
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Masamichi Hirose2019 年 42 巻 4 号 p. 517
発行日: 2019/04/01
公開日: 2019/04/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLPDF形式でダウンロード (180K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Masafumi Takahashi2019 年 42 巻 4 号 p. 518-523
発行日: 2019/04/01
公開日: 2019/04/01
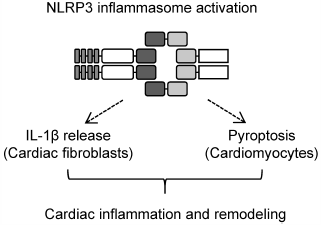
ジャーナル フリー HTMLAn accumulating body of evidence indicates that inflammation plays a crucial role in the pathophysiology of myocardial infarction (MI). Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor (NLR) family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome is an intracellular multiprotein complex that regulates caspase-1 activation and the subsequent processing of the potent inflammatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-1β as well as triggering inflammatory cell death pyroptosis. We and other investigators demonstrated that deficiency of the NLRP3 inflammasome components reduces inflammation and improves cardiac dysfunction and remodeling in rodent models of MI. Therefore, the regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome has been regarded as a potential therapeutic target for MI. Furthermore, a recent Canakinumab Antiinflammatory Thrombosis Outcome Study (CANTOS) trial revealed the efficacy of IL-1β inhibition in preventing recurrent cardiovascular events in patients with MI. This review focuses on the role of NLRP3 inflammasome in the process of cardiac inflammation and remodeling after MI, and discusses its potential as a therapeutic target for the prevention and treatment of MI.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (465K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (465K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Satomi Okano, Yuji Shiba2019 年 42 巻 4 号 p. 524-530
発行日: 2019/04/01
公開日: 2019/04/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLMyocardial infarction occurs as a result of acute arteriosclerotic plaque rupture in the coronary artery, triggering strong inflammatory responses. The necrotic cardiomyocytes are gradually replaced with noncontractile scar tissue that eventually manifests as heart failure. Pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) show great promise for widespread clinical applications, particularly for tissue regeneration, and are being actively studied around the world to help elucidate disease mechanisms and in the development of new drugs. Human induced PSCs also show potential for regeneration of the myocardial tissue in experiments with small animals and in in vitro studies. Although emerging evidence points to the effectiveness of these stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes in cardiac regeneration, several challenges remain before clinical application can become a reality. Here, we provide an overview of the present state of PSC-based heart regeneration and highlight the remaining hurdles, with a particular focus on graft survival, immunogenicity, posttransplant arrhythmia, maintained function, and tumor formation. Rapid progress in this field along with advances in biotechnology are expected to resolve these issues, which will require international collaboration and standardization.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (342K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (342K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Takafumi Ishida, Mari Ishida, Satoshi Tashiro, Yasuchika Takeishi2019 年 42 巻 4 号 p. 531-537
発行日: 2019/04/01
公開日: 2019/04/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLDNA suffers various types of damage even in a normal condition, although they are rapidly repaired by mechanisms called DNA repair. Most progeroid syndromes are caused by genetic defects in specific molecules involved in the DNA repair. DNA damage activates a broad range of signaling pathway that leads to repair, cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and so on, which is called DNA damage response. Recent studies revealed that persistent DNA damage response triggers induction of cell senescence and senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). Here, we review recent advances in the understanding of the molecular mechanisms by which SASP components are regulated, and discuss the possible roles of DNA damage and the DNA damage response, and SASP in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (491K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (491K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Miho Ibi2019 年 42 巻 4 号 p. 538-542
