- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1213-1224
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Download PDF (2480K) Full view HTML
-
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1225-1231
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Advance online publication: June 29, 2022Download PDF (669K) Full view HTML
-
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1232-1237
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Download PDF (484K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1238-1245
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Download PDF (5067K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1246-1253
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Download PDF (1882K) Full view HTML -
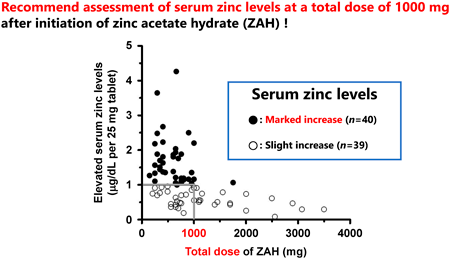
 2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1254-1258
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1254-1258
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
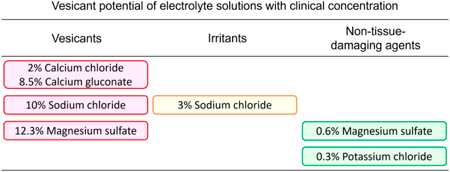
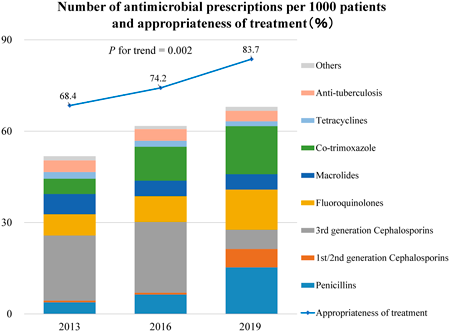
Editor's pickCytotoxic agents are classified according to the severity of skin injury after extravasation. However, injuries caused by extravasation of noncytotoxic agents have not been sufficiently investigated. In this study, the authors focused on noncytotoxic electrolyte solutions and infusions and evaluated skin injuries macroscopically and histopathologically using extravasation model rats. As a result, the electrolyte solutions and infusions were classified into three categories (vesicants, irritants, and non-tissue-damaging agents) depending on the degree of skin injury. The characteristic symptoms and severity of each drug extravasation revealed in this study will provide basic information for preparation of guidelines for treatment of extravasation.
Download PDF (3740K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1259-1268
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Download PDF (949K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1269-1275
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Download PDF (1484K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1276-1282
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Advance online publication: June 21, 2022Download PDF (7703K) Full view HTML -
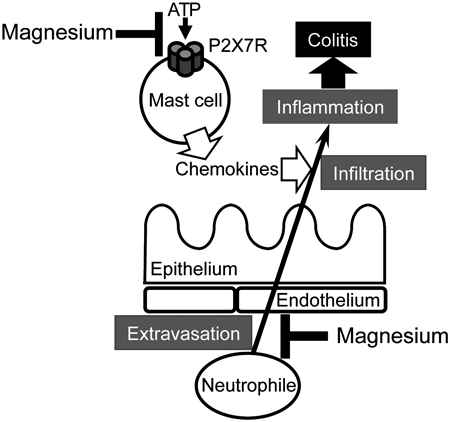
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1283-1290
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Download PDF (6054K) Full view HTML -
 2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1291-1299
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1291-1299
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
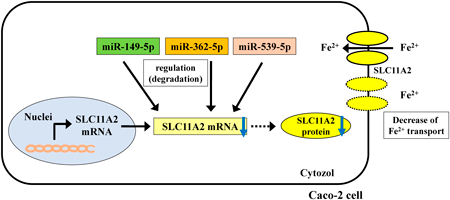
Editor's pickMicroRNAs (miRNAs) are known “key regulator” of numerous gene expressions. In this study, authors determined the effects of three miRNAs, miR-149-5p, miR-362-5p, and miR-539-5p, on iron-ion transporter, SLC11A2 mRNA using the cultured human colon carcinoma cell line. Authors found that they regulate SLC11A2 gene expression and iron-ion transporting function in an in vitro system. Authors believe that this study makes a significant contribution to the literature because the use of these three miRNAs as surrogate biomarkers could significantly advance the development of therapies for the treatments of diseases caused by transporter disorders, such as anemia.
