
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Hongping Yuan, Xiaoxuan Zhang, Wei Zheng, Hui Zhou, Bo-Yin Zhang, Dong ...2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1231-1237
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe effects of minocycline on the development of diabetic nephropathy (DN) in streptozotocin (STZ) induced diabetic rats were evaluated in this study. The diabetes rats with DN were induced by STZ (55 mg/kg) injection. The experiment included 5 groups 1) normal, 2) normal plus minocycline for 16 weeks, 3) DN plus vehicle, 4) DN plus minocycline 16 weeks and 5) DN plus minocycline for 8 weeks. The pathological changes were analyzed by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and the apoptotic cells were stained by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate nick-end labeling (TUNEL) staining. The mRNA expression of caspase-3, Bax and Bcl-2 in the kidney tissues was detected by quantitative RT-PCR. The biochemical parameters of blood and urine were determined by biochemical analyzer. Treatment with minocycline reduced the urine volume, 24-h urine protein, serum creatinine (Scr), blood urea nitrogen (BUN) but not blood alanine aminotransferase (ALT) in the DN rats. Furthermore, treatment with minocycline improved the pathological score of STZ-injured kidney and reduced the numbers of apoptotic cells in the kidney of DN rats. Moreover, minocycline mitigated the expression of caspase-3 and Bax mRNA, but increased Bcl-2 expression in the kidney of DN rats. These data indicated that minocycline improved the STZ-induced kidney damages, at least partially by protection form long-term hyperglycemia-induced kidney cell apoptosis.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (4286K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (4286K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Mahitab Elsayed, Daisuke Kobayashi, Toshio Kubota, Naoya Matsunaga, Ry ...2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1238-1246
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2016/05/14ジャーナル フリー HTMLBisphosphonates and statins are known to have antitumor activities against different types of cancer cell lines. In the present study, we investigated the antiproliferative effects of the combination of zoledronic acid (ZOL), a bisphophosphonate, and fluvastatin (FLU), a statin, in vitro on two types of human pancreatic cancer cell lines, Mia PaCa-2 and Suit-2. The pancreatic cancer cell lines were treated with ZOL and FLU both individually and in combination to evaluate their antiproliferative effects using WST-8 cell proliferation assay. In this study, we demonstrated a potent synergistic antiproliferative effect of both drugs when used in combination in both cell lines. Moreover, we studied the molecular mechanism behind this synergistic effect, which was inhibited by the addition of the mevalonate pathway products, farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP). Furthermore, we aimed to determine the effect of ZOL and FLU combination on RhoA and Ras guanosine 5′-triphosphate (GTP)-proteins. The combination induced a marked accumulation in RhoA and unprenylated Ras. GGPP and FPP reversed the increase in the amount of both proteins. These results indicated that the combination treatment impaired RhoA and Ras signaling pathway by the inhibition of geranylgeranylation and/or farnesylation. This study provides a potentially effective approach for the treatment of pancreatic cancer using a combination treatment of ZOL and FLU.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (985K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (985K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
JingZhe Li, ChangZhen Liu, Takashi Sato2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1247-1253
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLp-Cymene (4-isopropyltoluene) has been reported to have beneficial actions such as anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities. To evaluate whether p-cymene exhibits antitumor invasive actions, we examined the effects of p-cymene on the production of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9)/gelatinase B and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 (TIMP-1) in human fibrosarcoma HT-1080 cells. p-Cymene was found to dose-dependently inhibit the 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate (TPA)-augmented production and gene expression of MMP-9 in HT-1080 cells. In contrast, p-cymene enhanced the TPA-augmented production and gene expression of TIMP-1 in HT-1080 cells. However, there was no change in the constitutive level of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 mRNAs and TIMP-1 protein in p-cymene-treated cells. In addition, we found that the in-vitro TPA-augmented invasiveness of HT-1080 cells was inhibited by p-cymene in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, p-cymene was found to suppress the constitutive and/or TPA-augmented phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in HT-1080 cells. Thus, these results provide novel evidence that p-cymene is an effective candidate for the prevention of tumor invasion and metastasis through mechanisms that include the inhibition of MMP-9 expression and the augmentation of TIMP-1 production along with the suppression of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signal pathways in tumor cells.