発行日: 2019/04/01
公開日: 2019/04/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLTemporomandibular disorders (TMD) are a common stomatognathic disease affecting all age groups. Patients with internal derangement (ID) or osteoarthritis (OA) of temporomandibular joint (TMJ) often have TMJ synovitis. When TMJ synovial membrane is damaged, many inflammatory cytokines are produced and secreted from TMJ synoviocytes to synovial fluid of TMJ. It has been widely reported that many kinds of biologic factors are produced from TMJ synoviocytes stimulated with interleukin (IL)-1beta and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha. One of the major symptoms of TMD is pain of the TMJ. Many study groups have studied relations between the development of TMJ pain and biologic factors secreted into synovial fluid of TMJ. Here, we summarize previous reports trying to elucidate this correlation. On the other hand, it has been reported that a new molecular mechanism of IL-1beta secretion called inflammasome is involved in several diseases with sterile inflammation. Because TMJ synovitis with ID and OA of TMJ is also sterile inflammation, inflammasome may be involved in the development of TMJ synovial inflammation. This review describes some molecular mechanisms underlying inflammation in TMJ, especially in TMJ synovitis, which may be useful for the development of new therapies against TMD.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (755K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (755K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Naoko Matsushita, Nanae Ishida, Miho Ibi, Maki Saito, Masafumi Takahas ...2019 年 42 巻 4 号 p. 543-546
発行日: 2019/04/01
公開日: 2019/04/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLHypertension is one risk for atrial fibrillation (AF) and induces cardiac inflammation. Recent evidence indicates that pressure overload-induced ventricular structural remodeling is associated with the activation of nucleotide binding-oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptor P3 (NLRP3) inflammasomes, including an apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a C-terminal caspase recruitment domain (ASC). We hypothesized that NLRP3 inflammasomes are an initial sensor for danger signals in pressure overload-induced atrial remodeling, leading to AF. Transverse aortic constriction (TAC) or a sham procedure was performed in mice deficient for ASC−/− and interleukin-1β (IL-1β−/−). One week after the procedure, electrical left atrial burst pacing from the esophagus was performed for 30 s to induce AF. IL-1β, monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1), connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), and collagen 1 gene expression were also examined. The electrical burst pacing induced AF in TAC-operated wild-type (WT) (p < 0.001) and ASC−/− (p < 0.05) mice, compared to no AF in the sham-operated WT and ASC−/− mice, respectively. In contrast, the number of mice in which sustained AF was induced was similar between TAC-operated IL-1β−/− and sham-operated IL-1β−/− mice (p > 0.05). The expression of all genes tested was increased in TAC-operated WT and ASC−/− mice compared with sham-operated WT and ASC−/− mouse atria, respectively. CTGF and collagen 1, but not MCP-1, gene expressions were increased in TAC-operated IL-1β−/− mouse atria compared with sham-operated WT and IL-1β−/− mouse atria. In contrast, the IL-1β gene was not detected in either TAC-operated or sham-operated IL-1β−/− mouse atria. These results suggest that an IL-1β activation pathway, different from NLRP3 inflammasomes, plays an important role in pressure overload-induced sustained AF.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (525K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (525K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Tomoaki Tsutsumi, Hiroshi Akiyama, Yosuke Demizu, Nahoko Uchiyama, Say ...2019 年 42 巻 4 号 p. 547-551
発行日: 2019/04/01
