- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 869-873
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Download PDF (2637K) Full view HTML
-
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 874-882
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Download PDF (1592K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 883-892
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Download PDF (6044K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 893-897
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Download PDF (715K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 898-906
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Download PDF (751K) Full view HTML -
 2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 907-913
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 907-913
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Editor's pickPharmacogenomic (PGx) testing can predict therapeutic responses or adverse effects based on genetic variants and is expected to be the preemptive precision medicine for patient management. Tramadol is metabolized by CYP2D6 to an active metabolite, which in turn acts as an analgesic. From the retrospective cohort study in Japanese patients with postoperative pain after orthopedic arthroscopic surgery, the authors demonstrated that the analgesic effect in the early postoperative period was depended on CYP2D6 gene polymorphism. These results suggested the clinical utility of preemptive treatment based on the PGx test, which can consider dose adjustment or drug change in advance.
Download PDF (539K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 914-920
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Download PDF (836K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 921-928
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Advance online publication: May 11, 2023Download PDF (2003K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 929-938
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Download PDF (7893K) Full view HTML -
 2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 939-945
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 939-945
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Editor's pickTRP ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) is present in the afferent sensory neurons and is activated by food-derived ingredients, such as Japanese horseradish, cinnamon, and garlic. The present study aimed to investigate the expression of TRPA1 in taste buds, and determine its functional roles in taste perception using TRPA1-deficient mice. TRPA1-immunoreactivities are detectable in the taste nerve. TRPA1 deficiency significantly reduced sweet sensitivity compared to that in WT mice as per the two-bottle preference tests. Authors found that TRPA1 in the taste nerve contributes to the sense of sweet taste in mice.
Download PDF (5729K) Full view HTML -
 2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 946-954
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 946-954
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Advance online publication: May 13, 2023Editor's pickAllergic contact dermatitis is a common dermatitis and is induced by contact with allergens. The authors found that methionine suppressed this dermatitis in some strains of mice. They also found that the strength of the effect depended on the suppression of liver betaine homocysteine methyltransferase (Bhmt) expression by the dermatitis. Although the mechanism has not been elucidated, the authors propose that while dermatitis suppresses liver Bhmt expression in some strains of mice, the fact that the metabolic state of the liver affects the suppression of dermatitis suggests that there is at least a skin-liver interaction, especially a dermatitis-liver interaction.
Download PDF (1771K) Full view HTML -
 2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 955-963
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 955-963
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
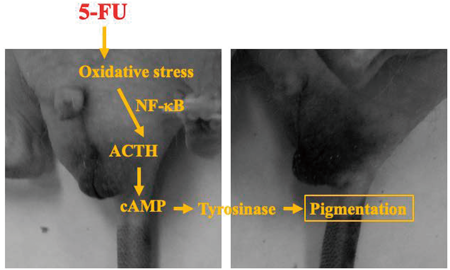
Advance online publication: May 17, 2023Editor's pickThis study aimed to investigate the mechanism underlying the skin pigmentation caused by anticancer drugs using 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), a widely used anticancer drug known to cause this complication. Authors believe our study makes a significant contribution to the literature because anticancer drug-induced skin pigmentation remarkably affects the quality of life of cancer patients, has no established treatment, and has an unknown mechanism. This result provides new insight into the role of the ACTH/cAMP/tyrosinase pathway in 5-FU-mediated skin pigmentation and may help manage this complication.
Download PDF (8059K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 964-968
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Download PDF (368K) Full view HTML -
 2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 969-978
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 969-978
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
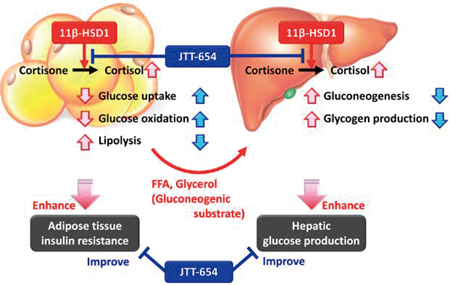
Editor's pick11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11β-HSD1) is the only enzyme that converts inactive glucocorticoids to active forms and plays an important role in regulating glucocorticoid action in target tissues. Excess glucocorticoids cause insulin resistance in the liver and adipose tissue. Several 11β-HSD1 inhibitors have been reported, but all have been evaluated in obese diabetes models. In the present study, the authors investigated the pharmacological properties of JTT-654, a selective 11β-HSD1 inhibitor, in cortisone-treated rats and non-obese Goto-Kakizaki rats with type 2 diabetes, because many Asians, including Japanese, have non-obese type 2 diabetes. Information gained from detailed analysis of the mechanism of action of JTT-654 may provide a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of non-obese type 2 diabetic patients.
Download PDF (1248K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 979-986
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Advance online publication: May 13, 2023Download PDF (4063K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 987-996
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Download PDF (886K) Full view HTML
-
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 997-1003
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Download PDF (1016K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 1004-1009
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Advance online publication: April 22, 2023Download PDF (3849K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 1010-1014
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Download PDF (1491K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 1015-1020
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Download PDF (2989K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 1021-1023
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Download PDF (417K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 1024-1026
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Download PDF (312K) Full view HTML -
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 1027-1030
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Download PDF (1280K) Full view HTML
-
2023 Volume 46 Issue 7 Pages 1031
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Download PDF (140K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|