- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1147-1153
2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1147-1153
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
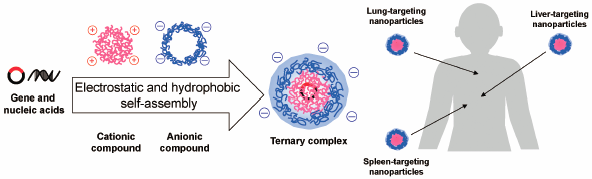
Editor's pickThe clinical application of gene/nucleic acid medicines is highly dependent on the development of effective and reliable drug delivery systems. Dr. Sasaki successfully developed several ternary complexes as novel gene delivery carriers, which were constructed by gene/nucleic acid medicine, the cationic polymer, and the anionic polymer. This ternary complex consists of biodegradable materials found in foods and medical products that are already in clinical use and can deliver gene/nucleic acid medicines to specific organs (liver, spleen, lung, and cancer cells etc.) without toxicity. The ternary complexes are expected to apply to clinical practice.
PDF形式でダウンロード (1782K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1154-1158
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (489K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1159-1171
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2020/05/23PDF形式でダウンロード (8291K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1172-1178
2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1172-1178
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
Editor's pickThe sodium salt of isosteviol (STVNa) is a beyerane diterpene synthesized through acid hydrolysis of stevioside. STVNa improves multiple types of tissue injuries. However, it is not known how Isosteviol sodium affects high-fat and high cholesterol diet (HFD)-induced kidney. The current study suggested that STVNa inhibited HFD-induced kidney injury evident by reducing the increased levels of serum CRE. Specifically, STVNa attenuated HFD-induced kidney injury by inhibiting inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. These findings indicate that STVNa may have a therapeutic potential for metabolic syndrome associated kidney dysfunction by inhibiting inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis.
PDF形式でダウンロード (2033K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1179-1187
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (796K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1188-1195
2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1188-1195
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
Editor's pickIncreasing the immunostimulatory activity of unmethylated cytosine-phosphate-guanine oligodeoxynucleotide (CpG ODN) is an important issue for its clinical application as immunoadjuvant. In this study, the authors combined two approaches, i.e., nanostructured DNA formation and mannose modification, for efficient delivery of CpG ODN to mannose receptor-positive immune cells. Mannosylated CpG ODN (Man-CpG ODN) loaded onto polypod-like structured nucleic acid (polypodna) induced a greater tumor necrosis factor-α release than Man-CpG ODN or CpG ODN/polypodna from the cells. Thus, this study provides a new and promising approach to increasing the therapeutic potency of CpG ODN.
PDF形式でダウンロード (1200K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1196-1201
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2020/05/30PDF形式でダウンロード (1801K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1202-1209
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (7298K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1210-1219
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (2303K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1220-1225
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1845K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1226-1234
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (928K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1235-1240
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2020/05/21PDF形式でダウンロード (346K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1241-1247
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (726K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1248-1252
2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1248-1252
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
Editor's pickThe detailed epidemiology of invasive mycoses and superficial mycoses has not been clarified in Japan. This is the first study to clarify the trends of antifungal use in Japan. The authors found that total antifungal use decreased over time. Notably, the trend of antifungal use for invasive mycoses was significantly increased by 19.9% whereas the trend of antifungal use for superficial mycoses significantly decreased by 49.8%. In Japan, the increase in the number of immunocompromised patients might be associated with an increase in the frequency of antifungal use for invasive mycoses.
PDF形式でダウンロード (699K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1253-1258
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (489K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1259-1266
2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1259-1266
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
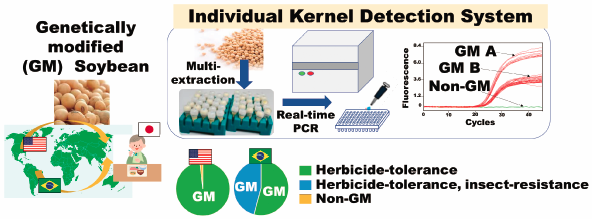
Editor's pickToday, majority of soybeans in Japan comes from foreign countries, where genetically modified (GM) soybeans are cultivated. The details of GM soybean actually consumed for food in Japan have been unknown. The article by Soga et al. reported a quantitative GM soybean kernel detection system and that the most of imported soybean in the non-identity-preserved soybean samples examined were herbicide-tolerant and insect-resistant GM soybean events that were authorized in Japan. These data would provide useful information on risk analysis concerning regulations on GM soybean for food use.
PDF形式でダウンロード (656K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1267-1271
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (3611K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1272-1274
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (361K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1275-1278
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (475K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1279-1282
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (455K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1283-1287
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (557K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2020 年 43 巻 8 号 p. 1288-1291
発行日: 2020/08/01
公開日: 2020/08/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2020/06/09PDF形式でダウンロード (1482K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|