公開日: 2019/04/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/02/07ジャーナル フリー HTMLValsartan products, commonly used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure, have been recalled in many countries due to the presence of an impurity, N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), in the recalled products. We present and evaluate a GC-MS-based analytical method for the determination of NDMA levels and attempt an investigation of NDMA concentrations in valsartan drug substances and associated products. The limit of detection and limit of quantification for the method were estimated to be 0.1 and 0.5 µg/g, respectively, when testing a 0.5-g sample. A good trueness (99%) with a small relative standard deviation (1.9%) was obtained for a valsartan product spiked with NDMA at a concentration of 1.0 µg/g. Additionally, a valsartan drug substance and the associated product, which were previously determined to have NDMA contamination, were analyzed by the method. The NDMA content by our method was very close to previously determined values. Finally, six samples, including valsartan drug substances and associated, commercially available products in Japan, all of which were derived from the company implicated in the NDMA contamination, were analyzed by our method, revealing that none of these samples contained detectable concentrations of NDMA. Overall, the data indicate that the present method is reliable and useful for determination of NDMA in valsartan drug substances and associated products.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (437K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (437K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Hiroaki Hayashi, Musavvara Shukurova, Shihoko Oikawa, Minami Ohta, Isa ...2019 年 42 巻 4 号 p. 552-560
発行日: 2019/04/01
公開日: 2019/04/01
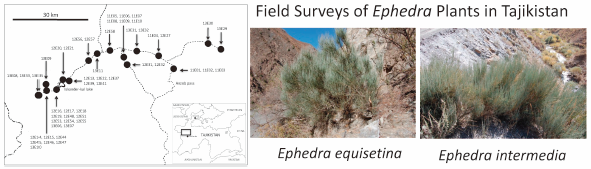
ジャーナル フリー HTMLField surveys of Ephedra plants were conducted in the Zaravshan Mountains of Tajikistan. E. equisetina, E. intermedia, and their putative hybrids were collected. They were identified based on their phenotypes and their sequences of nuclear ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer 1 (ITS1) region. Sequencing and species-specific PCR analyses of their ITS1 sequences revealed six putative hybrids of E. equisetina and E. intermedia. The total ephedrine and pseudoephedrine content of most of the Ephedra samples collected in Tajikistan were higher than the 0.7% lower limit prescribed by the Japanese pharmacopoeia, 17th edition (JP17), and varied from 0.34 to 3.21% by dry weight. The total alkaloid level of E. intermedia (11E08-1) cultivated in Japan varied from 1.77 to 2.30% by dry weight, which was much higher than the 0.7% lower limit prescribed by JP17.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2073K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2073K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Dawei He, Yubin Wang, Ruijiang Liu, Aolin He, Shasha Li, Xuejie Fu, Zh ...2019 年 42 巻 4 号 p. 561-567
発行日: 2019/04/01
公開日: 2019/04/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLDiabetes mellitus is a serious disease endangering human health worldwide. Vitamin D (Vit D) is a well-characterized regulator of calcium-phosphorus metabolism that also exerts other biological effects extending far beyond mineral homeostasis. Some epidemiological studies have suggested that Vit D has a role in defense against diabetes, although the mechanism remains unclear. Autophagy, an intracellular catabolic process, is necessary to maintain the normal structure and function of host cells. In our previous study, we found that Vit D could induce autophagy of pancreatic beta cells and prevent insulitis, although the underlying mechanisms remain to be fully elucidated. In this study, the protective effect of 1,25(OH)2D3, the physiologically active metabolite of Vit D, against streptozotocin-induced cytotoxicity in rat insulinoma cell line (INS-1) cells was explored. Cell viability and insulin secretion of INS-1 cells in response to different treatments were measured with a cell counting kit and enzyme-linked immune absorbent assay (ELISA), respectively. In addition, malondialdehyde (MDA) content and total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) were measured by ELISA. RT-PCR and Western blot analyses were used to detect autophagy levels, reactive oxygen species (ROS) was assessed by fluorescence microscope, ultrastructure analysis was performed using transmission electron microscopy. The results demonstrated that 1,25(OH)2D3 could increase cell viability and insulin secretion of INS-1 cells, and protected cells from oxidative damage induced by streptozotocin (STZ) through autophagy activation. These findings shed light on mechanisms underlying the ameliorative effects of Vit D on diabetes mellitus.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3153K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3153K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Baoyin Ren, Weijia Guo, Yawei Tang, Jing Zhang, Nan Xiao, Lin Zhang, W ...2019 年 42 巻 4 号 p. 568-572
発行日: 2019/04/01
