- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 2023 Volume 46 Issue 6 Pages 746-755
2023 Volume 46 Issue 6 Pages 746-755
Published: June 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2023
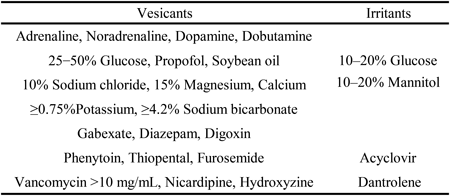
Editor's pickA typical manifestation of iatrogenic injury associated with intravenous injection is extravascular leakage. The severity of injury and treatment for extravascular leakage of cytotoxic agents is well known, however there is insufficient information on non-cytotoxic agents. The authors reviewed human and animal studies of extravascular injury induced by non-cytotoxic agents and classified them based on the severity of injury. The classification of non-cytotoxic agents in the extravasation is useful information in clinical practice to provide appropriate warning of the risk of injury and to prevent worsening of injury.
Download PDF (380K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 6 Pages 756-763
Published: June 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2023
Download PDF (1835K) Full view HTML
-
2023 Volume 46 Issue 6 Pages 764-772
Published: June 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2023
Download PDF (9865K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 6 Pages 773-780
Published: June 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2023
Advance online publication: April 14, 2023Download PDF (5653K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 6 Pages 781-787
Published: June 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2023
Download PDF (1034K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 6 Pages 788-795
Published: June 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2023
Download PDF (860K) Full view HTML -
 2023 Volume 46 Issue 6 Pages 796-802
2023 Volume 46 Issue 6 Pages 796-802
Published: June 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2023
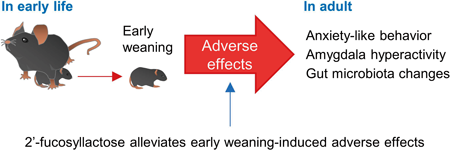
Editor's pickRecently, evidence is accumulating on functional communication between the central nervous system (CNS) and the gut microbiota. Given this, early prebiotic treatment may assist the development of the CNS through the gut microbiota. In this study, Araki et al. found that 2'-fucosyllactose (2´-FL), a human milk oligosaccharide, altered the fecal microbiota and reduced anxiety-like behavior and amygdala hyperactivity observed in mice exposed to early weaning stress. These findings suggest that prebiotic treatment with 2´-FL may alleviate the adverse effects of early life stress in the CNS such as anxiety and amygdala hyperactivity.
Download PDF (2822K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 6 Pages 803-810
Published: June 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2023
Download PDF (5813K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 6 Pages 811-816
Published: June 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2023
Download PDF (3236K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 6 Pages 817-823
Published: June 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2023
Download PDF (440K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 6 Pages 824-829
Published: June 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2023
Download PDF (800K) Full view HTML -
 2023 Volume 46 Issue 6 Pages 830-839
2023 Volume 46 Issue 6 Pages 830-839
Published: June 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2023
Editor's pickIt is believed that 15-lipoxygenase plays a role in tissue damage under conditions of low oxygen levels through lipid-derived radical chain reactions. The authors of this study discovered that when a higher content of linoleate than oxygen content was stood with 15-lipoxygenase in the presence of hydrogen polysulfides, which are believed to be endogenous bioactive substance in cells, the conjugated diene moiety of the oxidized linoleate derivatives was isomerized from E/Z form to E/E form. Based on these findings, authors proposed a hypothesis that hydrogen polysulfides scavenge lipid-derived radicals, generating thiyl radicals, which then isomerized the conjugated diene moiety.
Download PDF (1788K) Full view HTML -
 2023 Volume 46 Issue 6 Pages 840-847
2023 Volume 46 Issue 6 Pages 840-847
Published: June 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2023
Editor's pickLactic acid bacteria (LABs) are well known as beneficial microorganisms to maintain human health. Although LABs are recognized as probiotics, these bacteria produce many kinds of bioactive compounds. The mechanisms how LABs produce these bioactive substances are not well known. Additionally, unlike the cases of E. coli and yeast, there are not enough commercially available tools for a genetic approach of LABs. Therefore, in the present study, the authors have constructed a new plasmid as an efficient genetic engineering tool for random insertional mutagenesis in LABs using a combination of transposon Tn10 and the temperature-sensitive replication system.
Download PDF (1313K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 6 Pages 848-855
Published: June 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2023
Download PDF (678K) Full view HTML -
 2023 Volume 46 Issue 6 Pages 856-863
2023 Volume 46 Issue 6 Pages 856-863
Published: June 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2023
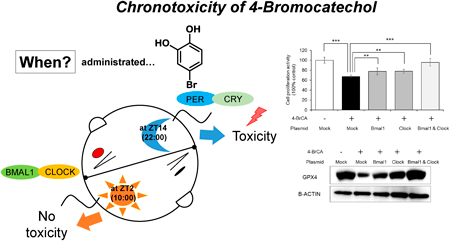
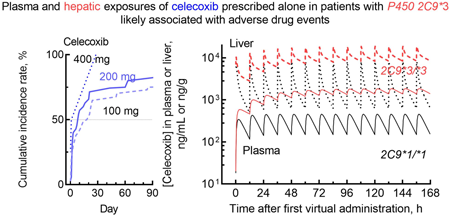
Advance online publication: April 15, 2023Editor's pickAlthough the potential for cytochrome P450 2C9 (CYP2C9) to cause drug interactions, there are few cases of information related to the influence of CYP2C9 polymorphism on drug labeling recommendations in Japan. Among the various factors related to adverse events in the database associated with the prescription of celecoxib or diclofenac alone, variations in the in vivo intrinsic clearance of the drug may exist. Virtual hepatic and plasma exposures estimated by pharmacokinetic modeling in patients harboring impaired CYP2C9*3 could represent a causal factor for adverse events induced by celecoxib or diclofenac in a manner similar to that for drug interactions.
Download PDF (2053K) Full view HTML
-
2023 Volume 46 Issue 6 Pages 864-868
Published: June 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2023
Download PDF (2282K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|