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
Download PDF (666K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 843-846
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
Download PDF (580K) Full view HTML
-
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 847-850
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
Download PDF (1015K) Full view HTML -
 2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 851-855
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 851-855
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
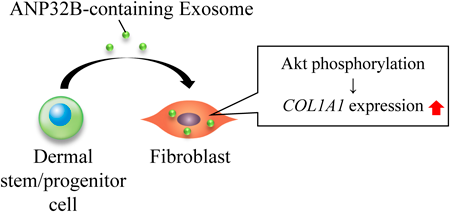
Editor's pickAntibodies that specifically target biomarkers are essential in clinical diagnosis. Genetic engineering has assisted in designing novel antibodies that offer greater antigen-binding affinities, thus providing more sensitive immunoassays. Authors have succeeded in generating a single-chain Fv fragment (scFv) targeted estradiol-17b (E2) with more than 370-fold improved affinity (Ka 3.2 ´ 1010 M-1), based on a strategy focusing the complementarity-determining region 3 in the VH domain (VH-CDR3). This improvement is the greatest reported for mutagenesis targeting anti-steroid antibodies. The scFv mutant enabled an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay that provided sensitive dose-response curves for determining E2, the midpoint of which was 4.46 pg/assay.
Download PDF (1478K) Full view HTML
-
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 856-862
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
Download PDF (794K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 863-871
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
Advance online publication: April 28, 2022Download PDF (7256K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 872-880
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
Download PDF (2825K) Full view HTML -
 2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 881-887
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 881-887
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
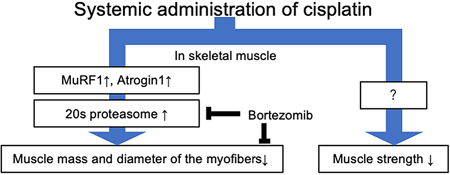
Advance online publication: April 27, 2022Editor's pickFracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX) is a well-known scoring system for predicting the probability of fragility fractures (FF). However, among the factors used in FRAX, glucocorticoid is the only medication factor. Authors assessed the risk of FF at each clinical department using FRAX and medication patterns. As a result, the departments included in the high-risk group by FRAX were not necessarily the same as the departments included in the top group, based on the administered medications. Authors recommend the use of FRAX together with prescribed medications on hospital-wide surveillance of fracture risk assessment.
Download PDF (331K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 888-894
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
Download PDF (1753K) Full view HTML -
 2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 895-903
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 895-903
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
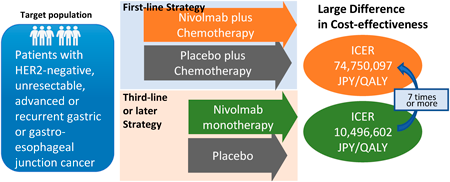
Editor's pickFor the patient, the national health insurance of Japan is a wonderful system which can be proud to the world. Efficiency of medical care is an important issue to make this system sustainable into the future. Nivolumab, a breakthrough cancer drug, is widely effective, but its high price raises efficiency concerns. Authors performed model-based cost-effectiveness analyses in first-line and late-line treatment for advanced gastric cancer. The first-line treatment had an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of more than 7 times that of the late-line treatment. Authors showed challenges between economics and best practices in healthcare.
Download PDF (731K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 904-909
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
Download PDF (683K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 910-918
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
Download PDF (6290K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 919-925
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
Advance online publication: May 14, 2022Download PDF (9686K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 926-933
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
Download PDF (1061K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 934-939
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
Advance online publication: May 17, 2022Download PDF (2913K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 940-947
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
Download PDF (1800K) Full view HTML
-
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 948-954
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
Download PDF (811K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 955-961
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
Download PDF (7649K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 962-967
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
Download PDF (2829K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 7 Pages 968-971
Published: July 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2022
Download PDF (599K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|