公開日: 2019/04/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe root of Rheum officinale BAILL as a traditional Chinese medicine, which main function is removing heat from the blood, promoting blood circulation and clearing toxins away. Rhein (4,5-dihydroxyanthraquinone-2-carboxylic acid) is one of the most important active components in the root of Rheum officinale BAILL, which could inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells. However, the study on the mechanism of anti-cell migration capacity of Rhein on ovarian cancer is not yet clear. Here, we demonstrated that Rhein had dose-dependent effects of ovarian tumors on drugs and could inhibit the proliferations and migration of two typical ovarian cancer cell lines, A2780 and OV2008. Furthermore, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assays showed that the survival rate of ovarian cancer cells was significantly decreased when treated with Rhein. Rhein inhibited the proliferation of ovarian cancer cells in dose-dependent manner. Moreover, the wound healing assay and transwell assay indicated that the cell migratory potential and expression of matrix metalloproteinases were markedly inhibited by Rhein. Our findings suggested that Rhein could be a potential candidate to be developed as a drug for the prevention of ovarian cancer cell migration.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1604K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1604K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Zhiwei Gu, Changjie Lin, Jian Hu, Jing Xia, Shaohua Wei, Dekang Gao2019 年 42 巻 4 号 p. 573-579
発行日: 2019/04/01
公開日: 2019/04/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/01/26ジャーナル フリー HTMLPancreatic cancer is known to be a fatal disease, which is difficult to be diagnosed in its early stages. Ubiquitin-Specific Protease 34 (USP34) are closely related to human cancers in the development and progression. However, there are rarely studies about the role of USP34 in pancreatic cancer. Thus, we aimed to investigate the effect of USP34 in human pancreatic cancer. Short-hairpin RNA targeting USP34 (USP34-shRNA) and USP34 overexpression lentivirus were used in the current study. The level of USP34 in human pancreatic cancer (PANC-1) cells were then analyzed by quantitative (q)RT-PCR. In addition, Western blotting was used to examine phosphorylated (p)-AKT, p-protein kinase C (PKC) and p-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) protein levels. CCK-8 assay, flow cytometry, and migration assay were used to detect cell proliferation, apoptosis and migration, respectively in vitro. According to the result of qRT-PCR and Western blotting, USP34-shRNA1 significantly downregulated USP34 gene level in PANC-1 cell. Subsequently, Western blotting assay indicated that USP34 silencing significantly down-regulated the expression of p-AKT and p-PKC in cells. On the other hand, USP34 overexpressing remarkably up-regulated the expression of p-AKT and p-PKC in cells. In addition, USP34 overexpression promoted PANC-1 cell proliferation and migration via up-regulating the proteins of p-AKT and p-PKC. Moreover, USP34 overexpression reversed AKT inhibitor and PKC inhibitor induced PACN-1 cell apoptosis. Our results indicated USP34 regulated h PANC-1 cell survival via AKT and PKC pathways, and which played a pro-survival role in human pancreatic cancer. Therefore, we suggested USP34 could be a potential therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5104K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5104K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Maojian Chen, Chao Ou, Chun Yang, Weiping Yang, Qinghong Qin, Wei Jian ...2019 年 42 巻 4 号 p. 580-585
発行日: 2019/04/01
公開日: 2019/04/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/01/24ジャーナル フリー HTMLChinese tree shrew, an animal exhibited closer evolutionary relationship with humans compared to rodents, is getting increasingly attentions as an appealing experimental animal model for human diseases. However, a high-efficiency and stable method to establish tree shrew breast precancerous lesions model has not been clearly elucidated. Thus, the current study aimed to explore the way of establishing breast precancerous model in tree shrew and investigate the pathologic characteristics of induced breast precancerous lesions. The results indicated that 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene (DMBA) could induce breast lesions in tree shrews. However, comparing to DMBA alone, an addition of medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) to