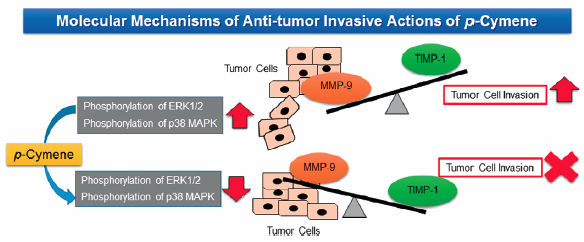 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1014K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1014K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Worranan Rangsimawong, Praneet Opanasopit, Theerasak Rojanarata, Suree ...2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1254-1262
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe effect of surface grafting with N-(carbonyl-methoxypolyethylene glycol-2000)-1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (PEG2000-DSPE) onto three types of lipid nanocarriers, liposomes, niosomes and solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) on the skin penetration of sodium fluorescein (NaFI) was investigated. Confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) was used to visualize the penetration pathways. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) was used to determine the skin hydration. The results showed that the physicochemical properties of each nanocarrier were modified after PEG grafting. In the skin penetration study, PEG grafting increased the flux of NaFI-loaded PEGylated liposomes and significantly decreased the flux of NaFI-loaded PEGylated niosomes and NaFI-loaded PEGylated SLNs. The skin deposition study and CLSM images showed that the intact liposome vesicles permeated into the skin. The niosomes and SLNs had little or no vesicles in the skin, suggesting that NaFI may have been released from these nanocarriers before permeation. Additionally, the fluorescent CLSM images of the SLNs showed that NaFI deposited along the length of hair follicles inside the skin, indicating that the skin penetration route may be through the transfollicular pathway. For the PEGylated nanocarriers, the PEGylated liposomes had higher fluorescence intensities than the non-PEGylated liposomes, indicating higher NaFI concentrations. The PEGylated niosomes and PEGylated SLNs had lower fluorescence intensities than those of the non-PEG modified niosomes and SLNs. For FT-IR results, PEGylated liposomes increased the skin hydration, while the grafting PEG onto niosomes and SLN surfaces decreased the skin hydration. This study showed that the surface grafting of PEG onto various nanocarriers affected the skin transport of NaFI.
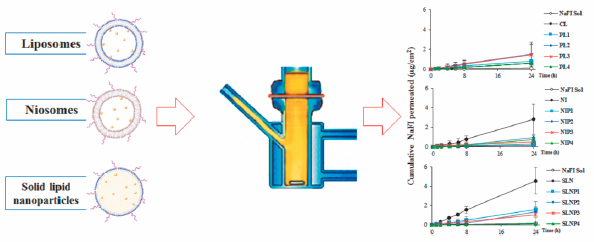 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1515K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1515K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Hiroko Tokumoto, Hiroko Shimomura, Takashi Hakamatsuka, Yoshihiro Ozek ...2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1263-1272
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2016/05/25ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Nicotiana tabacum (Solanaceae) is the only species whose leaves can be legally marketed as tobacco according to the Japanese Tobacco Business Act. Nicotine, a major alkaloid produced by N. tabacum leaves, is regulated in pharmaceuticals by the Japanese Pharmaceutical Affairs Law. However, the use of N. tabacum stems as an excipient in pharmaceuticals is permitted, because these contained only a small amount of nicotine. Recently, several reports showed that a substantial amount of nicotine was detected in an OTC pharmaceutical product, in which N. tabacum stems were used as an excipient. Therefore, products containing N. tabacum stems could be contaminated with the leaf material. In the present study, we established a method to detect contamination of N. tabacum stem materials with its leaves, using microscopy to obtain standard reference microphotographs for identification. Cultivated N. tabacum stems and leaves, commercial cigarette leaves, and N. tabacum tissue imported as excipient material were used for preparing the microphotographs. The characteristic N. tabacum leaf structures found in the powdered fragments included: epidermal cells with sinuous anticlinal cell walls, hairs, mesophyll parenchyma with crystalized calcium oxalate (calciphytoliths), and branching vascular bundles derived from reticulate net-veins. A comparison of the microscopic characteristics of an OTC powder with those from the standard reference microphotographs was an effective method for N. tabacum stem and leaf identification. Thus, we evaluated the powdered pharmaceutical product containing N. tabacum stem tissue and Hydrangea serrata (Hydrangeaceae) leaf tissue as excipients, and confirmed the presence of N. tabacum leaf material.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (28598K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (28598K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Jung-Il Kang, Eun-Sook Yoo, Jin-Won Hyun, Young-Sang Koh, Nam Ho Lee, ...2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1273-1283
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThis study was conducted to evaluate the effects of Sargassum muticum extract and apo-9′-fucoxanthinone, a principal component of S. muticum, on hair growth. When rat vibrissa follicles were treated with S. muticum extract for 21 d, the hair-fiber lengths for the vibrissa follicles increased significantly. Treatment with the S. muticum extract and the EtOAc fraction of the S. muticum extract markedly increased the proliferation of dermal papilla cells (DPCs) and decreased the 5α-reductase activity. In addition, the EtOAc fraction of the S. muticum extract significantly promoted anagen initiation in C57BL/6 mice. Especially, apo-9′-fucoxanthinone, an active constituent from the S. muticum extract, caused an increase in DPC proliferation and a decrease in 5α-reductase activity. To elucidate the molecular mechanisms of apo-9′-fucoxanthinone on the proliferation of DPCs, we examined the level of various signaling proteins. Apo-9′-fucoxanthinone increased the level of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGF-R2), Wnt/β-catenin signaling proteins such as phospho(ser9)-glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) and phospho(ser552)-β-catenin, whereas apo-9′-fucoxanthinone did not affect the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling proteins such as Smad2/3. These results suggest that apo-9′-fucoxanthinone from S. muticum could have the potential for hair growth with DPC proliferation via the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and the VEGF-R2 pathway.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2771K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2771K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Heqin Zhan, Feng Huang, Wenzhuo Ma, Zhenghang Zhao, Haifang Zhang, Cho ...2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1284-1292
