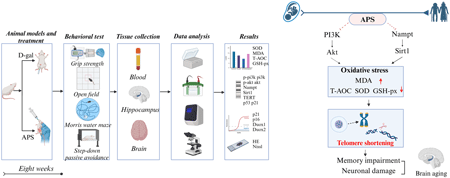
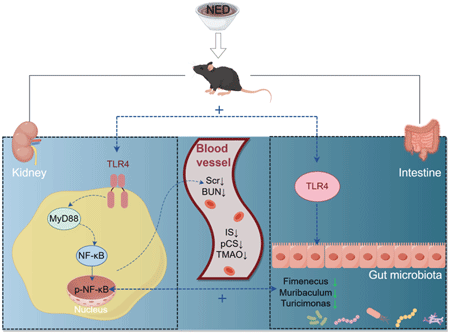
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 475-494
Published: May 01, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2025
Download PDF (6966K) Full view HTML -
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 495-506
Published: May 01, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2025
Download PDF (2104K) Full view HTML
-
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 507-514
Published: May 02, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 02, 2025
Download PDF (1231K) Full view HTML -
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 515-522
Published: May 02, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 02, 2025
Download PDF (2342K) Full view HTML -
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 523-536
Published: May 02, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 02, 2025
Download PDF (12252K) Full view HTML -
 2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 537-544
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 537-544
Published: May 08, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 08, 2025
Editor's pickThe pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) parameter of the exposure time that the unbound drug concentration remains above the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) for a bacterium (fT ≥ MIC) is used in establishing optimal dosing regimens. The authors revealed that the optimal fT ≥ MIC for the clinical efficacy of de-escalation to cefmetazole (CMZ) for patients with extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli (ESBL-E) bacteremic urinary tract infection (UTI) was clarified as fT ≥ MIC ≥ 57%. These results may lead to optimal dosing regimens when using CMZ for patients with bacteremic UTI caused by ESBL-E.
Download PDF (610K) Full view HTML -
 2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 545-554
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 545-554
Published: May 09, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 09, 2025
Editor's pickAbnormal behaviors such as low anxiety, impulsivity, hyperactivity, and inattention-like traits have been observed in mice with disrupted sleep patterns, mirroring symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and the central histamine system plays a role in various physiological and neurological functions, including the regulation of the sleep-wake cycle, anxiety-related behaviors (ranging from high to low anxiety), and ADHD. In this study, the authors revealed that the low-anxiety behavior and impulsive-like ADHD symptoms induced by intermittent sleep deprivation may result from the overstimulation of histamine H1 and H3 receptors by elevated histamine together with increased hypothalamic HDC expression. These findings suggest that sufficient sleep may contribute to ameliorating ADHD symptoms.
Download PDF (3508K) Full view HTML -
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 555-562
Published: May 09, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 09, 2025
Download PDF (8109K) Full view HTML -
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 563-570
Published: May 09, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 09, 2025
Download PDF (3082K) Full view HTML
-
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 571-576
Published: May 09, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 09, 2025
Download PDF (1228K) Full view HTML
-
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 577-594
Published: May 10, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2025
Download PDF (28452K) Full view HTML -
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 595-605
Published: May 10, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2025
Download PDF (2364K) Full view HTML -
 2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 606-612
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 606-612
Published: May 14, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 14, 2025
Editor's pick[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
Detecting low-frequency genetic mutations is crucial in genetic testing, particularly for cancer diagnostics. Wild-type blocking PCR (WTB-PCR) utilizes a blocking oligonucleotide fully complementary to wild-type DNA to suppress its amplification, thereby enabling selective detection of mutant alleles. Incorporating bridged nucleic acids (BNAs) into blocking oligonucleotides can enhance binding affinity, consequently improving inhibitory efficiency. However, the optimal placement of BNAs within blocking oligonucleotides remains uncertain. This study systematically evaluated the effects of BNA positioning and identified significant variations in inhibition efficacy dependent on position, offering essential insights for optimizing WTB-PCR design.Download PDF (1083K) Full view HTML
-
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 613-621
Published: May 14, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 14, 2025
Download PDF (4316K) Full view HTML -
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 622-631
Published: May 17, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 17, 2025
Download PDF (4973K) Full view HTML
-
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 632-640
Published: May 17, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 17, 2025
Download PDF (3484K) Full view HTML -
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 641-649
Published: May 17, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 17, 2025
Download PDF (4531K) Full view HTML -
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 650-656
Published: May 20, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 20, 2025
Download PDF (1152K) Full view HTML -
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 657-671
Published: May 22, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 22, 2025
Download PDF (5438K) Full view HTML -
 2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 672-681
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 672-681
Published: May 22, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 22, 2025
Editor's pickErgothioneine (ERGO), an amino acid with potent antioxidant activity, is abundantly found in certain mushroom species. The authors demonstrated that dietary ERGO-rich mushrooms significantly alleviated the epidermal thickening, reduction in skin moisture content, and increase in TEWL induced by UVB in mice, at clinically relevant plasma ERGO levels. These protective effects were accompanied by reductions in oxidative stress markers and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Furthermore, ERGO-rich mushroom intake increased epidermal ERGO levels to approx. 100 times the concentration required to inhibit UVB-induced intracellular ROS in keratinocytes. These findings suggest that ERGO-rich mushrooms are promising beneficial foods for the prevention and/or treatment of photoaging.
Download PDF (9507K) Full view HTML
-
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 682-686
Published: May 23, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 23, 2025
Download PDF (2629K) Full view HTML
-
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 687-693
Published: May 23, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 23, 2025
Download PDF (741K) Full view HTML -
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 694-705
Published: May 24, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 24, 2025
Download PDF (705K) Full view HTML -
 2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 706-712
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 706-712
Published: May 24, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 24, 2025
Editor's pickThis study systematically compares natural and synthetic signal peptides for boosting extracellular NanoLuc luciferase secretion in HEK293, C2C12, and HepG2 cells. Signal peptides from cystatin S, lactotransferrin, tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), and artificial sequences were tested, with cystatin S driving the highest luciferase secretion in all cell types. Notably, the cystatin S peptide outperformed the commonly used tPA signal peptide. These findings suggest that optimizing signal peptides—such as using cystatin S—could increase antigen expression for mRNA vaccines, potentially enabling robust immune responses at lower mRNA doses.
Download PDF (910K) Full view HTML -
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 713-720
Published: May 28, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2025
Download PDF (1603K) Full view HTML
-
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 721-727
Published: May 29, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 29, 2025
Download PDF (3635K) Full view HTML -
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 728-732
Published: May 29, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 29, 2025
Download PDF (2425K) Full view HTML
-
2025Volume 48Issue 5 Pages 733-743
Published: May 30, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: May 30, 2025
Download PDF (2191K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|