DMBA critically increased the rate of induced breast lesion in tree shrews. Half of induced breast lesions were intraductal papilloma and the others were atypical ductal hyperplasia. Induced lesions showed positive expression of estrogen receptor α (ERα), progesterone receptor (PR) and cytokeratin 5/6 (CK5/6), but negative expression of human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (Her-2). The expression of B cell lymphoma-extra large (Bcl-xl) was significantly higher and the expression of B cell lymphoma 2 associated X protein (Bax) was significantly lower in the precancerous lesions (atypical ductal hyperplasia) compared to benign tumor (intraductal papilloma). These results suggest that DMBA is able to induce breast lesions in tree shrews. Combination of DMBA and MPA may be more effective to establish breast precancerous lesion tree shrew models. Tree shrew might be a promising animal model for studying the tumorogenesis of breast cancer.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (20751K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (20751K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Yoshihito Murakami, Hidehisa Sekijima, Yutaka Fujisawa, Kazuya Ooi2019 年 42 巻 4 号 p. 586-593
発行日: 2019/04/01
公開日: 2019/04/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/01/25ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe combination of skin external preparation and transdermal patch is influenced by drug absorption through the skin. We investigated the effect of heparinoid cream on the transdermal absorption of oxybutynin hydrochloride using an oxybutynin transdermal patch and determined the combined effect of these medications. Normal skin and dry dorsal skin in hairless mice were treated with heparinoid cream, followed by the application of the oxybutynin transdermal patch. A blood sample was collected from the mouse tail vein and the blood concentration of oxybutynin hydrochloride was analyzed by LC-MS/MS. Transepidermal water loss, the hydration level of the stratum corneum, and the stratum corneum thickness in the dorsal skin were measured. The blood concentration and area under the curve (AUC)0→24 of oxybutynin hydrochloride increased when the 4.0-cm2 oxybutynin transdermal patch was applied 1 h after the application of the moisturizer, compared to the values without moisturizer. Normal skin and dry skin did not affect this result. As the hydration level of the stratum corneum and stratum corneum thickness increased before patch application by pre-treatment with moisturizer, it was suggested that transdermal absorption of oxybutynin hydrochloride was increased by skin hydration. The increased blood concentration of oxybutynin hydrochloride was regulated by changing the effective area of the patch and applying additional moisturizer at intervals. The pharmacokinetics of oxybutynin hydrochloride under the regulation of combination treatment was similar to that of treatment without moisturizer. These findings indicate that the application conditions of the oxybutynin transdermal patch and heparinoid cream influence the proper use of the patch.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1001K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1001K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Hyesol Lim, Sun Young Kim, Eunhye Lee, Seungeun Lee, Sungryong Oh, Joo ...2019 年 42 巻 4 号 p. 594-600
発行日: 2019/04/01
公開日: 2019/04/01
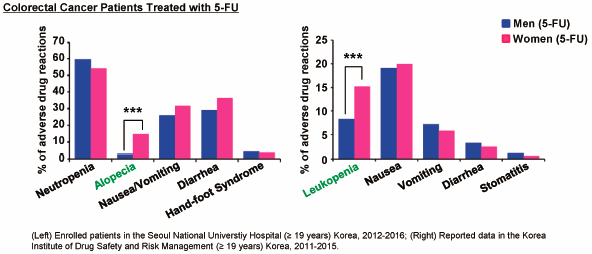
ジャーナル フリー HTMLSex-related incidence and outcomes were reported in various cancers, including colorectal cancer. 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) is widely used as an essential chemotherapeutic agent for colorectal cancer. However, sex-based differences in 5-FU toxicity have yet to be reported in human cancer cell lines and xenograft mouse models to date. Here, we investigated, for the first time, sex-based differences in 5-FU toxicity using human colon cancer cell lines, xenograft mouse models, and Korean patients’ data. Female-derived colon cancer cell lines exhibited greater 5-FU-induced cytotoxicity than male-derived colon cancer cell lines. We established two xenograft mouse models: one with a male-derived human colon cancer cell line injected into male mice (a male-xenograft model) and another involving a female-derived human colon cancer cell line injected into female mice (a female xenograft model). Treatment with 5-FU inhibited tumor growth and led to hematological toxicity in a female xenograft model more potently than in a male xenograft model. We analyzed the data obtained from Korean patients with colorectal cancer to examine sex differences in adverse drug reactions caused by 5-FU. Korean female patients with colorectal cancer who received 5-FU chemotherapy experienced more frequent adverse drug reactions including alopecia and leukopenia than male patients. Taken together, we demonstrated that female may be associated with increased risk of toxicity to 5-FU treatment in colorectal cancer based on in vitro and in vivo investigations and clinical data analysis. Our study suggests sex as an important clinical factor, which predicts induction of toxicity related to 5-FU treatment.