- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1577-1584
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1577-1584
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
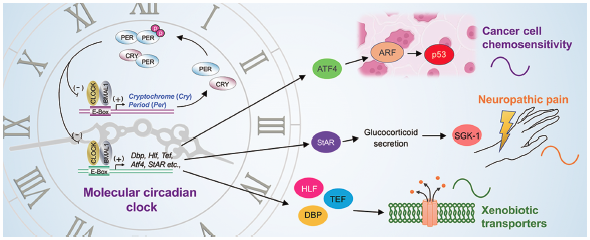
Editor's pickThe sensitivity to drugs and their disposition are changed depending on the circadian time. Hence, choosing appropriate times of day to administer drugs enables to enhance the therapeutic index of pharmacotherapy. On the other hand, various disease conditions also exhibit circadian changes in symptom intensity. Several therapeutic approaches are facilitated by the identification of chemical compound targeted to key molecules that cause circadian exacerbation of disease events. The author describes the current understanding of the role of the circadian biological clock in regulating drug efficacy and disease condition, and also presents ‘chrono-pharmaceutical’ strategy for treatment of diseases and drug development.
Download PDF (3111K) Full view HTML -
 2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1585-1592
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1585-1592
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
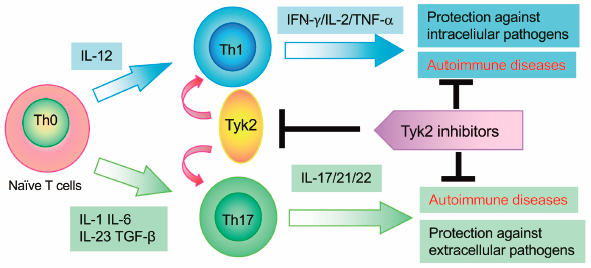
Editor's pickTyrosine kinase 2 (Tyk2) is a member of the Janus family of protein tyrosine kinases (JAKs). Tyk2 associates with interferon (IFN)-α, IFN-β, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-10, IL-12, and IL-23 receptors and mediates their downstream signaling pathways. The authors summarize that Tyk2 plays crucial roles in the differentiation, maintenance, and function of T helper 1 (Th1) and Th17 cells and that its dysregulation in autoimmune and/or inflammatory diseases using Tyk2-deficient mice and cells. The authors further describe that Tyk2 inhibition has great potential for clinical application in the management of a variety of immune-relating diseases.
Download PDF (5274K) Full view HTML
-
 2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1593
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1593
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
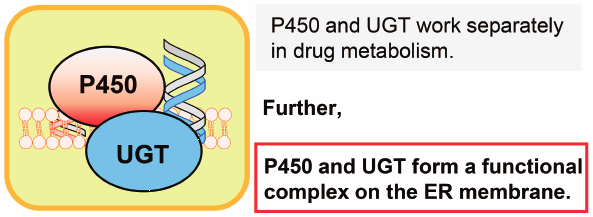
Editor's pickThis Current Topics includes 5 reviews, and the authors for individual reviews were invited to contribute papers updating/improving readers’ understanding of the nuclear receptors- and drug-metabolizing enzymes-mediated inter-individual differences. Nuclear receptors (e.g., ERα/β, PPARβ/δ, and RORα) are basically ligand-inducible and are known to be involved in the regulation of numerous physiological processes. At the post-transcriptional level, some microRNAs are involved in the regulation of CYP3A protein expression. In addition, at the post-translational levels, there are functional protein-protein interactions between different kinds of drug-metabolizing enzymes i.e., P450 and UGT, which results in modulation of the enzyme(s) activities.
Download PDF (210K) Full view HTML
-
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1594-1597
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Download PDF (455K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1598-1606
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Download PDF (868K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1607-1616
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Download PDF (609K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1617-1634
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Download PDF (681K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1635-1644
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Download PDF (1743K) Full view HTML
-
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1645-1652
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Advance online publication: August 26, 2021Download PDF (3373K) Full view HTML
-
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1653-1661
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Download PDF (1008K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1662-1669
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Download PDF (3450K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1670-1680
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Download PDF (993K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1681-1687
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Download PDF (3727K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1688-1696
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Advance online publication: August 25, 2021Download PDF (6324K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1697-1706
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Download PDF (4738K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1707-1716
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Download PDF (8826K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1717-1723
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Download PDF (942K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1724-1731
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Advance online publication: September 02, 2021Download PDF (7623K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1732-1737
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Download PDF (3622K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1738-1745
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Advance online publication: September 01, 2021Download PDF (7587K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1746-1751
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Download PDF (873K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1752-1758
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Download PDF (1110K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1759-1766
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Download PDF (2011K) Full view HTML -
 2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1767-1774
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1767-1774
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
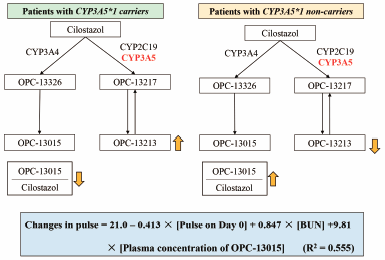
Editor's pickCilostazol is metabolized to two active metabolites in humans. This study investigated the influence of the plasma concentrations of cilostazol and the metabolites on pulse rate in patients with cerebral infarction. Polymorphisms of metabolic enzymes significantly influenced plasma disposition of OPC-13015, a metabolite by CYP3A4, and OPC-13213, another metabolite by CYP3A5 and CYP2C19. A multiple regression model, consisting of factors of the plasma concentration of OPC-13015, levels of blood urea nitrogen, and pulse rate at the start of cilostazol therapy explained 55.5% of the interindividual variability of the changes in pulse rate before and after the treatment.
Download PDF (585K) Full view HTML -
 2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1775-1780
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1775-1780
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Advance online publication: August 26, 2021Editor's pickAniline and its dimethyl derivatives reportedly become haematotoxic after metabolic N-hydroxylation of their amino groups. The elimination rate of 3,5-dimethylaniline based on rat plasma versus time curves was rapid compared with that of 2,6-dimethylaniline after single oral doses of 25 mg/kg. The areas under the curve of unmetabolized (remaining) dimethylaniline derivatives estimated using pharmacokinetic models showed an apparently positive correlation with the reported lowest-observed-effect levels for haematotoxicity of these chemicals. These results suggest that the presence of a methyl group at the C2-positon may generally suppress fast metabolic rates of dimethylaniline derivatives that promote metabolic activation reactions at NH2 moieties.
Download PDF (855K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1781-1789
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Download PDF (1558K) Full view HTML
-
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1790-1795
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Download PDF (2072K) Full view HTML -
2021Volume 44Issue 11 Pages 1796-1799
Published: November 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2021
Download PDF (715K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|