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLIdiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a progressive disease with poor prognosis and high mortality rate. Panax Notoginseng Saponins (PNS), extracted from Panax Notoginseng as a traditional Asian medicine, displayed a significant anti-fibrosis effect in liver and lung. However, whether Ginsenoside Rg1 (Rg1), an important and active ingredient of PNS, exerts anti-fibrotic activity on IPF still remain unclear. In this study, we investigated the effect of Rg1 on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Bleomycin (5 mg/kg body weight) was intratracheally administrated to male rats. Rg1 (18, 36 and 72 mg/kg) was orally administered on the next day after bleomycin. Lungs were harvested at day 7 and 28 for the further experiments. Histological analysis revealed that bleomycin successfully induced pulmonary fibrosis, and that Rg1 restored the histological alteration of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis (PF), significantly decreased lung coefficient, scores of alveolitis, scores of PF as well as contents of alpha smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and hydroxyproline (Hyp) in a dose-dependent manner in PF rats. Moreover, Rg1 increased the expression levels of Caveolin-1 (Cav-1) mRNA and protein, lowered the expression of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) mRNA and protein in the lung tissues of PF rats. These data suggest that Rg1 exhibits protective effect against bleomycin-induced PF in rats, which is potentially associated with the down-regulation of TGF-β1 and up-regulation of Cav-1.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5248K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5248K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Yusuke Kono, Ayu Iwasaki, Kenta Matsuoka, Takuya Fujita2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1293-1299
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録To develop an effective oral delivery system for plasmid DNA (pDNA) using cationic liposomes, it is necessary to clarify the characteristics of uptake and transport of cationic liposome/pDNA complexes into the intestinal epithelium. In particular, evaluation of the involvement of an unstirred water layer (UWL), which is a considerable permeability barrier, in cationic liposome transport is very important. Here, we investigated the effects of a UWL on the transfection efficiency of cationic liposome/pDNA complexes into a Caco-2 cell monolayer. When Caco-2 cells were transfected with cationic liposome/pDNA complexes in shaking cultures to reduce the thickness of the UWL, gene expression was significantly higher in Caco-2 cells compared with static cultures. We also found that this enhancement of gene expression by shaking was not attributable to activation of transcription factors such as activator protein-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB). In addition, the increase in gene expression by mechanical agitation was observed at all charge ratios (1.5, 2.3, 3.1, 4.5) of cationic liposome/pDNA complexes. Transport experiments using Transwells demonstrated that mechanical agitation increased the uptake of cationic liposome/pDNA complexes by Caco-2 cells, whereas transport of the complexes across a Caco-2 cell monolayer did not occurr. Moreover, the augmentation of the gene expression of cationic liposome/pDNA complexes by shaking was observed in Madin–Darby canine kidney cells. These results indicate that a UWL greatly affects the uptake and transfection efficiency of cationic liposome/pDNA complexes into an epithelial monolayer in vitro.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (633K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (633K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Aili Cao, Li Wang, Xia Chen, Hengjiang Guo, Shuang Chu, Xuemei Zhang, ...2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1300-1308
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2016/05/18ジャーナル フリー HTMLOxidative stress has a great role in diabetes and diabetes induced organ damage. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is involved in the onset of diabetic nephropathy. We hypothesize that ER stress inhibition could protect against kidney injury through anti-oxidative effects. To test whether block ER stress could attenuate oxidative stress and improve diabetic nephropathy in vivo and in vitro, the effect of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), an ER stress inhibitor, on spontaneous diabetic nephropathy db/db mice, ER stress inducer or high glucose-triggered podocytes were studied. Mice were assigned to 3 groups (n=6 per group): control group (treated with vehicle), db/db group (treated with vehicle), and UDCA group (db/db mice treated with 40 mg/kg/d UDCA). After 8 weeks treatment, mice were sacrificed. Blood and kidneys were collected for the assessment of albumin/creatinine ratio, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), serum creatinine (SCr), insulin, total cholesterol, triglyceride, low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), oxidized LDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), non-esterified fatty acid (NEFA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), methane dicarboxylic aldehyde (MDA), the expressions of SOD isoforms and glutathione peroxidase 1, as well as histopathological examination. In addition, generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) was detected by 2′7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) fluorescence. The results showed that UDCA alleviated renal ER stress-evoked cell death, oxidative stress, renal dysfunction, ROS production, upregulated the expression of Bcl-2 and suppressed Bax in vivo and in vitro. Hence, inhibition ER stress diminishes oxidative stress and exerts renoprotective effects.