- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2020Volume 43Issue 7 Pages 1027-1034
Published: July 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2020
Advance online publication: May 13, 2020Download PDF (1151K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 7 Pages 1035-1045
Published: July 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2020
Download PDF (15850K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 7 Pages 1046-1051
Published: July 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2020
Advance online publication: April 22, 2020Download PDF (5522K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 7 Pages 1052-1060
Published: July 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2020
Advance online publication: April 21, 2020Download PDF (4534K) Full view HTML -
 2020Volume 43Issue 7 Pages 1061-1066
2020Volume 43Issue 7 Pages 1061-1066
Published: July 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2020
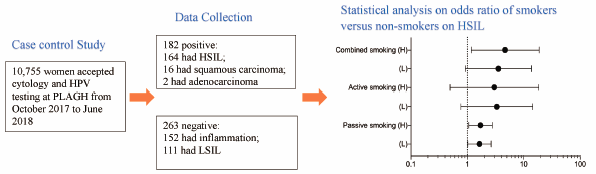
Editor's pickThe association between risk factors and occurrence or development of cervical intraepithelial lesions, such as persistent infection with high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV), multiple sexual partners and smoking have been discussed. However, the effect of passive smoking on the disease is unclear. In this case-control study, Du et al. found that passive smoking was a significant independent risk factor on the occurrence of HSIL and showed a positive correlated dose-response relationship. HPV infection interacting with passive smoking led to an even higher disease risk. Adolescent exposure to passive smoking persistent for more than 20 years would also increase the HSIL risk.
Download PDF (501K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 7 Pages 1067-1072
Published: July 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2020
Download PDF (341K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 7 Pages 1073-1080
Published: July 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2020
Download PDF (6841K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 7 Pages 1081-1087
Published: July 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2020
Advance online publication: April 14, 2020Download PDF (752K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 7 Pages 1088-1095
Published: July 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2020
Download PDF (6860K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 7 Pages 1096-1103
Published: July 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2020
Download PDF (3735K) Full view HTML -
 2020Volume 43Issue 7 Pages 1104-1110
2020Volume 43Issue 7 Pages 1104-1110
Published: July 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2020
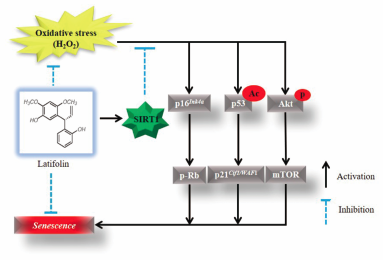
Advance online publication: May 12, 2020Editor's pickAging is the most important risk factor for various diseases such as cancer, osteoarthritis, dementia, atherosclerosis, and infection. Therefore, the researchers has attempted to find phytochemicals for ameliorating aging-related diseased. Latifolin, isolated from Dalbergia odorifera T. Chen, has been reported to exhibit anti-inflammatory and anti-carcinogenic activities. In present study, the authors investigated the anti-aging effect of latifolin in human dermal fibroblasts. Modulation of SIRT1 may be involved in latifolin protective effect against H2O2-induced oxidant injury. These results suggest that latifolin supplementation might be a possible route for improving aging and age-related diseases.
Download PDF (1913K) Full view HTML -
 2020Volume 43Issue 7 Pages 1111-1117
2020Volume 43Issue 7 Pages 1111-1117
Published: July 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2020
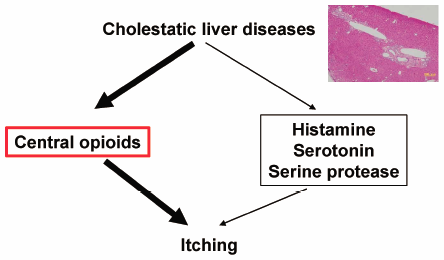
Editor's pickPatients with cholestatic liver diseases, such as primary biliary cirrhosis, usually suffer from pruritus. However, the pathogenesis of cholestatic pruritus is unclear, and there is no current effective treatment for it. In order to find a treatment for the condition, an appropriate mouse model should be developed. Andoh et al. established a surgically-induced mouse model of cholestatic pruritus and evaluated anti-pruritic effects of several drugs using this mouse model. In results, they suggested that partial obstruction of bile secretion in mice induced anti-histamine-resistant itching and that central opioid system is involved in cholestatic itching.
Download PDF (2297K) Full view HTML -
 2020Volume 43Issue 7 Pages 1118-1122
2020Volume 43Issue 7 Pages 1118-1122
Published: July 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2020
Editor's pickLarge conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BKCa) channels possess significant physiological functions in various types of cells. The stoichiometry between BKa and newly identified ɤ1 subunits (BKɤ1) remains unclear. Here, the authors utilized a single molecule fluorescence imaging with a total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) microscope to directly count the number of GFP-tagged BKɤ1 within a single BKCa channel complex in HEK293 expression system. Counting of GFP bleaching steps revealed that a BKCa channel contains mainly four BKɤ1 per channel. These results suggest that BKɤ1 forms a BKCa channel complex with BKa in a 1:1 stoichiometry in a human cell line.
Download PDF (682K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 7 Pages 1123-1127
Published: July 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2020
Download PDF (1118K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 7 Pages 1128-1134
Published: July 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2020
Download PDF (1207K) Full view HTML
-
2020Volume 43Issue 7 Pages 1135-1140
Published: July 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2020
Advance online publication: May 12, 2020Download PDF (428K) Full view HTML -
2020Volume 43Issue 7 Pages 1141-1145
Published: July 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2020
Advance online publication: May 02, 2020Download PDF (1687K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|