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (516K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (516K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Weibin Du, Chiharu Fukano, Mari Yonemoto, Tomokazu Matsuoka, Keisuke M ...2019 年 42 巻 4 号 p. 601-606
発行日: 2019/04/01
公開日: 2019/04/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLSubcutaneous allergen immunotherapy (SCIT) with non-standardized house dust (HD) extracts has been used in Japan since 1963 for house dust mite (HDM)-allergic patients. Since the potencies of HD extracts are unknown, the allergenic potency of HD extracts was examined by comparing with a standardized HDM allergen extracts. The major allergen content of HDM in the extracts was measured using a sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The immunoglobulin E (IgE) inhibitory activities of the extracts were measured by a competitive ELISA. The extract concentrations giving 50% inhibition of IgE binding (log10 IC50) were determined from dose–response curves and defined as inhibitory activities. A linear regression line was constructed from the log10 IC50 values of the standardized HDM extract to interpolate the relative potency of the HD extract with strength of 1 : 10 w/v (HD 1 : 10). The amounts of major allergens (Der f 1, Der p 1 and Der 2) were 116.3 µg/mL in the HDM allergen extract (100000 Japanese Allergy Units [JAU]/mL) and 0.77 µg/mL in the HD 1 : 10. The inhibitory activity (log10 IC50 values) of HD 1 : 10 was 2.389 ± 0.078, indicating the allergenic potency was between 200 and 2000 JAU/mL. Based on regression analysis (R2 >0.99), the allergenic potency of HD 1 : 10 was estimated to be 842 ± 128 JAU/mL. The present study determined the major allergen content of HD extract, which contributes to its allergenic potency. The allergenic potency of HD 1 : 10 was ca. 100-fold less than that of HDM allergen extract.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (610K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (610K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Tae Hee Lee, Dong Sun Park, Ja Young Jang, Isaac Lee, Jong Man Kim, Gy ...2019 年 42 巻 4 号 p. 607-616
発行日: 2019/04/01
公開日: 2019/04/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLLiver regeneration is a very complex process and is regulated by several cytokines and growth factors. It is also known that liver transplantation and the regeneration process cause massive oxidative stress, which interferes with liver regeneration. The placenta is known to contain various physiologically active ingredients such as cytokines, growth factors, and amino acids. In particular, human placenta hydrolysate (hPH) has been found to contain many amino acids. Most of the growth factors found in the placenta are known to be closely related to liver regeneration. Therefore, in this study, we investigated whether hPH is effective in promoting liver regeneration in rats undergoing partial hepatectomy. We confirmed that cell proliferation was significantly increased in HepG2 and human primary cells. Hepatocyte proliferation was also promoted in partial hepatectomized rats by hPH treatment. hPH increased liver regeneration rate, double nucleic cell ratio, mitotic cell ratio, proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), and Ki-67 positive cells in vivo as well as interleukin (IL)-6, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). Moreover, Kupffer cells secreting IL-6 and TNF-α were activated by hPH treatment. In addition, hPH reduced thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARs) and significantly increased glutathione (GSH), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and superoxide dismutase (SOD). Taken together, these results suggest that hPH promotes liver regeneration by activating cytokines and growth factors associated with liver regeneration and eliminating oxidative stress.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (7070K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (7070K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