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (9333K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (9333K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Asuka Takeuchi, Yusuke Nomoto, Mai Watanabe, Soichiro Kimura, Yasunori ...2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1309-1318
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2016/06/01ジャーナル フリー HTMLAn adequate immune response to percutaneous vaccine application is generated by delivery of sufficient amounts of antigen to skin and by administration of toxin adjuvants or invasive skin abrasion that leads to an adjuvant effect. Microneedles penetrate the stratum corneum, the outermost layer of the skin, and enable direct delivery of vaccines from the surface into the skin, where immunocompetent dendritic cells are densely distributed. However, whether the application of microneedles to the skin activates antigen-presenting cells (APCs) has not been demonstrated. Here we aimed to demonstrate that microneedles may act as a potent physical adjuvant for successful transcutaneous immunization (TCI). We prepared samples of isolated epidermal and dermal cells and analyzed the expression of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II and costimulatory molecules on Langerhans or dermal dendritic cells in the prepared samples using flow cytometry. The expression of MHC class II and costimulatory molecules demonstrated an upward trend in APCs in the skin after the application of 500- and 300-µm microneedles. In addition, in the epidermal cells, application of microneedles induced more effective activation of Langerhans cells than did an invasive tape-stripping (positive control). In conclusion, the use of microneedles is likely to have a positive effect not only as an antigen delivery system but also as a physical technique inducing an adjuvant-like effect for TCI.
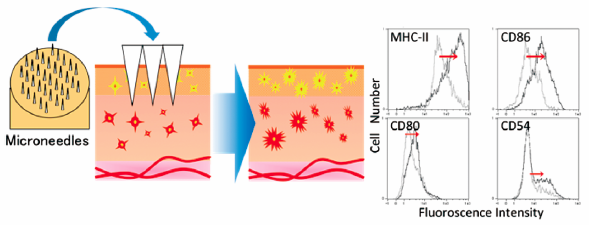 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5901K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5901K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Yoshiyuki Kubo, Narumi Seko, Takuya Usui, Shin-ichi Akanuma, Ken-ichi ...2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1319-1324
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Lysosomal trapping was investigated in the retinal capillary endothelial cells that are responsible for the inner blood–retinal barrier (BRB) using LysoTracker® Red (LTR). Using confocal microscopy on TR-iBRB2 cells, an in vitro model of the inner BRB, the presence of lysosomal trapping in retinal capillary endothelial cells was suggested since TR-iBRB2 cells exhibited punctuate intracellular localization of LTR that was attenuated by NH4Cl treatment. The study confirmed that LTR uptake by retinal capillary endothelial cells took place in a time- and temperature-dependent manner, and exhibited the 1.58-fold greater uptake at pH 8.4 than that at pH 7.4 while there was no change in uptake between pH 6.4 and pH 7.4, suggesting that passive diffusion is not enough to explain LTR uptake. The inhibition study showed the possible influence of lysosomal trapping on cationic drug transport by retinal capillary endothelial cells since LTR uptake was significantly inhibited by cationic amphiphilic drugs. Inhibition profiling and the estimation of IC50 suggested the influence of lysosomal trapping on propranolol and low-affinity pyrilamine transport while lysosomal trapping had only a partial effect on verapamil, clonidine, nicotine and high-affinity pyrilamine transport in retinal capillary endothelial cells.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1006K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1006K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Zhipeng Zhang, Yang Zhang, Zhao Zhang, Hui Yao, Haitao Liu, Ben’gang Z ...2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1325-1330
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2016/06/07ジャーナル フリー HTMLPhellodendri Cortex is derived from the dried barks of Phellodendron genus species, has been extensively used in traditional Chinese medicine. The cortex is divided into two odorless crude drugs Guanhuangbo and Huangbo. Historically, it has been difficult to distinguish their identities due to a lack of identification methods. This study was executed to confirm the identity and to ensure the species traceability of Phellodendri Cortex. In the current study, analysis is based on the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) and psbA–trnH intergenic spacer (psbA–trnH) barcodes and HPLC fingerprint was carried out to guarantee the species traceability of Guanhuangbo and Huangbo. DNA barcoding data successfully identified the three plants of the Phellodendron genus species by ITS+psbA–trnH, with the ability to distinguish the species origin of Huangbo. Moreover, the psbA–trnH data distinguished Guanhuangbo and Huangbo except to trace species. The HPLC fingerprint data showed that Guanhuangbo was clearly different from Huangbo, but there was no difference between the two origins of Huangbo. Additionally, the result of hierarchical clustering analysis, based on chlorogenic acid, phellodendrine, magnoflorine, jatrorrhizine, palmatine and berberine, was consistent with the HPLC fingerprint analysis. These results show that DNA barcoding and HPLC fingerprint can discriminate Guanhuangbo and Huangbo. However, DNA barcoding is more powerful than HPLC fingerprint for species traceability in the identification of related species that are genetically similar. DNA barcoding is a useful scientific tool to accurately confirm the identities of medicinal materials from multiple sources.