- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 2021 Volume 44 Issue 12 Pages 1801-1809
2021 Volume 44 Issue 12 Pages 1801-1809
Published: December 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2021
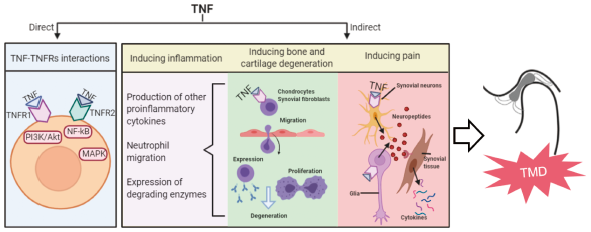
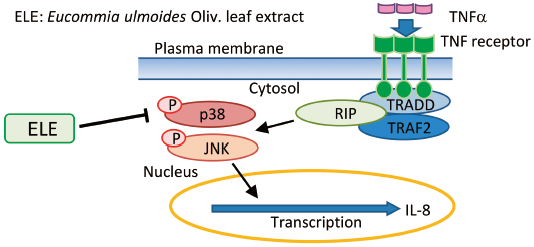
Editor's pickThis article concludes the underlying responses of inflammation in temporomandibular disorder(TMD), a complex and common oral dentofacial disease. One of the most involved inflammatory cytokines--TNF-α, has effects on TMD and its inflammation. These effects are summarized comprehensively and explicitly as triggering immune responses, degenerating bone and cartilage and mediating pain of temporomandibular joint. This review gives an insight into this connection between TNF-α and TMD, which may highlight TNF-α as a new therapeutic target for TMD treatment and therefore provide new insight for therapeutic intervention for TMD.
Download PDF (866K) Full view HTML -
 2021 Volume 44 Issue 12 Pages 1810-1818
2021 Volume 44 Issue 12 Pages 1810-1818
Published: December 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2021
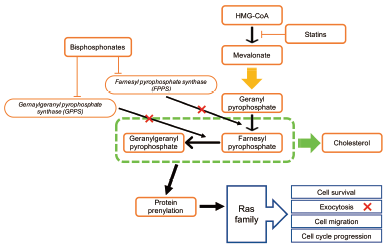
Editor's pickThe signal-transducing adaptor protein (STAP) family, including STAP-1 and STAP-2, contributes to a variety of intracellular signaling pathways. STAP proteins bind to IκB kinase complex, BRK, STAT3, and STAT5, during tumorigenesis and inflammatory/immune responses. STAP proteins positively or negatively regulate critical steps in intracellular signaling pathways through individually unique mechanisms. In this review, the authors describe that STAP proteins are involved in the development and/or progression of some types of malignancies. The authors further describe the possible therapeutic applications of targeting STAP proteins in cancer.
Download PDF (3255K) Full view HTML
-
2021 Volume 44 Issue 12 Pages 1819-1823
Published: December 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2021
Download PDF (644K) Full view HTML
-
2021 Volume 44 Issue 12 Pages 1824-1831
Published: December 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2021
Download PDF (1767K) Full view HTML -
 2021 Volume 44 Issue 12 Pages 1832-1836
2021 Volume 44 Issue 12 Pages 1832-1836
Published: December 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2021
Editor's pickGamma-glutamylcysteine (g-EC) has antioxidant properties similar to those of glutathione (GSH) and acts as its precursor in mammals. In this paper, the reaction conditions of the phytochelatin synthase-like enzyme derived from Nostoc sp. (NsPCS) which hydrolyzes GSH to g-EC was optimized, resulting that high yield conversion from 100 mM GSH to g -EC was achieved in the absence of ATP and other additives. These results suggest that the NsPCS reaction has great potential for the low-cost industrial-scale production of g-EC from GSH.
Download PDF (490K) Full view HTML -
2021 Volume 44 Issue 12 Pages 1837-1842
Published: December 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2021
Advance online publication: October 06, 2021Download PDF (1242K) Full view HTML -
2021 Volume 44 Issue 12 Pages 1843-1850
Published: December 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2021
Advance online publication: October 01, 2021Download PDF (2063K) Full view HTML -
2021 Volume 44 Issue 12 Pages 1851-1859
Published: December 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2021
Download PDF (719K) Full view HTML -
 2021 Volume 44 Issue 12 Pages 1860-1865
2021 Volume 44 Issue 12 Pages 1860-1865
Published: December 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2021
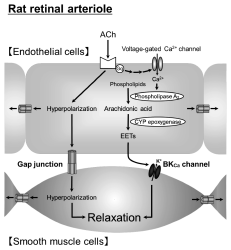
Editor's pickAcetylcholine (ACh) stimulates the production of cytochrome P450 (CYP) epoxygenase-derived epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), which activate large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BKCa) channels. The article by Mori et al. provides evidence suggesting that ACh-induced hyperpolarization of endothelial cells transmits to adjacent smooth muscle cells via myoendothelial gap junctions. ACh can also facilitate gap junctional communication between endothelial cells and/or between smooth muscle cells. These pathways contribute to the hyperpolarization and relaxation of vascular smooth muscle cells in rat retinal arterioles.
Download PDF (1227K) Full view HTML -
2021 Volume 44 Issue 12 Pages 1866-1871
Published: December 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2021
Download PDF (573K) Full view HTML -
2021 Volume 44 Issue 12 Pages 1872-1877
Published: December 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2021
Download PDF (1506K) Full view HTML -
2021 Volume 44 Issue 12 Pages 1878-1885
Published: December 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2021
Download PDF (1629K) Full view HTML
-
2021 Volume 44 Issue 12 Pages 1886-1890
Published: December 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2021
Download PDF (757K) Full view HTML -
2021 Volume 44 Issue 12 Pages 1891-1893
Published: December 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2021
Download PDF (446K) Full view HTML -
 2021 Volume 44 Issue 12 Pages 1894-1897
2021 Volume 44 Issue 12 Pages 1894-1897
Published: December 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2021
Editor's pickDiastolic dysfunction is a major cardiac deficit underlying heart failure accompanying hypertension, coronary artery disease, and diabetes mellitus and is partly mediated by impaired myocardial relaxation and Ca2+ handling. Therapeutic agents targeting diastolic dysfunction are not yet clinically available. Quercetin is one of the major flavonoid compounds contained in fruits and vegetables. The authors examined the lusitropic effect of quercetin on isolated ventricular myocardial tissue preparations from normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice and showed that quercetin accelerated myocardial relaxation through activation of the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. This finding may lead to the development of novel therapeutic agents of natural origin.
Download PDF (390K) Full view HTML -
2021 Volume 44 Issue 12 Pages 1898-1901
Published: December 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2021
Download PDF (1302K) Full view HTML -
2021 Volume 44 Issue 12 Pages 1902-1906
Published: December 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2021
Download PDF (1413K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|