- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 195
Published: March 01, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2025
Download PDF (213K) Full view HTML
-
 2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 196-204
2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 196-204
Published: March 01, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2025
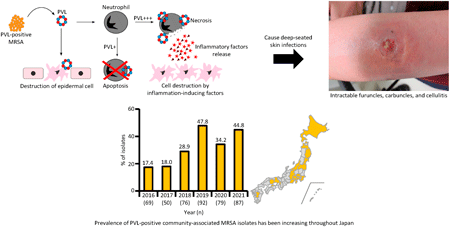
Editor's pickThis review shows how the prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Japan has changed significantly in just a decade. In particular, the prevalence of the USA300 clone, a highly virulent community-associated MRSA, has become a serious problem in the community, and the number of patients with severe skin infections has increased. If such highly virulent strains of MRSA spread to hospitals, where there are many compromised patients, there is a risk of serious outbreaks. This review highlights the importance of staying abreast of the latest MRSA prevalence and implementing appropriate infection control.
Download PDF (1642K) Full view HTML -
 2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 205-212
2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 205-212
Published: March 01, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2025
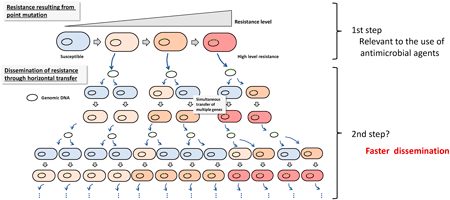
Editor's pickHaemophilus influenzae is one of the most common pathogens causing community infections. Historically, H. influenzae has been known for its rapid emergence of antimicrobial-resistant isolates in response to antimicrobial usage. In this paper, the authors summarised the mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance to therapeutic agents based on recently published studies. Furthermore, they highlighted the transformation ability of H. influenzae, which allows it to adapt to its environment by acquiring extracellular DNA. This unique and ingenious feature could serve as an efficient system for the spread of antimicrobial resistance.
Download PDF (775K) Full view HTML -
2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 213-221
Published: March 01, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2025
Download PDF (1918K) Full view HTML -
2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 222-229
Published: March 01, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2025
Download PDF (1045K) Full view HTML
-
2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 230-233
Published: March 01, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2025
Download PDF (432K) Full view HTML
-
2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 234-240
Published: March 11, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 11, 2025
Download PDF (1451K) Full view HTML
-
2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 241-245
Published: March 12, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 12, 2025
Download PDF (713K) Full view HTML
-
2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 246-261
Published: March 18, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 18, 2025
Download PDF (19033K) Full view HTML -
2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 262-266
Published: March 18, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 18, 2025
Download PDF (1098K) Full view HTML -
2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 267-278
Published: March 20, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 20, 2025
Download PDF (2228K) Full view HTML -
2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 279-285
Published: March 22, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 22, 2025
Download PDF (3727K) Full view HTML -
2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 286-297
Published: March 22, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 22, 2025
Download PDF (2756K) Full view HTML -
 2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 298-307
2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 298-307
Published: March 22, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 22, 2025
Editor's pick[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
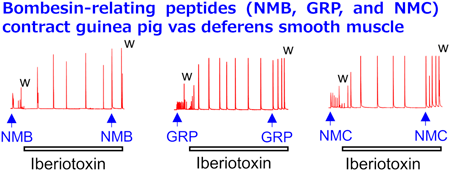
This study is the first to demonstrate that bombesin-like peptides—neuromedin B, gastrin-releasing peptide, and neuromedin C—induce contraction in guinea pig vas deferens smooth muscle (VDSM), likely through activation of bombesin BB2 receptors, highlighting a novel physiological role for these peptides. It further reveals that large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels act as key negative regulators of VDSM contractility by suppressing voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels. These findings provide new insights into the regulation of the reproductive system and suggest potential therapeutic targets in urogenital physiology.Download PDF (5541K) Full view HTML -
 2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 308-313
2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 308-313
Published: March 26, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 26, 2025
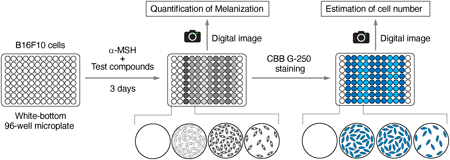
Editor's pickThe authors established a simple method to quantify melanization by analyzing the digital images of the entire microplates. Compared to the conventional method measuring the absorbance of cell lysates at UV-A wavelengths, their digital image-based method was found to have higher sensitivity and be applicable to high-throughput screening assays to identify molecules that affect melanization.
Download PDF (1097K) Full view HTML -
2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 314-322
Published: March 29, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 29, 2025
Download PDF (2836K) Full view HTML -
 2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 323-335
2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 323-335
Published: March 29, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 29, 2025
Download PDF (9579K) Full view HTML
-
2025Volume 48Issue 3 Pages 336
Published: March 31, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 31, 2025
Download PDF (140K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|