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (625K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (625K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Masatomo Miura, Satohiro Masuda, Hiroto Egawa, Kenji Yuzawa, Kazuo Mat ...2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1331-1337
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2016/06/04ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe aim of this study was to assess inter-hospital laboratory variability (coefficient of variation; CV) of immunoassay methods for tacrolimus and the comparability of control samples and results obtained by immunoassay measurements. One hundred seven hospital laboratories routinely performing therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) of tacrolimus participated in the study. Thirteen spiked samples with known tacrolimus concentrations in the range of 0–26.0 ng/mL were prepared. Each spiked sample was analyzed according to the manufacturer’s instructions using an affinity column-mediated immunoassay (ACMIA) on a Dimension® analyzer, the enzyme multiplied immunoassay technique (EMIT) on a Viva-E® analyzer, a chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay (CLIA) on the Architect® system, and the electro-chemiluminescence immunoassay (ECLIA) on a cobas® analyzer. The 20% coefficient of variation values for the CLIA, ACMIA, EMIT, and ECLIA assays in the hospital laboratories were 1.82, 5.36, 4.59, and 0.89 ng/mL, respectively. CLIA and ECLIA had positive biases at concentrations of tacrolimus above 12 ng/mL relative to the spiked concentration, whereas the assay bias for ACMIA tended to be more negative at concentrations of tacrolimus above 6 ng/mL. EMIT had positive biases over the wide concentration range of 0.0–26.0 ng/mL (mean of mean errors 1.224). CLIA and ECLIA provided adequate precision at the target tacrolimus concentration of 3.0 ng/mL, whereas ACMIA and EMIT were unable to respond to target concentrations between 3.0 and 5.0 ng/mL for renal transplant recipients. Appropriate assessment of tacrolimus concentration by an assay having higher sensitivity, precision, and accuracy is necessary to ensure long-term survival of transplant recipients receiving tacrolimus.
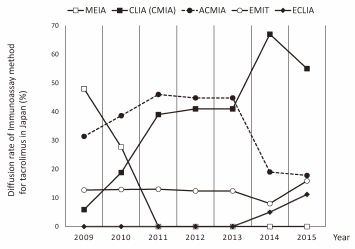 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (691K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (691K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Chul-Ho Yun, Chun-Sik Bae, Taeho Ahn2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1338-1346
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLNanoparticles (NPs) containing cationic monovalent lipids such as 1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium-propane (DOTAP) and N-(1-[2,3-dioleyloxy]propyl)-N,N,N-trimethylammonium chloride (DOTMA), have been widely used for the delivery of nucleic acid such as small-interfering RNA and polypeptide to cells as cancer therapies and vaccine development. Several previous reports have suggested that cationic liposomes induce reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-mediated toxicity in cells. Here, we systematically investigated the effects of DOTAP- or DOTMA-containing NPs without any cargo on the human carcinoma cells, HepG2. Treatment with NPs containing DOTAP or DOTMA increased the production of cellular ROS, such as H2O2 and lipid peroxidation, in HepG2 cells and concomitantly decreased cell viability. These effects were dependent on the lipid concentration, surface density of cationic lipids, and particle size of NPs. However, neutral NPs consisting of 1,2-dioleoyl-3-phosphocholine did not elicit the effective ROS generation or cell death regardless of the lipid concentration and particle size. The present study suggests that DOTAP- and DOTMA-NPs are able to induce cancer cell death through production of ROS in the absence of any therapeutic cancer reagents. These results also provide a rational background for the design of delivery systems using cationic lipid-based NP formulations.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3659K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3659K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Masumi Takemoto, Hiroaki Takemoto, Ryoyasu Saijo2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1347-1352
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2016/05/25ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe polyphenolic compound theaflavin, which is the main red pigment present in black tea, is reported to elicit various physiological effects. Because of the extremely low concentration of theaflavin present in black tea, its extraction from black tea leaves in quantities sufficient for use in medical studies has been difficult. We have developed a simple, inexpensive, selective, domino-type, one-pot enzymatic biotransformation method for the synthesis of theaflavin that is suitable for use in medical studies. Subsequent administration of this synthetic theaflavin to high-fat diet-induced obese mice inhibited both body weight gain and visceral fat accumulation, with no significant difference in the amount of faeces between the experimental and control mice.