Download PDF (712K) Full view HTML -
 2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1300-1305
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1300-1305
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
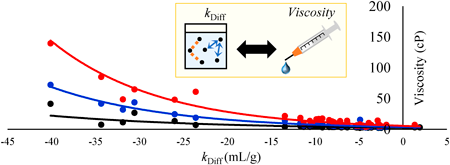
Editor's pickIn antibody drugs, estimating the viscosity at high concentrations is crucial in terms of designing drug formulations since high viscosity could limit the choice of administration routes. The authors hypothesized that the diffusion interaction coefficient may be a key factor in estimating the viscosity and analyzed the relation between them. Not only have the results showed the viscosity can be estimated by using the diffusion interaction coefficient, but it has also succeeded in setting criterions for the feasibility of high concentration formulations. Such findings will deepen the understanding of the physicochemical properties, leading to the promotion of future drug development.
Download PDF (779K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1306-1311
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Download PDF (723K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1312-1320
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Download PDF (5806K) Full view HTML -
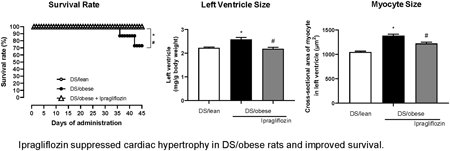
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1321-1331
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Download PDF (5759K) Full view HTML -
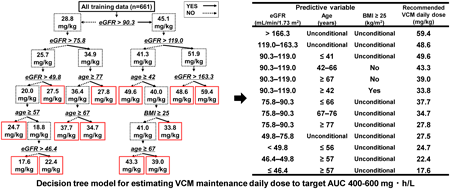
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1332-1339
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Download PDF (730K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1340-1346
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Download PDF (406K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1347-1353
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Download PDF (3611K) Full view HTML -
 2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1354-1363
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1354-1363
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
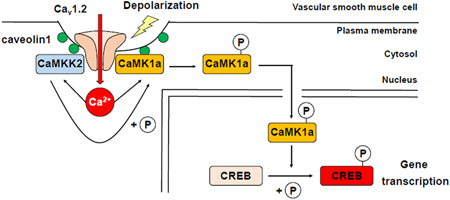
Editor's pickAn increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration activates Ca2+-sensitive enzymes such as Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinases (CaMK) and induces gene transcription in various types of cells through excitation-transcription (E-T) coupling. In this study, the authors revealed that CaMK1α can be fully activated by both Ca2+ influx through of L-type Ca2+ channels, Cav1.2, and phosphorylation by CaMKK2 within caveolae in mouse vascular smooth muscle cells. This activated (phosphorylated) CaMK1a can translocate from the cytosol to the nucleus. These findings strongly suggest that CaMK1a can transduce Ca2+ signaling generated within or very near caveolae to the nucleus and thus, promote E-T coupling.
Download PDF (5170K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1364-1372
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Download PDF (3934K) Full view HTML -
 2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1373-1377
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1373-1377
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Editor's pickProton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or potassium-competitive acid blocker (PCAB) are widely used in Japan. PPIs or PCAB is known to have cardiovascular risk. Authors revealed the cardiovascular risk in each PPI or PCAB components using a large claims data in 91,098 working-age workers. Finally, authors reveal that lansoprazole, a higher CYP2C19 inhibition activity as compared other PPIs or PCAB, is a higher risk for cardiovascular risk.
Download PDF (406K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1378-1384
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Download PDF (2646K) Full view HTML
-
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1385-1388
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Download PDF (513K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1389-1393
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Download PDF (1496K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1394-1397
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Advance online publication: June 25, 2022Download PDF (1018K) Full view HTML -
2022Volume 45Issue 9 Pages 1398-1402
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Download PDF (462K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|