MengTing Liu, YingJuan Huang, Jian Qin, YuanYuan Wang, Bin Ke, YuBin Y ...2019 年 42 巻 4 号 p. 617-622
発行日: 2019/04/01
公開日: 2019/04/01
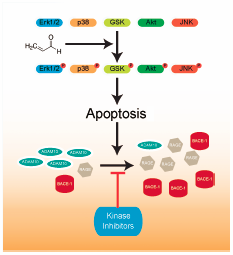
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/01/29ジャーナル フリー HTMLActivation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) in neurons may underlie the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Acrolein, a ubiquitous pollutant, has been reported to implicate in the etiology of AD. Our previous data showed that acrolein changed the levels of key AD-associated proteins, including advanced glycation end products (RAGE), A-disintegrin and metalloprotease (ADAM-10), and beta-site amyloid-beta peptide cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE-1). In this study, we investigated whether acrolein-induced alterations of AD-associated proteins are relevant to MAPKs activation, and strategies to inhibit MAPKs activation yield benefits to acrolein-induced neurotoxicity in HT22 mouse hippocampal cells. We found that acrolein activated MAPKs signaling pathways to mediate cells apoptosis, and then altered the levels of AD-associated proteins ADAM-10, BACE-1 and RAGE. Inhibitors of MAPKs signaling pathways attenuated the cells death and restored the proteins levels of ADAM-10, BACE-1 and RAGE in varying degrees induced by acrolein. Taken together, activated MAPKs signaling pathways should be underlying the pathology of acrolein-induced neuronal disorders. Inhibitors of MAPKs pathways might be promising agents for acrolein-related diseases, such as AD.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1206K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1206K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Tatsuyuki Kanamori, Yuko Togawa Iwata, Hiroki Segawa, Tadashi Yamamuro ...2019 年 42 巻 4 号 p. 623-630
発行日: 2019/04/01
公開日: 2019/04/01
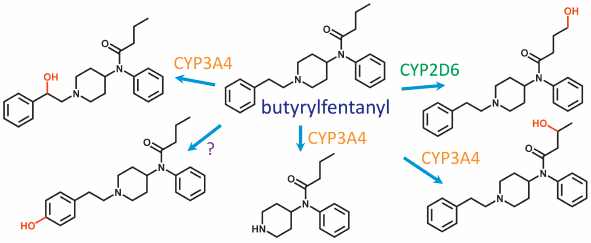
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe metabolism of butyrylfentanyl, a new designer drug, was investigated using fresh human hepatocytes isolated from a liver-humanized mouse model. In the culture medium of hepatocytes incubated with butyrylfentanyl, the desphenethylated metabolite (nor-butyrylfentanyl), ω-hydroxy-butyrylfentanyl, (ω-1)-hydroxy-butyrylfentanyl, 4′-hydroxy-butyrylfentanyl, β-hydroxy-butyrylfentanyl, 4′-hydroxy-3′-methoxy-butyrylfentanyl, and ω-carboxy-fentanyl were identified as the metabolites of butyrylfentanyl. Each metabolite was definitively identified by comparing the analytical data with those of authentic standards. The amount of the main metabolite, nor-butyrylfentanyl, reached 37% of the initial amount of butyrylfentanyl at 48 h. ω-Hydroxy-butyrylfentanyl and (ω-1)-hydroxy-butyrylfentanyl, formed by hydroxylation at the N-butyryl group of butyrylfentanyl, were the second and third largest metabolites, respectively. The majority of 4′-hydroxy-butyrylfentanyl and 4′-hydroxy-3′-methoxy-butyrylfentanyl was considered to be conjugated. CYP reaction phenotyping for butyrylfentanyl using human liver microsomes and various anti-CYP antibodies revealed that CYP3A4 was involved in the formation of nor-butyrylfentanyl, (ω-1)-hydroxy-butyrylfentanyl, and β-hydroxy-butyrylfentanyl. In contrast, CYP2D6 was involved in the formation of ω-hydroxy-butyrylfentanyl.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1081K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1081K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Kota Naito, Kazuki Kurihara, Hajime Moteki, Mitsutoshi Kimura, Hideshi ...2019 年 42 巻 4 号 p. 631-637
発行日: 2019/04/01
公開日: 2019/04/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/02/01ジャーナル フリー HTMLSerotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT) can induce hepatocyte DNA synthesis and proliferation by autocrine secretion of transforming growth factor (TGF)-α through 5-HT2B receptor/phospholipase C (PLC)/Ca2+ and a signaling pathway involving epidermal growth factor (EGF)/TGF-α receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 (ERK2)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). In the present study, we investigated whether 5-HT or a selective 5-HT2B receptor agonist BW723C86, would stimulate phosphorylation of TGF-α RTK and ribosomal p70 S6 kinase (p70S6K) in primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. Western blotting analysis was