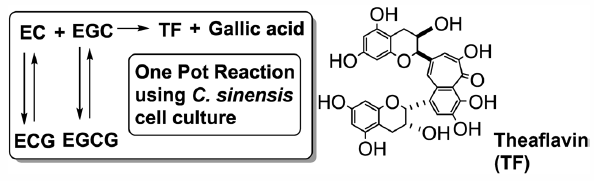 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (656K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (656K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Ryosuke Nakamura, Yasukazu Takanezawa, Yuka Sone, Shimpei Uraguchi, Ko ...2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1353-1358
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLMethylmercury (MeHg) is one of the most toxic environmental pollutants and presents a serious hazard to health worldwide. Although the adverse effects of MeHg, including neurotoxicity, have been studied, its effects on immune function, in particular the immune response, remain unclear. This study examined the effects of low-dose MeHg on immune responses in mice. Mice were orally immunized with ovalbumin (OVA) or subcutaneously injected with mite extract to induce a T-helper 2 (Th2) allergic response. They were then exposed to MeHg (0, 0.02, 1.0, or 5.0 mg·kg−1·d−1). Immunization with oral OVA or subcutaneous mite extract increased serum levels of OVA-specific immunoglobulin (Ig) E (OVA-IgE), OVA-IgG1, interleukin (IL)-4, and IL-13, and total IgE, total IgG, and IL-13 when compared with levels in non-immunized mice. However, no interferon (IFN)-γ was detected. By contrast, serum levels of OVA-IgE, OVA-IgG1, IL-4, and IL-13, or total IgE, total IgG, and IL-13 in Th2 allergy model mice subsequently treated with MeHg were no higher than those in MeHg-untreated mice. These results suggest that MeHg exposure has no adverse effects on Th2 immune responses in antigen-immunized mice.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (735K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (735K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Makoto Sekimoto, Toru Takamori, Saki Nakamura, Masato Taguchi2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1359-1363
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLCarvedilol is mainly metabolized in the liver to O-glucuronide (O-Glu). We previously found that the glucuronidation activity of racemic carvedilol in pooled human liver microsomes (HLM) was increased, R-selectively, in the presence of amiodarone. The aim of this study was to clarify the mechanisms for the enhancing effect of amiodarone on R- and S-carvedilol glucuronidation. We evaluated O-Glu formation of R- and S-carvedilol enantiomers in a reaction mixture of HLM including 0.2% bovine serum albumin (BSA). In the absence of amiodarone, glucuronidation activity of R- and S-carvedilol for 25 min was 0.026, and 0.51 pmol/min/mg protein, and that was increased by 6.15 and 1.60-fold in the presence of 50 µM amiodarone, respectively. On the other hand, in the absence of BSA, or when BSA was replaced with human serum albumin, no enhancing effect of amiodarone on glucuronidation activity was observed, suggesting that BSA played a role in the mechanisms for the enhancement of glucuronidation activity. Unbound fraction of S-carvedilol in the reaction mixture was greater than that of R-carvedilol in the absence of amiodarone. Also, the addition of amiodarone caused a greater increase of unbound fraction of R-carvedilol than that of S-carvedilol. These results suggest that the altered protein binding by amiodarone is a key mechanism for R-selective stimulation of carvedilol glucuronidation.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (576K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (576K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Akitoshi Tatsumi, Masaya Okada, Yoshihiro Inagaki, Sachiyo Inoue, Tsun ...2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1364-1369
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLHuman serum albumin (HSA) has two major ligand-binding sites, sites I and II, and also hydrolyzes some compounds at both sites. In the present study, we investigated differences in esterase activity among HSA preparations, and also the effects of warfarin, indomethacin, and naproxen on the hydrolytic activities of HSA to aspirin and p-nitrophenyl acetate. The esterase activities of HSA to aspirin or p-nitrophenyl acetate were measured from the pseudo-first-order formation rate constant (kobs) of salicylic acid or p-nitrophenol by HSA. Inter-lot variations were observed in the esterase activities of HSA to aspirin and p-nitrophenyl acetate; however, the esterase activity of HSA to aspirin did not correlate with that to p-nitrophenyl acetate. The inhibitory effects of warfarin and indomethacin on the esterase activity of HSA to aspirin were stronger than that of naproxen. In contrast, the inhibitory effect of naproxen on the esterase activity of HSA to p-nitrophenyl acetate was stronger than those of warfarin and indomethacin. These results suggest that the administration of different commercial HSA preparations and the co-administration with site I or II high-affinity binding drugs may change the pharmacokinetic profiles of drugs that are hydrolyzed by HSA.
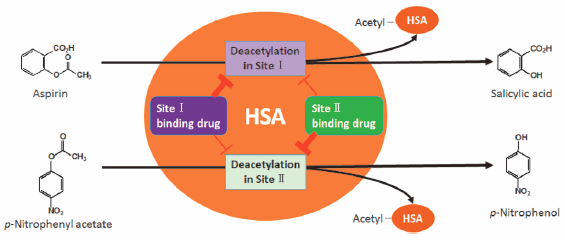 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (480K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (480K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Xin Cao, Yuji Nakamura, Takeshi Wada, Takuya Kishie, Azjargal Enkhsaik ...2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1370-1373
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLIntravenous tetramethylpyrazine has been widely used in China as a complementary and/or alternative medicine to treat patients with ischemic heart disease. We assessed the anti-anginal effect of tetramethylpyrazine (10 mg/kg, intravenously (i.v.), n=6) in comparison with that of its vehicle, saline (1 mL/kg, i.v., n=6), using vasopressin-induced angina model rats. First, Donryu rats were anesthetized with pentobarbital sodium (60 mg/kg, intraperitoneally (i.p.)), and the surface lead I electrocardiogram was continuously monitored. Administration of vasopressin (0.5 IU/kg, i.v.) to the rats depressed the S-wave level of the electrocardiogram, indicating the onset of subendocardial ischemia. However, pretreatment with tetramethylpyrazine suppressed the vasopressin-induced depression of the S-wave level, which was not observed following pretreatment with its vehicle alone (saline), suggesting that tetramethylpyrazine ameliorated the vasopressin-induced subendocardial ischemia in vivo. These results may provide experimental evidence for the empirically known clinical efficacy of tetramethylpyrazine against ischemic heart disease, and could provide clues to better understanding its in vivo mechanism of action.
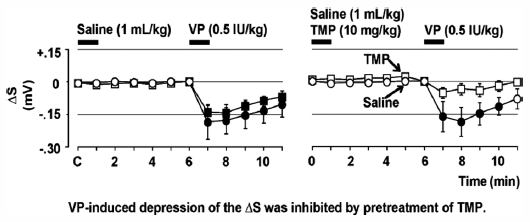 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (505K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (505K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Shun Watanabe, Takayuki Matsumoto, Makoto Ando, Shota Kobayashi, Maika ...2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1374-1380
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLWe investigated superior mesenteric arteries from spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) to determine the relaxation responses induced by ATP, ADP, and adenosine and the relationship between the relaxant effects of these compounds and nitric oxide (NO) or cyclooxygenase (COX)-derived prostanoids. In rat superior mesenteric artery, relaxation induced by ATP and ADP but not by adenosine was completely eliminated by endothelial denudation. In the superior mesenteric arteries isolated from SHR [vs. age-matched control Wistar Kyoto rats (WKY)], a) ATP- and ADP-induced relaxations were weaker, whereas adenosine-induced relaxation was similar in both groups, b) ATP- and ADP-induced relaxations were substantially and partly reduced by NG-nitro-L-arginine [a NO synthase (NOS) inhibitor], respectively, c) indomethacin, an inhibitor of COX, increased ATP- and ADP-induced relaxations, d) ADP-induced relaxation was weaker under combined inhibition by NOS and COX, and e) adenosine-induced relaxation was not altered by treatment with these inhibitors. These data indicate that levels of responsiveness to these nucleotides/adenosine vary in the superior mesenteric arteries from SHR and WKY and are differentially modulated by NO and COX-derived prostanoids.