used to detect 5-HT- or BW723C86 (10−6 M)-induced phosphorylation of EGF/TGF-α RTK and p70S6K. Our results showed that 5-HT- or BW723C86 (10−6 M)-induced phosphorylation of EGF/TGF-α RTK peaked at between 5 and 10 min. On the other hand, 5-HT- or BW723C86 (10−6 M)-induced phosphorylation of p70S6K peaked at about 30 min. Furthermore, a selective 5-HT2B receptor antagonist LY272015, a specific PLC inhibitor U-73122, a membrane-permeable Ca2+ chelator BAPTA/AM, an L-type Ca2+ channel blocker verapamil, somatostatin, and a specific p70S6K inhibitor LY2584702 completely abolished the phosphorylation of p70S6K induced by both 5-HT and BW723C86. These results indicate that phosphorylation of p70S6K is dependent on the 5-HT2B-receptor-mediated autocrine secretion of TGF-α. In addition, these results demonstrate that the hepatocyte proliferating action of 5-HT and BW723C86 are mediated by phosphorylation of p70S6K, a downstream element of the EGF/TGF-α RTK signaling pathway.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1204K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1204K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Anna Miyagi, Takehiro Kawashiri, Shiori Shimizu, Nao Shigematsu, Daisu ...2019 年 42 巻 4 号 p. 638-644
発行日: 2019/04/01
公開日: 2019/04/01
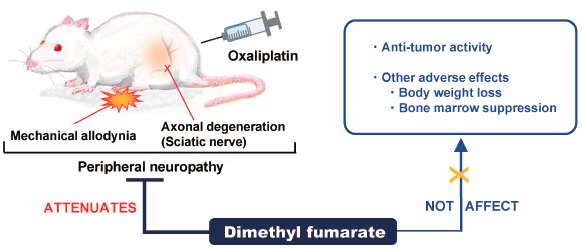
ジャーナル フリー HTMLOxaliplatin has been used as a first choice for colorectal, gastric and pancreatic cancer, but it induces peripheral neuropathies. Dimethyl fumarate (DMF) is an oral drug for multiple sclerosis with neuroprotective effects on oxidative stress. Using both in vivo and in vitro models, we investigated the effects of DMF on oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy and other side effects, as well as on the anti-tumor activity of oxaliplatin. Repeated intraperitoneal injection of 4 mg/kg oxaliplatin (twice per week for 4 weeks) caused mechanical allodynia (as revealed by the von Frey tests), cold hyperalgesia (as revealed by the acetone tests), and axonal degeneration in the sciatic nerve of rats. Co-administration of oral DMF (200 mg/kg, five times per week for 4 weeks) relieved oxaliplatin-induced mechanical allodynia but not cold hyperalgesia, and ameliorated axonal degeneration. In addition, DMF did not exacerbate oxaliplatin-induced body weight loss or bone marrow suppression, such as reduction in red blood cells, white blood cells, neutrophils and lymphocytes. Furthermore, DMF did not inhibit the anti-tumor activity of oxaliplatin in any cultured cancer cell line (C26, mouse colon carcinoma; HCT116, human colon carcinoma; MKN45, human gastric adenocarcinoma; MIA PaCa-2, human pancreatic carcinoma) or C26-bearing mice. These results suggest that DMF prevents oxaliplatin-induced mechanical allodynia and axonal degeneration without affecting the anti-tumor activity of oxaliplatin. Therefore, DMF may be useful for managing oxaliplatin-induced chronic peripheral neuropathy.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1469K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1469K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Tetsuya Nomura, Makie Yamakawa, Takuto Shimaoka, Takamasa Hirai, Naoya ...2019 年 42 巻 4 号 p. 645-648
発行日: 2019/04/01
公開日: 2019/04/01
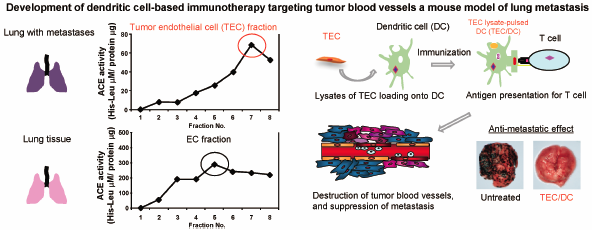
ジャーナル フリー HTMLTumor blood vessels supply cancer tissues with oxygen and nutrients, and it was therefore believed that inhibition of angiogenesis would induce tumor regression. In fact, the situation is complicated by the presence of normal blood vessels in cancer tissues such as carcinomas and sarcomas as well as abnormal vessels. Here, we describe the development of a dendritic cell (DC)-based immunotherapy which targets tumor endothelial cells (TECs) rather than normal endothelial cells (ECs) or cancer cells themselves. After density gradient centrifugation, the TEC-rich fraction from lungs invaded by B16 melanoma cells was separated from the endothelial cell (EC)-rich fraction on the basis of positivity for angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) activity. Prophylactic vaccination with DCs pulsed with lysates of TECs isolated from lungs with metastases significantly suppressed lung metastasis in this B16/BL6 mouse melanoma model. This suggests that DC-based vaccine therapy targeting TECs in cancers tissue could show promise as an effective therapy for distant metastasis.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (720K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (720K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|