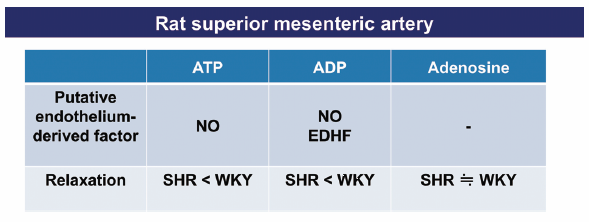 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (822K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (822K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Nozomu Moriya, Hiromi Kataoka, Jun-ichi Nishikawa, Fumihiko Kugawa2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1381-1386
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2016/05/24ジャーナル フリー HTMLMicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that are involved in mRNA post-transcriptional regulation. The deregulation of miRNAs affects the expression of drug-metabolizing enzymes, drug transporters, and nuclear receptors, all of which are important in regulating drug metabolism. miRNA expression can be altered by several endogenous or exogenous agents, such as steroid hormones, carcinogens, and therapeutic drugs. However, it is unclear whether hepatic miRNA expression is regulated by nuclear receptors, such as pregnane X receptor (PXR) and constitutive androstane receptor (CAR), which are indispensable for the expression of the CYPs. Here we investigated the effects of the mouse PXR and CAR ligands pregnenolone-16α-carbonitrile (PCN) and 1,4-bis[(3,5-dichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy]benzene (TCPOBOP) on hepatic miRNA expression in mice. We found that the expression of 9 miRNAs was increased (>2-fold) and of 4 miRNAs was decreased (>50%) in response to PCN, while TCPOBOP treatment led to the up-regulation of 8 miRNAs and down-regulation of 6 miRNAs. Using several miRNA target prediction algorithms, we found that the predicted target genes included several lesser known Cyp genes (Cyp1a1, Cyp1b1, Cyp2b10, Cyp2c38, Cyp2u1, Cyp4a12a/b, Cyp4v3, Cyp17a1, Cyp39a1, and Cyp51). We analyzed the expression of these genes in response to PCN and TCPOBOP and found changes in their mRNA levels, some of which were negatively correlated with the expression of their corresponding miRNAs, suggesting that miRNAs may play a role in regulating Cyp enzyme expression. Further studies will be required to fully elucidate the miRNA regulatory mechanisms that contribute to modulating CYP expression.
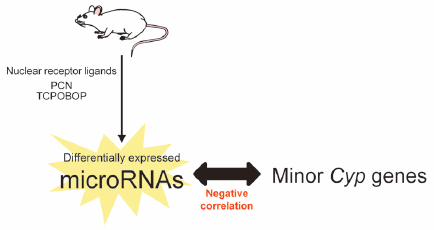 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (424K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (424K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Tanima Biswas, Yusuke Akagi, Kosuke Usuda, Koji Yasui, Isao Shimizu, M ...2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1387-1391
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLTwo vitamin D3 derivatives, namely 24,24-difluoro-1β,3β,25-dihydroxy-19-norvitamin D3 (6a) and 24,24-difluoro-1α,3α,25-dihydroxy-19-norvitamin D3 (6b), were synthesized via a convergent route employing Julia–Kocienski olefination as a key step. Compounds 6a and b bound to vitamin D receptor (VDR) with IC50 values of 64.8 and 57.6 nM, respectively, exhibiting about 400- and 30-fold greater binding affinity than the corresponding non-fluorinated derivatives 5a and b.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (549K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (549K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Tetsuya Suzuki, Takashi Imada, Natsuki Nishigaki, Miwako Kobayashi, Ic ...2016 年39 巻8 号 p. 1392-1395
発行日: 2016/08/01
公開日: 2016/08/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLBase sequence conversion in target DNA is achieved when a 5′-tailed duplex (TD) is introduced into cells. In this study, the effects of target DNA cleavage on sequence conversion with a TD were examined. Plasmid DNAs with and without cleavage near the target position were each introduced into HeLa cells, together with the TD. The cleavage promoted the sequence alteration efficiency by ca. 7-fold. These results suggested that the sequence conversion efficiency with the TD fragment is increased when an artificial nuclease introduces cleavage near the target site.
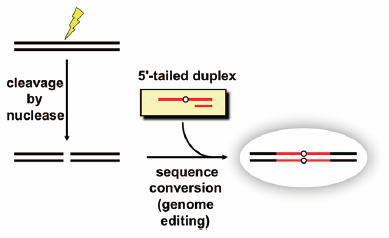 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (482K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (482K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|